Name: ___________________________ Date: ____________
advertisement

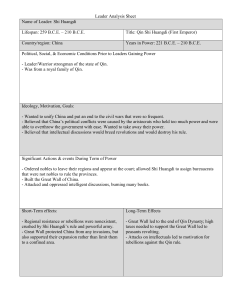
Name: ___________________________ Date: ____________ Period: _________ Reading Quiz: Chapter 4.4- An Empire Unifies China 1. List the Five Relationships of Confucianism and explain their significance. 1)Parent to child 2)Husband to wife 3)Ruler to subject 4)Older sibling to younger sibling 5)Friend to Friend In the first 4 relationships, somebody has more power…other person defers to them…only equal relationship was friend to friend…idea was that these relationships would promote social harmony. 2. Who was Shi Huangdi? (Time period, location, key achievements) Seized power at the age of 13 in early 200’s BCE…established the Qin Dynasty…based on Legalism…instituted standardized language and weights and measures…also connected the Great Wall…possible died by an immortality potion made from mercury 3. What are the basic tenets of Daoism? Founded by Laozi…following the rhythms of nature…”let nature take its course”…wuwei “action through nonaction”…philosophy led to medicine (acupuncture), exercise (tai chi), architecture, etc. Chapter 4.4: An Empire Unifies China I. Philosophy and the Social Order At the end of the Zhou dynasty, there was a lot of chaos, to restore the values of social order, harmony, and respect for authority, new philosophies arose. A. Confucius Urges Harmony Confucius (Kong Fuzi) 551 BCE…during Zhou Dynasty…led a scholarly life Five Relationships: 1. Ruler and subject 2. Father and son 3. Husband and wife 4. Older brother and younger brother 5. Friend and friend o Code of proper conduct with each of these relationships…#1-4, one person has more power than the other person…only friend to friend was equal Filial Piety= respect for parents and elders…central to Confucianism Duke of Lu appointed Confucius as a Minister of Justice…allegedly Confucius was able to rid the region of crime virtually overnight The Analects- stories attributed to Confucius, written down by some of his students o Important disciple of Confucius= Mencius o Taught leaders should be virtuous B. Confucian Ideas About Government Confucius said education could transform a humbly born person into a gentleman Bureaucracy= trained civil service to run the government…meritocracy…eventually based on the Civil Service Examination (based on Confucianism) Confucianism as an ethical system…foundation for Chinese government and social order…ideas of Confucianism also spread (Sinification) C. Daoists Seek Harmony Founder- Laozi (6th century BCE) only natural order was important Book: Dao De Ching (The Way of Virtue) Universal force (the Dao/ “the Way”) guides all things Nothing in nature strives for fame, power or wisdom…”Let nature take its course” Laozi said of all the creatures in nature, only humans fail to follow the Dao Daoism: philosophy of Laozi…search for knowledge and understanding of nature…many followers pursued scientific studies (alchemy, astronomy, medicine) D. Legalists Urge Harsh Rule Practical political thinkers- Legalists Highly efficient and powerful government was the key to restoring order Belief that government should use the law to end civil disorder and restore harmony Founders: Hanfeizi and Li Si Taught that ruler should provide rich rewards for people who carried out their duties well…disobedient should be harshly punished…stressed punishment more than rewards Said rulers should burn all writings that might encourage people to think critically about government It was for the prince to govern, and the people to obey Legalist thinkers found a supporter in Qin Shi Huangdi (Qin Dynasty) E. I Ching and Yin and Yang Book of oracles (I Ching/ Yi Jing) to answer ethical or practical problems I Ching= Book of Changes…common sense answers Yin and Yang…two power that together represent the natural rhythms of life…Yang= male, sun, light…Yin= female, moon, dark Pain in body as imbalance between yin and yang…acupuncture II. The Qin Dynasty Qin Dynasty was short-lived, emerged in the 3rd century BCE…ruler was 13, employed Legalist ideas A. A New Emperor Takes Control 221BCE= Qin Ruler assumed the name Shi Huangdi (“First Emperor”) o Halted internal battles o Attacked the invaders north of the Yellow River and south to Vietnam…doubled China’s size Qin emperor also crushed political opposition at home…take down rival warlords: “strengthening the trunk and weakening the branches.” Commanded all the noble families to live at the capital city…uprooted 120,000 noble families…confiscated their lands, and carved China into 36 administrative districts…officials sent to control them Qin Shi Huangdi and his prime minister, Li Su, murdered hundreds of Confucian scholars o Ordered “useless” books burned…(Confucianist works) Autocracy= a government in which the ruler has unlimited power and uses it in an arbitrary manner B.A Program of Centralization Built a highway network of over 4,000 miles Peasants had to work on roads against their will (corvee) Uniform standards for Chinese writing, law, currency, and weights and measures…(even length of cart axles) Irrigation projects increased farm production…trade blossomed Merchant class rose to prominence Qin regime still unpopular due to harsh taxes and the repressive government C. Great Wall of China Shi Huangdi wanted to close the gaps between smaller walls and unify the wall to 1,400 miles Great Wall of China was built by hundreds of thousands of peasants o Forced labor for free (corvee) o One of the few human-made features on Earth visible from space D. The Fall of the Qin Shi Huangdi’s son and successor wasn’t as strong…peasants rebelled…peasant from the land of Han seized the capital city…by 202BCE the Han Dynasty began