Student name:……………………………………… Registration no……………………………….. Section no.:………………. Philadelphia University
advertisement

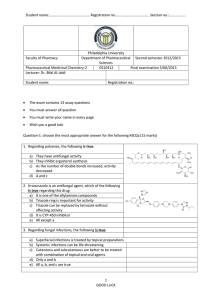
Student name:……………………………………… Registration no……………………………….. Section no.:………………. Philadelphia University Department of Pharmaceutical First semester 2011/2012 Sciences Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry-2 0511322 Final examination 15/01/2012 Lecturer: Dr. Bilal Al-Jaidi Internal reviewer: Dr. Mwaffaq Badawneh Faculty of Pharmacy Student name: Registration no.: Question-1: Choose the most appropriate answer for all the following questions: (8 marks) 1. Regarding Mustine, the following is true: A. B. C. D. E. It acts as alkylating agent The nitrogen might play a role in the mechanism of action No role for the chlorine atom in activity A and B All of the above 2. Regarding Treosulfon, the following is true: A. B. C. D. The sulfonate group is important for activity The removal of OH group will abolish the activity The selected carbon is the reactive part in the structure All of the above 3. Carmustine is an anticancer agent, which of the following is true regarding this drug: a) Used in brain tumour because it has the reactive nitroso group b) The dichloroethyl group is responsible for the alkylating activity c) It can only form one covalent bond with DNA d) Only a and b e) All of the above GOOD LUCK Student name:……………………………………… Registration no……………………………….. Section no.:………………. 4. The following is one of the carrier group added to nitrogen mustard to enhance their absorption and cell uptake: A. B. C. D. E. Amino acid Steroid ring Nucleic acid Only A and B All of the above 5. The following are DNA alkylating agents except: A. B. C. D. Only B and C 6. The following is true regarding Thiotepa A. B. C. D. E. Is a safe anticancer agent Urethane group acts as a leaving group Could form more than one bond with DNA Chemically stable structure All except A 7. The following could be true regarding 6-mercaptopurine: A. B. C. D. It is active in this form, not a prodrug Thiol group is important for activity Inhibits Pyrimidine biosynthesis Oxidation of pteridine ring will reduce activity E. Only B and C GOOD LUCK Student name:……………………………………… Registration no……………………………….. Section no.:………………. 8. Fludarabine is used for the treatment of chronic lymphatic leukaemia, the structure acts as a prodrug. What is the active compound? A. Monophosphate B. Diphosphate C. Polyphosphate D. Triphosphate 9. The following diagram is representative of a group of naturally occurring compounds that is used in combination therapy to treat a variety of tumours, Which group of compounds is represented by this structure: A. Podophyllotoxins teniposide B. Camptothecins irinotecan C. Taxanes D. Vinca alkaloids 10. How do Taxanes plant alkaloids work? A. It inhibits tubulin depolymerisation B. it inhibits tubulin polymerisation C. It inhibits both processes D. It inhibits neither process 11. The following group of structures is intercalating anticancer agents, to which family of compounds do these structures belong? A. Podophyllotoxins B. Camptothecins C. Anthracyclines D. Bleomycins GOOD LUCK Student name:……………………………………… Registration no……………………………….. Section no.:………………. 12. Which of the following drugs inhibits topoisomerase II? A. B. C. D. Uracil mustard Daunorubicin Cyclophosphamide Cisplatin 13. The following structure is called lomustine and is used in the treatment of brain tumours. Which of the following statements is true regarding the above structure? A. It cannot cross the blood brain barrier. B. It is activated by an enzymatic metabolic reaction C. It cannot be given orally. D. It is both an alkylating and a carbamoylating agent. 14. The following structure is a biosynthetic precursor for an important enzyme cofactor required by the enzyme thymidylate synthase: what is this cofactor A. Folic acid B. Dihydrofolic acid C. Tetrahydrofolic acid D. N5, N10-methylene tetrahydrofolic acid 15. The following structure is used in the treatment of breast, liver and skin cancers, What is the target for the structure A. B. C. D. Thymidylate synthase Dihydrofolate reductase Adenosine deaminase Ribonucleotide reductase GOOD LUCK Student name:……………………………………… Registration no……………………………….. Section no.:………………. Question-2 Identify the following structures: Question-5: (3 marks) Melphalan is an anti-cancer agent, answer the following questions based on its structure below: 1. It is an alkylating agent, explain? ..................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................... 2. Is there any role for the circled group in the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic properties of melphalan, discuss your answer? GOOD LUCK Student name:……………………………………… Registration no……………………………….. Section no.:………………. ..................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................... Question-7 Draw the messing structures in Chlorambucil synthetic scheme: Look carefully to the illustrated structures in the table and then answer the following questions? (22 marks) 1. 3. GOOD LUCK Student name:……………………………………… Registration no……………………………….. Section no.:………………. 1. What is the name of compound 1................................, which region of the molecule is involved in intercalation..........................................................................., they chelate a ferrous ion as part of their mechanism of action, which region of the molecule is important in chelating ions, .................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................ GOOD LUCK Student name:……………………………………… Registration no……………………………….. Section no.:………………. 3. What is the name of compound 3................................, side effect associated with this compound is........................................................, which can be avoided by co-administration with ........................................................., Draw its mode of action, and mention the name of metabolite responsible for its side effect? 4. What is the name of compound 4................................, What sort of agent is it ................... ............................................., The structure is a prodrug which is converted in the body to the active compound. Draw the steps in this activation process? GOOD LUCK Student name:……………………………………… Registration no……………………………….. Section no.:………………. GOOD LUCK