Amith Shetty SMEDSA study Westmead
advertisement

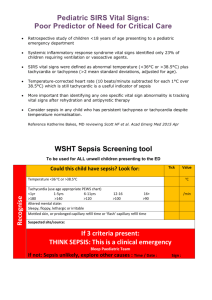
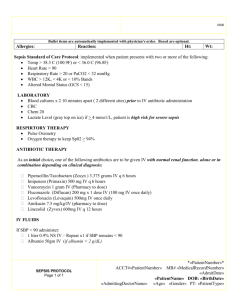
Amith Shetty SMEDSA study Westmead Sepsis noted as leading cause for SAC 1 incidents and RCAs in NSW A process for early recognition, review and resuscitation of septic patients Timely early interventions – antibiotics and intravenous fluids CEC Sepsis kills program http://www.cec.health.nsw.gov.au/programs/sepsis RECOGNISE - risk factors, signs and symptoms of sepsis RESUSCITATE with rapid intravenous fluids and antibiotics within the first hour of recognition of sepsis REFER to senior clinicians and specialty teams, including retrieval as required Initiate sepsis pathway based on suspected infection + 2 SIRS criteria Up-triaging to ATS category 2 Sepsis bomb Oxygen Blood cultures Lactate Intravenous fluids – 20ml/kg crystalloid bolus Antibiotics <60 minutes ◦ Based on clinician predicted source ◦ Antibiotic stewardship program and guidelines Monitoring Early senior review and assessment Early referral to intensive care services Inpatient sepsis management pathway being launched soon 24-48 hr sepsis management tool in pipeline • Improvement in time to antibiotics to 60 minutes in last three years • >18000 patients registered on CEC sepsis archive • Crude patient level data available on archive – time to antibiotics , lactate level, SIRS data Retrospective evaluation of prospectively identified patients presenting to ED with sepsis Multicentre approval ◦ Westmead ◦ Concord ◦ RPA Single centre data collection and analysis 850 bed tertiary hospital 45 treatment space Emergency department >65000 annual census ED presentations 35-40% ED to ward admission rates Sepsis kills pathway ATS category 2 for suspected infection + 2 SIRS criteria Clinicians encouraged to report Sepsis pathway antibiotic guidelines Antibiotic stewardship guidance Patient safety officer and audits ~1200 patients recorded at Westmead in past 24 months Interim analysis at 590 patients Median age of patients = 59.5 (IQR 36-75) Females = 306 median age 54.5 (IQR 32-76) Males = 284 median age 63 (IQR 46-75) Antibiotics ceased or not given in 48 hours – non bacterial etiology, DNR Exclusions (no antibiotics 9 + antibiotics ceased <48 hours 76) 85 Median age of female (44 exclusions) = 33 (IQR27.5-43.5) Median age for males (41 exclusions) = 49 (IQR 26-68) Mann-Whitney U test comparing Age in inclusions versus exclusions Median difference = -17 (CI: -24 to -11) (p<0.001) Total number of inclusions = 505 Median age of patients = 63 (IQR 42-78) Females = 262 median age 59.5 (IQR 35-78) Males = 243 median age 64 (IQR 50-77) 507/ 590 patients triaged to ATS category 2 85.9% adherence to guideline Median time to clinician 36 mins (IQR 16-73) ATS<2 versus >2 Time to clinician– 35 versus 84 minutes (p<0.001) Time to antibiotics – 66.5 versus 129 minutes (p<0.001) Time to 2nd L fluids – 99.5 versus 228 minutes 492/590 (83.4% 95%CI 80.2-86.2) underwent lactate testing Exclusions vs inclusions – median 1.4 v 1.8 (p<0.01) Sepsis versus severe sepsis/ septic shock – median 1.5 v 2.2 (p<0.01) Dead versus alive – 2.8 v 1.7 (p<0.001) But significant overlap of tails 484/505 patients had blood cultures collected 95.8% adherence (95% CI 93.7-97.3) 94 /484 (19.4%) positive BC, 13/94 (13.8% contamination rates) → 81/ 484 (16.7% 95%CI 13.7-20.3) significant results 26.5% BC + for severe sepsis group versus 13.4% BC + in plain sepsis group 329/505 Urine cultures – 62/329 positive results 193/ 505 other cultures – 100/193 positive results 297/ 505 (58.8%) received appropriate antibiotics according to guidelines 192 / 505 (38.0%) received at least one antibiotic as per guidelines 16 / 505 (3.2%) received antibiotics not according to guidelines Severe sepsis definition = sepsis-induced tissue hypoperfusion or organ dysfunction (any of the following thought to be due to the infection) Sepsis-induced hypotension Lactate above upper limits laboratory normal (>2) Urine output < 0.5 mL/kg/hr for more than 2 hrs despite adequate fluid resuscitation Acute lung injury with Pao2/Fio2 < 250 in the absence of pneumonia as infection source Acute lung injury with Pao2/Fio2 < 200 in the presence of pneumonia as infection source Creatinine > 2.0 mg/dL (176.8 μmol/L) Bilirubin > 2 mg/dL (34.2 μmol/L) Platelet count < 100,000 μL Coagulopathy (international normalized ratio > 1.5) Age – 58 (IQR 38-75) versus 67 (49-80) Lactate value → 1.5 (1.1-2.2) v 2.2 (1.4-3.8) Total MEDS score → 5 (3-9) v 8 (6-12) Charlson score → 3 (0-7) v 5 (2-9) Hospital LOS → 4 (2-8.5) v 7 (3-13) Time to antibiotics →69 minutes (IQR 42126.5) in patients with plain sepsis versus 67 minutes (IQRR 49-80) in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock Time to second litre fluids → 196 minutes (107.5-403.5) v 249 minutes (136-489) no sepsis severe sepsis/ septic shock Plain sepsis SIRS 0 17 6 14 37 SIRS 1 14 28 55 97 SIRS 2 28 46 116 190 SIRS 3 18 57 78 153 SIRS 4 6 42 34 82 SIRS 5 2 16 8 26 SIRS 6 0 5 0 5 total 85 200 305 590 Sensitivity 0.80 95%CI 0.76- 0.83 Specificity 0.36 95%CI 0.27- 0.48 Positive predictive value = 0.88 Negative predictive value = 0.25 Patients with severe sepsis more likely to have >3 SIRS criteria (p<0.001) AMBULANCE vs PRIVATE transport 274 vs 231 (Mann-Whitney) Median age 74 versus 48 (MD 23 p<0.01) >SIRS 3 vs 2 (MD 1 p<0.01) Higher lactate 2.2 vs 1.5 (MD 0.6 p<0.01) Severe sepsis rates 132/274 (48.2% 95% CI 42.354.1) versus 68/231 (29.4% 95% CI 23.9-35.6) (p<0.01) ◦ MEDS score 9 vs 3 (MD 5 p<0.01) ◦ Mortality (51/231 22.1% 95%CI 17.2-27.9%) versus (6/231 2.6% 95% CI 1.2-5.5%) ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ 478/ 505 (94.7%) concurrence of clinician prediction of presumed source of diagnosis when compared to final discharge diagnosis Source Number Chest/ respiratory 219 Urine 84 Skin/ soft tissue/ Orthopedic 44 Abdominal / biliary 41 PUO/ unknown 51 Neuro/ CNS 6 Bloodstream 10 Oral/ Dental 22 Mixed / others 28 Total 505 Mortality rates – in-hospital, 30-day or 90day Hospital LOS Discharge location Occurrence of severe sepsis or septic shock Time to antibiotic Total patients ≤ 1 hour 224 127 97 X >1 to ≤ 2 hours 134 95 39 x > 2 to ≤ 3 hours 57 33 24 x > 3 hours 86 47 39 x 501 302 199 x Total Plain sepsis Severe sepsis and septic shock Mortality Time to second litre fluids Total patients Plain sepsis Severe sepsis and septic shock In-hospital mortality ≤ 1 hour 35 13 22 X >1 to ≤ 2 hours 65 35 30 X >2 to ≤ 3 hours 76 46 30 X >3 hours 279 177 102 X Total 455 271 184 x More clinical trials needed on sepsis patients not just focus on severe sepsis and septic shock – ED from ICU shopfront Overall benefit of bundles care – risk versus benefit ? RCT on antibiotics after source identification versus clinician prediction based – stratified risk tool development Risk factors for progression to severe sepsis Bundled care can lead to significant improvements in delivery of care to sepsis patients Ambulance cohort significantly more unwell – focus for future studies Senior clinicians are able to reliably predict source of infection