Water Use Trends & Forecasting Lecture 1 Dr. Jawad Al-rifai
advertisement

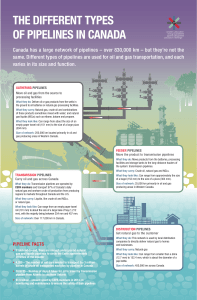
Water Use Trends & Forecasting Lecture 1 Dr. Jawad Al-rifai 1 Water supply Water supply is one of balancing Availability & demands. Availability means: Quality of resources Depletion & Replenishment Demands (current & Future) Domestic Use Industrial Activity Commercial Ecology & Economic conditions Technical & Social factors Decisions on designing of water distribution system and treatment plant should rely on the above factors. 2 Water use sectors are: ◦ Agriculture (critical in arid and semiarid regions- up to100%) ◦ Thermoelectric power (plant size & cooling heat transfer efficiency) ◦ Cities & Communities (drinking, cooking, showering, lawn watering, pool, street cleaning, fire freighting, etc) ◦ Industry & Commercial activities (Recycling and Process changes) ◦ Natural Systems ◦ Recreation ◦ Energy Resource Development When water supplies are limited, conflicts among users become intense and tradeoffs must be made 3 Factors Affecting Water Use Population Climate Types of water uses (industrial, commercial, agriculture, etc) Economic conditions Conservation (water saving) Management practices (including reuse of wastewater & storm water) Tourism 4 5 Average day demand. The total annual quantity of water production for an agency or municipality divided by 365. Maximum day demand. The highest water demand of the year during any 24-h period. Peak hour demand. The highest water demand of the year during any 1-h period. Peaking factors. The increase above average annual demand, experienced during a specified time period. Peaking factors are customarily used as multipliers of average day demand to express maximum day and peak hour demands. Distribution pipeline or main. A smaller diameter water distribution pipeline that serves a relatively small area. Water services to individual consumers are normally placed on distribution pipelines. Distribution system pipelines are normally between 150 and 400 mm (6-16 in.). Transmission pipeline or main. A larger-diameter pipeline, designed to transport larger quantities of water during peak demand-periods. Water services for small individual consumers are normally not placed on transmission pipelines. Transmission mains are normally pipelines larger than 400 mm (16 in.). Definitions 6 Fluctuation of daily water use patters 7