Document 17575856

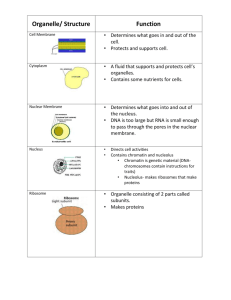
The largest organelle in animals
Contains the organism’s genetic material in the form of DNA
Controls cell function by regulating gene expression (protein synthesis)
Controls DNA replication during the cell cycle
Located towards the center of the cell for protection
Nuclear envelope (membrane) – surrounds the nucleus to separate it from the cytoplasm
Contains pores to allow RNA and proteins to enter and leave the nucleus
DNA within the nucleus is in the form of chromatin
Found within the nucleus
Function is to create rRNA and form ribosomes for gene expression
Ribosomes pass through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm
Consists of rRNA and proteins
Used during translation of gene expression by linking amino acids together to form proteins
Exist all through out the cell
Two types: Rough and Smooth
Bumpy appearance due to ribosomes that cover the outside membrane
Synthesizes and packs proteins
Transports the proteins that are made from the ribosomes
Forms vesicles around the proteins and pinches off
Smooth appearance because it lacks ribosomes
Acts as storage for ions and steroids for when the cell may need them.
Creates steroids and lipids
Breaks down toxic substances.
Small, membrane-bound spheres whose contents are isolated from the surrounding cytoplasm
Transport materials into and out of the cell using endocytosis and exocytosis
Endocytosis: Movement of a substance into the cell
Cell membrane forms a pouch around a substance, then pinches off from the membrane to form a vesicle with the substance inside.
Vesicle is fused with a lysosome, which breaks down the membrane to release the food
Three types: Pinocytosis , phagocytosis , and receptor-mediated endocytosis
Pinocytosis: “cell drinking”. Cell is taking in a liquid substance such as extracellular fluid or dissolved particles.
Phagocytosis: “cell eating”. Cell is taking in a solid substance such as bacteria, debris, or other large objects
Receptor proteins on the cell membrane recognize specific molecules that the cell needs
After ligand binds to receptor, a message is sent through the membrane to the nucleus
A protein coat forms when enough receptors are bound
Vesicle forms with the protein coat surrounding it
Vesicle will fuse with a lysosome to release the contents
Movement of a substance by a vesicle to the outside of a cell.
Vesicle fuses with the membrane and releases contents, such as proteins.
Vesicles with newly made proteins are transported from the ER to the Golgi Complex.
A set of flattened, membrane-bound sacs that pack and distribute proteins
Enzymes within Golgi modify proteins and create new vesicles
Vesicles with newly made proteins may stay in the cell and become lysosomes while some are released outside of the cell via exocytosis
Holds digestive enzymes
Breaks down the cell when it dies, damaged organelles, or foreign materials
1. Nucleolus creates ribosomes
2. Ribosomes move to rough ER
3. Ribosomes on rough ER create proteins
4. Rough ER transports the proteins to the Golgi complex using vesicles
5. The vesicles fuse with the
Golgi complex
6. The Golgi complex modifies the proteins using enzymes and creates another vesicle
7. The new vesicle travels to the cell membrane to be released or stays within the cell to become a lysosome
Harvests energy from organic compounds to make ATP
Some cells have much more mitochondria than others, such as muscle cells.
Contains two membranes – smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane with large surface area.
Also contains its own DNA and ribosomes
Where cellular respiration occurs
Process of creating cell energy
The cell uses oxygen to break down glucose
(sugar), which creates energy
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
⇒ 6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O + energy
Sugar + Oxygen ⇒ Carbon Dioxide + water + energy
Only in plant cells
Contains chlorophyll – gives the plant a green color
Contains a double outer membrane.
Stroma - an area inside of the chloroplast where reactions occur and sugars are created
Carry out photosynthesis by capturing light and creating energy
Energy is in the form of ATP:
Adenosine Tri-Phosphate
Uses the sun to convert water and
CO2 into oxygen and sugar
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O ⇒ C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
Carbon Dioxide + Water ⇒ Sugar + Oxygen
Only found in plant cells
NOT the same as the cell membrane
Composed of proteins and carbohydrates (cellulose)
For support and shape of the cell – Rigid shape
Protects cell from damage
– Strong structure
Connects with adjacent cells
Are in both plant and animals cells, but much larger in plant cells.
Stores food, waste, and water
In plants, it stores a lot of water and takes up more than ½ of the cell’s volume.
Gives a plant cell support and structure