FINA 351 – Managerial Finance, Chapter 12, (Ref. 12b)
advertisement

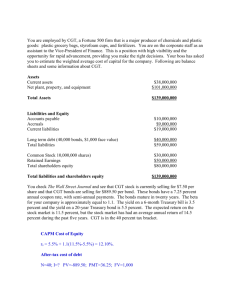
FINA 351 – Managerial Finance, Chapter 12, (Ref. 12b) 1. Refer to the “Finance Matters” box in your chapter about the popular business concept of EVA. (A) T or F: Briggs & Stratton, Coca-Cola, and Toys ‘R’ Us are examples of companies that use EVA as a way to measure corporate performance. (B) What does a positive EVA mean? (C) T or F: Companies that have been most successful at generating value for shareholders (EVA) include GM, Time Warner, and Goodyear Tire & Rubber. 2. Review the information for Company A and B below. Company A Company B Return on investment (ROI) 14% 8% WACC 13% 6% (A) Of the two companies, which company is better at generating net value for shareholders? Explain. (B) T or F: A good investment is one where the return on investment (ROI) is smaller than the WACC. (C) T or F: The WACC represents the minimum return required if the company wants to at least break even. (D) T or F: A higher WACC is not necessarily bad, as long as the company is able to generate returns (EVA) in excess of WACC, resulting in a positive net return. 3. T or F: According to the instructor notes, more than half of nearly 42,000 companies surveyed in 2015 did not generate high enough return to cover their cost of capital. (Their medium return was 3.1% less than their cost of capital). 4. Suppose you started a coffee shop by purchasing a trailer for $50,000 and converting it into a drive-thru latte shop. You move the trailer to strategic locations, which may vary depending on time of day. To get the long-term financing, you borrowed $30,000 from Umpqua Bank at a rate of 6%, due in a balloon payment in five years. The interest is tax deductible, and your applicable tax rate is 25%. The other $20,000 you obtained from your dad, who became a passive equity capital partner in your business (i.e. is only interested in the dividend and will not participate in management). You agree to pay him an annual dividend of 8%, which is not tax deductible. (A) Calculate the cost of obtaining long-time financing (WACC) for your business. (B) After a few years of successful operations, how might you be able to lower your WACC? 5. Why is WACC an important calculation to a business valuation specialist? 6. ABC Corporation makes children’s toys. It based in Washington State. It is having a hard time competing, especially with companies based in China. ABC has asked you to help calculate its cost of capital in order to determine how it stacks up against similar companies. a) Calculate ABC’s cost of debt based on the following information: 30-year bonds were issued 7 years ago that pay a fixed coupon of 8% annually; the bonds are currently priced at 108, based on an annual market interest rate (YTM) of 7.273%. ABC has taxable income of $20,000,000. b) Calculate ABC’s cost of common equity based on the following information: Beta = 1.1; Expected return on the market = 12.5%; T-Bills yield = 4.5%; the next dividend (annualized) = $2.73 per share; dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 5.0% per year; common stock is currently priced at $48 per share. c) Calculate ABC’s cost of preferred stock assuming it is currently priced at $94 and pays a $6 dividend each year. d) Calculate ABC’s overall weighted-average cost of capital, assuming following market-based capital structure: Debt: 6,000 bonds, each priced at 108 Common Equity: 625,000 shares outstanding, each priced at $48 Preferred equity: 106,000 shares outstanding, each priced at $94 (d) WACC = a) Cost of Debt [Cd x weight] Cd = YTM (1 - T) Optional Solutions Grid b) Cost of Common Stock [ Ccs x weight] Method 1 (DGM): Ccs = (D1 / P0) + g c) Cost of Preferred Stock [Cps x weight] Cps = D / P0 Method 2 (CAPM): Ccs = Rrf + (Rm - Rrf) b 7. A complex online model called ValuePro estimates the current WACC% of Kellogs (K) to be around 6%, and the WACC of Boeing (BA) around 9%. Speculate why the WACC differs between the two companies. 8. Suppose that Ignatius Ifferty, a graduate of WSU, is CEO of IgyIfy Corp. He has hired you to review his cost of capital calculation to help determine if it would be cheaper to obtain more financing by selling stock or bonds. Since the stock is selling for $50/share and the dividend is $5/share, Igy concludes that the cost of equity is 10%. Also, he has determined that the cost of debt is 12.5%, based on $1 million of interest expense paid on $8 million of bonds (1/8 = 12.5%). Since he had concluded that the cost of debt is more expensive that the cost of equity, Igy is planning to issue more debt. Evaluate Igy’s reasoning (note that he graduated from WSU, not WWU). BONUS (worth 5 points): Go to http://www.wacccalculator.com/ and enter fictitious variables. Prove the calculated answer by using the WACC formula discussed in this chapter.