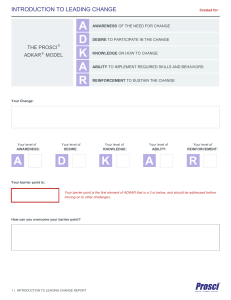
“A GREAT IDEA WON’T MATTER IF YOU CAN’T CARRY IT THROUGH”
advertisement

“A GREAT IDEA WON’T MATTER IF YOU CAN’T CARRY IT THROUGH” A presentation by Mark Casey CHANGE MANAGEMENT Change management is a structured approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organisations from a current state to a desired future state, to fulfill or implement a vision and strategy. KURT LEWIN 1890 - 1947 Change Theory – 3 Stage Process UNFREEZE CHANGE REFREEZE UNFREEZING What ever assists people to accept that change is needed because the existing situation is not adequate CHANGING Involves rearranging of current work practices and procedures to meet new needs REFREEZING Reinforces the changes made so that the new practices of behaving become established. FORCE FIELD ANALYSIS Process of analysing the forces that drive change and the forces that restrain it DRIVING FORCES Factors that push towards the new, more desirable status RESTRAINING FORCES Factors that exert pressure to continue past behaviour or resist new actions ORGANISATIONAL CHANGE Three options to bring about change: 1. 2. 3. Increase the driving forces Decrease the restraining forces Do a combination of the two approaches JOHN P KOTTER 1947 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. CHANGE MODEL Create Urgency Form a Powerful Coalition Create a Vision for Change Communicate the Vision Remove Obstacles Create Short-term Wins Build on the Change Anchor the Changes in Corporate Culture INDIVIDUAL CHANGE “Everyone thinks of changing the world, but no one thinks of changing himself” Leo Tolstoy ADKAR MODEL – PROSCI 1994 ADKAR describes the required phases that an individual will go through when faced with change. ADKAR is a foundational tool for understanding “how, why and when” to use different change management tools. FIVE BUILDING BLOCKS OF CHANGE Awareness Desire Knowledge of the need for change to participate & support change on how to change Ability to implement skills & behaviours Reinforcement to sustain the change PROCHASKA STAGES OF CHANGE MODEL The stages of change are: Pre-contemplation (Not yet acknowledging that there is a problem behavior that needs to be changed) Contemplation (Acknowledging that there is a problem but not yet ready or sure of wanting to make a change) Preparation/Determination (Getting ready to change) Action/Willpower (Changing behavior) Maintenance (Maintaining the behavior change) and Relapse (Returning to older behaviors and abandoning the new changes) CHANGE MANAGEMENT Four key areas of successful change management. They are: Understanding change. Planning change. Managing resistance to change. Implementing change. UNDERSTANDING CHANGE Before you manage a project that involves changing the way that people work, you must first understand how people react to change. Reactions can range from "shock and denial," when business as usual is first disrupted, to "acceptance" and "commitment," as the change is implemented. Levels of performance may fall as they learn how to use new systems and processes. “Unfreeze-Change-Refreeze" highlights why you need to build sufficient time into the process for people to adjust. PLANNING CHANGE Conducting an impact analysis/ will assist you to understand the possible positive and negative consequences of change, so that you can develop contingency plans to deal with any issues that may arise [driving forces/restraining forces]. MANAGING RESISTENCE TO CHANGE For people to be motivated to change, they must be dissatisfied with the current situation, and must think that the proposed solution is desirable and practical. Use this equation to assess readiness for change, so you can ensure that a change is actually needed, and that your planned changes will result in significant benefits. IMPLEMENTING CHANGE When you implement change, communication is crucial – you'll almost certainly have problems at some point, and if you aren't regularly talking about the plan and communicating your successes, people may go back to the preferred ways of doing things. CHANGE EXAMPLE One particular example of my direction and facilitation of change management was with a manufacturing company based in Queensland. My role as project manager was to address issues of a declining market share due to a lack of coordination of production processing, quality and the delivery of product. As an established business the practices and procedures had become stale and complacent. Fundamental to this business was the performance of the management team and the approach they presented which can only be best described as “management by department silos”. This fragmentation of the business was evident in the raw product ordering, production area, manufacture / quality as well as the sales and marketing of the product. CHANGE EXAMPLE - CONTINUED Change Tools Applied: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Structure analysis – fit for purpose Key stake-holder interviews Social Network / Stake holder analysis Meeting/s analysis – effective representation Planned vs. actual analysis Operations monitoring / reporting Supervisor development RESISTANCE TO CHANGE Identifying resistance - Lack of participation - Openly expressing emotion - Lack of attendance and absenteeism - Reverting to old ways - A decrease in productivity and missed deadlines RESISTANCE TO CHANGE Ineffective methods for dealing with resistance - Ignoring resistance and expecting it to go away on its own - Not listening to and understanding the concerns of those impacted - Not gaining input from those impacted - Underestimating the resistance - Poor communication RESISTANCE TO CHANGE Employee resistance - Lack of understanding around the vision and need for change. - Comfort with the status quo and fear of the unknown. - Corporate history and culture. - Opposition to the new technologies, requirements and processes introduced by the change. - Fear of job loss. RESISTANCE TO CHANGE Manager resistance - Loss of power and control. - Overload of current tasks, pressures of daily activities and limited resources. - Lack of skills and experience needed to manage the change effectively. - Fear of job loss. - Disagreement with the new way. - Scepticism about the need for change.