Genetics: Part II Predicting Offspring
advertisement

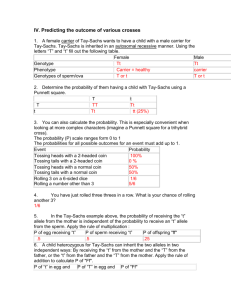
Genetics: Part II Predicting Offspring 2 Key Male 1st generation Affected male Female Affected female Mating 1st generation Ww ww Ww ww 2nd generation Ww ww 3rd generation WW or Ww Widow’s peak ff ff (a) Is a widow’s peak a dominant or recessive trait? Ff Ff Ff ff ff FF or Ff 3rd generation ww No widow’s peak ff Ff 2nd generation FF or Ff Ww ww ww Ww Ff Offspring Attached earlobe Free earlobe b) Is an attached earlobe a dominant or recessive trait? Interpret this Pedigree Is the trait dominant or recessive? What is the genotype of the first born male in generation II? What is the genotype of the youngest female in generation II? Explain. Curriculum Framework 3A EK 3 inheritance provides an understanding of the pattern of passage (transmission) of genes from parent to offspring. a. Rules of probability can be applied to analyze passage of single gene traits from parent to offspring. Probability 6 Rule of Addition • Rule of addition: Chance that an event can occur 2 or more different ways. – Sum of separate probabilities – Ex.1/4 Pp +1/4 Pp 1/2 Pp 7 Rule of Multiplication • The multiplication rule states that the probability that two or more independent events will occur together is the product of their individual probabilities • Chance that 2 or more independent events will occur together – Ex. Probability that 2 coins tossed at the same time will land heads up – Probability of H x H HH –½ x ½ = ¼ Rule of Multiplication Cross: GgSs x GgSS • What is the probability of producing green, smooth seeds in this cross? • Solution • Green = 3/4 Smooth = 4/4 • 3/4 X 4/4 = 12/16 = 3/4 probability of producing green smooth seed From your formula chart: If A and B are mutually exclusive, then P (A or B) = P (A) + P (B) If A and B are independent, then P (A and B) = P(A) X P(B) Ex. Probability of a couple having three girls? Ex. Probability of a couple having three boys? Ex. Probability of having three boys or three girls? 10 For example: In a heterozygous cross YyRr Probability of YYRR 1/4 (probability of YY) 1/4 (RR) 1/16 Probability of YyRR 1/2 (Yy) 1/4 (RR) 1/8 Cross PpYyRr x PPyyrr ppyyRr ppYyrr Ppyyrr PPyyrr ppyyrr 1/ 1/ (yy) 1/ (Rr) (probability of pp) 1/16 4 2 2 1/16 ? ? 1/16 Chance of at least two recessive traits 6/16 or 3/8 Cross PpYyRr x Ppyyrr (Answer) ppyyRr ppYyrr Ppyyrr PPyyrr ppyyrr 1/ (yy) 1/ (Rr) (probability of pp) 4 2 2 1/ 1/ 1/ 4 2 2 1/ 1/ 1/ 2 2 2 1/ 1/ 1/ 4 2 2 1/ 1/ 1/ 4 2 2 1/ Chance of at least two recessive traits 1/16 1/16 2/16 1/16 1/16 6/16 or 3/8 Practice definitions • • • • • • • Genotype Phenotype Monohybrid Dominant Recessive P1 Homozygous • • • • • Heterozygous Allele Test cross F1 F2 14 Practice • Now that you have reviewed some basic genetics concepts solidify your skill by completing the set of practice problems available at http://anthro.palomar.edu/practice/mendqui2.htm 15 Created by: Debra Richards Coordinator of K-12 Science Programs Bryan ISD Bryan, TX