USAID TB Technical Assistance Model June 19, 2014

USAID TB Technical
Assistance Model
June 19, 2014
Overview
• TA in the Context of USG TB Strategy
• Accomplishments and Approach of TB Strategy
• USAID TA Model
2
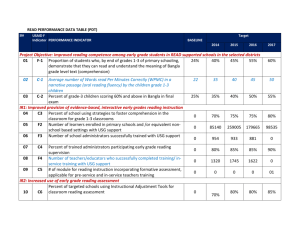
USAID TB Funding Trends 1998 –2013
* FY funds including all accounts
By 2012, TB prevalence in 27 USAID-supported countries decreased by 40% .
4
By 2012, TB mortality in 27 USAID-supported countries decreased by 41% .
5
Treatment Success Rate in Select Countries
6
Case Detection Rate in Select Countries
(all forms of TB)
7
New patients with MDR TB initiated on treatment each year:
(USAID focus countries)
Target
* These numbers differ from the past reports because they are adjusted to include only the current USAID countries to accurately reflect the trends.
8
USG TB Strategy: Key Approaches
Approach
Promote country ownership
Examples
• Develop 5-year NTP Strategic Plans
• Support development and implementation of GF grants
• Support NTP routine monitoring and supervisory systems
• Support participatory MOH led external evaluations
• Joint annual work planning with NTP and other partners
Sustainable systems • Strengthen drug/supply chain management
• Strengthen facility level routine M&E system
• Develop/improve lab network at all levels
• Build primary health care capacity
Leverage resources • Develop GF proposals to cover unmet needs in NSPs
• Coordinate TB/HIV funds through PEPFAR
• Expand health platforms (community, lab, drug mgmt.)
Provide global technical leadership
• Develop and pilot new tools, policies, guidelines
• Provide TA to countries/in targeted technical areas
• Participate in WHO core working groups and STAG-TB
• Lead USG international TB efforts
9
Country Level Focus – supporting the field
Field and
Regional
84%
($188 in FY13)
GH 16%
($36m in FY13)
Field level support:
• Response to local needs/gaps based on NTP
Strategic Plan, GF grant, and PEPFAR COP
• TA to MOHs, private sector, and NGOs; coordinate with other partners
• Expansion of new approaches/technologies (e.g.,
PMDT and Xpert)
• Global Drug Facility (GDF)
GH/regional bureaus support:
• Global policy and guideline development
• Global operational and implementation research
• Technical support for evaluation, program design, monitoring, mentoring, and project management
Implementers: STB Partnership, WHO, CDC, TB CARE
I and II, TO 2015, TREAT TB, SIAPS, USP, TB Alliance,
GLC, TB TEAM
• In FY13, Washington managed 51% of the total USAID TB funding and
10
36% of the field support resources.
USAID TB Technical Assistance Model
• USG convenes
and leverages existing USAID bilateral program support to NTPs, preventing duplication, optimizing areas coverage and dovetailing
• Focus and concentrate
in response to the GF changes, the new funding model, and evolution of the TB grants
Principles of Approach
• Mirrors the inherently disease-specific NFM
• Focus on development and implementation of National
TB Strategic Plans
• On-going Country dialogue
• Development of a disease-specific concept note and funding envelope – assist with technical trade-offs
• Disease-specific TA to ensure quality programming
11
Convener : Model focuses on actively triangulating information among all partners
In-country technical partners
GF/FPM
USAID TB Team
Convener Role
•
Regular country phone calls with key stakeholders
•
Ensure clear roles and responsibilities of stakeholders
•
Monitor and evaluate progress
PR/NTP
12
USG Approach to Address GF grant TA support
• Shift in prioritized focus on a number of countries covering:
• 70% of the total GF grant funding for TB
• 88% of TB prevalence
• 88% of MDR-TB
• 84% of TB/HIV co-infection
• Focus on quality programming and areas of technical expertise required
• Focus on more in-country approach: more consistent TA providers that less fly-in and fly-out TA
• More strategically wrap around USG bilateral program and
USG TB working group partners
Priority Country Selection & Analysis
Criteria:
• Burden (TB, MDR-TB, TB/HIV)
• Global Fund Performance Data (rating, disbursement rate, expenditures)
• Number and size of grants
• For MDR-TB: minimum of 1,000 projected treatments for 2012-2014
Analysis of types of TA needed:
• Burden and performance thus far (are things moving?)
• Review t ypes of TA currently available through USG mechanisms
• Review of issues within countries based on past performance, stakeholders meetings/calls, discussions with partners and FPMs
14
PRINCIPLES TO RESULTS
USG TA
Model
Accelerated impact
In-country TA:
• TB CARE I and II
• PATH TB TO
Targeted TA:
• GDI (GLC)
• CDC
Multi-partner TA:
• TBTEAM
• SIAPS
• GDF
RESULTS
1. Full Implementation of National Strategic Plan
2. Meets GF grant targets with quality
3. Expends funds appropriately
15
USAID Country Mapping Example: Bangladesh
Technical experts visit countries to provide MDR-TB
TA, and then project in country follows up.
Experts provide additional virtual assistance to ensure things are moving forward
Assists with partner coordination meetings/calls and
Phase 2 renewal preparation
Bangladesh
MDR Short-Term TA
(NTP& GF)
Grant
Management/Program
Expansion TA
In-country advisor works with partners/USG project to ensure that grant is moving forward and expanding, and identifies any TA needs. Also ensures that countries understand all CPs CDC USAID
In-country advisor (hired through TBCARE 2, builds coordination)
Coordination TA (bringing partners together)
TBTEAM
Drug Management
TA
MSH/SIAPS Project
(Mission funded)
Ensures that country is doing proper quantification and that there is an adequate supply of drugs. Works with in-country advisor on any GF grant bottlenecks related to drug management
16