Habitat Study Guide
advertisement

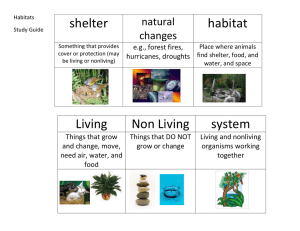
Habitat Study Guide Vocabulary Definition Adaptation Anything an animal does to help it live in a habitat. Camouflage A way an animal looks that helps it blend in with its surroundings. (Helps the animals hide) Desert Dormancy Has a hot climate with little rainfall. Not active (After a tree loses its leaves, it is dormant in winter) Environment Is made up of all the living and non-living things in a place Estivate To stay in a deep sleep during the summer Food chain The order in which animals eat plants and other animals. (Energy is exchanged) Grasslands (Savanna) Forest Tall grasses and hot climate Habitat The place an animal or plant gets what it needs to live Hibernate To stay in a deep sleep during the winter Migrate To move to another place to live, usually due to weather Water Habitats Fresh water – pond Salt water - ocean Rain Forest Type of forest habitat – has hot weather and a lot of rain Tundra (Polar) Frozen much of the year Fossils Help scientists (paleontologists) learn about animals and plants that lived long ago. Many marine fossils (clams, scallops, whale bones, shark teeth) are found along the Virginia coastline. Virginia’s state fossil is the Chesapecten Jeffersonius, named after Thomas Jefferson. Has many different types of trees Essential Knowledge: -Living things are part of a system -Living organisms are interdependent with their living and nonliving surroundings -Habitats change over time, and from season to season -Shelter may be living or nonliving -Classify parts of an animal’s habitat as living or nonliving -Be able to describe how animals and plants are dependent on their surroundings -Be able to explain how animals adapt to the changes in their habitat -Be able to describe how scientists use the study of fossils to show past weather and climate conditions and environmental characteristics