Balloon Race Write Up Chapter 2: Motion In One-Dimension

Balloon Race Write Up
Chapter 2: Motion In One-Dimension
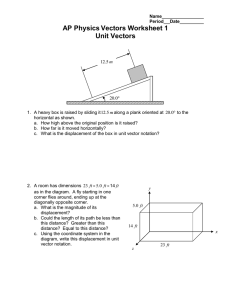
___ one dimensional motion
___ displacement
___ + and – displacement
___ velocity (# and direction)
___ acceleration (# and direction)
Other:
Chapter 3: Two-Dimensional Motion & Vectors
___ vectors indicate direction
___ frame of reference
Other:
Chapter 4: Forces & The Laws of Motion
___ force
___ contact or field force
___ free body diagram
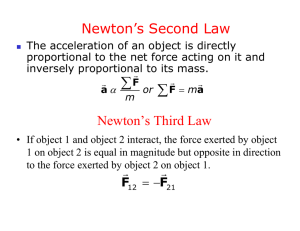
___ inertia = Newton’s First Law
___ acceleration is determine by the net external force
___ F=ma = Newton’s Second Law
___ Equal/Opposite = Newton’s Third Law
___ Normal force, friction force, gravitational force, applied force
___ friction depends on surface
___ air resistance
___ free-body diagrams / force diagrams
Other:
Chapter 5: Work & Energy
___ force causes a displacement called work
___work done when force is parallel to displacement
___ kinetic energy (energy due to motion)
___potential energy (energy due to its position)
___ gravitational potential energy & elastic potential energy
___energy can change forms but never created or destroyed
___ power is the rate at which work is done or rate of energy transfer
Other:
Chapter 10: Heat
___temperature is proportional to the kinetic energy of atoms/molecules
___ energy is transferred between substances as heat
___thermal conduction
___specific heat
Other:
Chapter 12: Vibrations & Waves
___elastic potential energy properties
Other:
Chapter 13: Sound
___medium is air
___sound coming from balloon or tires makes waves
___waves travel three dimensionally
___pitch is determined by frequency
Other:
Chapter 14/15: Light & Reflection /Reflection
___visible light includes a spectrum
___see color because color is reflected
___cannot see colors because they are absorbed
___lenses – in case you wear contacts or glasses
Other: