Epoxide Synthesis & Reactions: Organic Chemistry Notes
advertisement

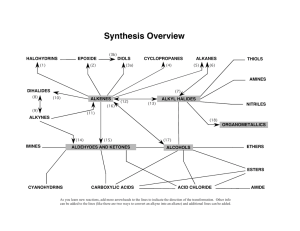
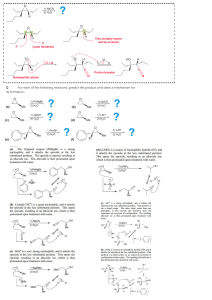
CH 11-4: Epoxide Synthesis and Reactions •Ring with three atoms (C, C, O) •Very reactive due to ring strain •Formed during the metabolism of some toxic compounds. •Epoxide Synthesis: Intramolecular SN1 or SN2: Reactions of Epoxides Nucleophilic substitution resulting in epoxide ring opening: (1) If acid-mediated (or catalyzed), the nucleophile adds to the most substituted carbon by anti addition. (2) If the nucleophile is a strong base (base catalyzed) all aspects of the reaction resemble SN2 (anti addition). (3) All epoxide reactions are stereospecific (anti addition). •General Reaction: Acid-Mediated Epoxide Ring Opening Mechanism. Write a complete mechanism for the balanced equation below. Your mechanism must consist of a series of numbered, balanced equations for each chemical step, and curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs. Note the regiochemistry and stereochemistry. Base Catalyzed Epoxide Ring Opening Mechanism. Write a complete mechanism for the balanced equation below. Your mechanism must consist of a series of numbered, balanced equations for each chemical step, and curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs. Note the regiochemistry and stereochemistry.