Price
advertisement

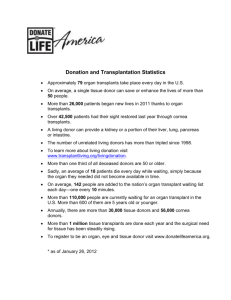
Price ($thousands/organ transplant) 95 Supply Curve: What Sellers are Willing and able To sell at different prices 40 Equilibrium @ Price=$40,000 Demand Curve: What Buyers are Willing and able To buy at different prices Organ Transplants (number per year) Markets Want to Work • Markets = the process of procuring and allocating a good • The market can “fail” in that the resulting allocation of goods is either inadequate or viewed as inappropriate Disequilibrium Due to Government Regulation (A) (B) Current Price P (C) Current Price Supply Demand P Demand (D) Current Price Supply P Current Price P Demand Supply Demand Supply Supply Limit Q Q Q Q Price ($thousands/organ transplant) 95 Surplus @ Price= $60,000 60 40 36 Supply Curve: What Sellers are Willing and able To sell at different prices Equilibrium @ Price=$40,000 Demand Curve: What Buyers are Willing and able Shortage @ Price = $36,000 To buy at different prices Organ Transplants (number per year) Price ($thousands/organ transplant) 95 Supply 40 36 Equilibrium @ Price=$40,000 PRICE CEILING At $36 causes Shortage Demand Organ Transplants (number per year) Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplie Price ($thousands/organ transplant) 95 Supply 40 36 Equilibrium @ Price=$40,000 PRICE CEILING At $36 causes Shortage Demand Organ Transplants (number per year) Price Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied ($thousands/organ transplant) Black market prices exceed legal prices 95 Supply 40 36 Equilibrium @ Price=$40,000 PRICE CEILING At $36 causes Shortage Demand Organ Transplants (number per year) Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied ($thousands/organ transplant) Black market prices exceed legal prices 95 Lines of people with first-come-first-served rationing Price Supply 40 36 Equilibrium @ Price=$40,000 PRICE CEILING At $36 causes Shortage Demand Organ Transplants (number per year) Price Quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded ($thousands/organ transplant) 95 Supply Price Floor of $60,000 CausesSurplus Supply 60 40 Equilibrium @ Price=$40,000 Demand Demand Organ Transplants (number per year) Quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded Price ($thousands/organ transplant) Black market prices below legal prices 95 Supply Price Floor of $60,000 CausesSurplus Supply 60 40 Equilibrium @ Price=$40,000 Demand Demand Organ Transplants (number per year) Quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded Black market prices below legal prices ($thousands/organ transplant) Lines of product (inventories) can’t be sold and 95 Supply are dumped. Price Price Floor of $60,000 CausesSurplus Supply 60 40 Equilibrium @ Price=$40,000 Demand Demand Organ Transplants (number per year) Quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded ($thousands/organ transplant) Black market prices below legal prices Lines of product (inventories) can’t be sold and 95 are dumped. Supply Price Price Floor of $60,000 CausesSurplus Supply 60 40 Equilibrium @ Price=$40,000 Demand Demand Organ Transplants (number per year) GENERALIZED DEMAND FUNCTION f = f( Price: Taxes, Price of Complements Price of Substitutes Tastes for good/service Income, Buyer Expectations, Number of buyers) GENERALIZED SUPPLY FUNCTION f = f( Price: Price of Resources Technology, Seller Expectations, Number of Sellers) HOW TO BE SHERLOCK HOLMES IN READING BETWEEN THE LINES If You Know P and Q then you know whether demand or supply is involved as well as the direction of the shift. If You Know the shift in demand or supply, then you know what is likely to happen to price and quantity If You Know the determinant that has changed and price, then you know what is happening to quantity demanded. If You Know the determinant that has changed and quantity demanded, then you know what is happening to price. Figure 1. Shifts of Supply and Demand (A) (B) SUPPLY SHIFTS: LEFTWARD (up) P Supply Q (C) RIGHTWARD (down) DEMAND SHIFTS: LEFTWARD (down) P P Supply Q (D) RIGHTWARD (up) P Demand Q Demand Q Lower Price Lower Output Higher Price Leftward (downward) Shift of Demand Leftward (upward) Shift of Supply Higher Output Rightward (downward) Shift of Supply Rightward (upward) Shift of Demand Breakdown all shifts into their output and price vectors THE GRAND MACRO DESIGN!!! (the causes of aggregate demand shifts) Injections Leakages Balance Consumption Consumption 0 Exports - Imports Trade Balance Govt. Expenditures Taxes Federal Balance Investment Savings ___________________________________________________ E+G+I = Imp + T + S Which means: X-M (Trade Balance)= T- G (Federal Balance) + S-I Lower Price (deflation) Higher Price (inflation) Lower Output (slow Growth) RECESSION/DEPRESSION Leftward (downward) Shift of Aggregate Demand: STAGFLATION Leftward (upward) Shift of Aggregate Supply: less injections, or more leakages Less factors or higher factor prices Higher Output (fast Growth) HIGH GROWTH -LOW INFLATION Rightward (downward) Shift of Supply : More factors or lower factor prices HIGH GROWTH -HIGH INFLATION Rightward (upward) Shift of Demand: mor injections, or less leakages Breakdown all shifts into their output and price vectors Lower Price Lower Output Higher Price Less productivity (technological change) Higher price of resources Seller expectations of future surpluses Less number of sellers Leftward (downward) Shift of Demand less income less tastes for good less buyers less complement lower priuce for substitutes Buyer expectations about future shortages Higher Output Rightward (downward) Shift of Supply Leftward (upward) Shift of Supply More productivity (technological change) Lower price of resources Seller expectations of future shortages More number of sellers Rightward (upward) Shift of Demand Breakdown all shifts into their output and price vectors More income More tastes for good More buyers More complement Higher priuce for substitutes Buyer expectations about future shortages B A L A N C E O F P A Y M E N T S Currrent account = trade balance= net exports Real goods and services - imports Money Home Abroad Real goods and services - exports CAPITAL ACCOUNT Titles to foreign wealth sold to Americans Money Home Abroad Titles to American wealth sold to foreigners Unilateral transfers Home Money Abroad 19 47 Percentage 20 15 10 5 0 -5 -10 -15 GDP%chg Year UnemplRate 20 01 19 95 19 89 19 83 19 77 19 71 19 65 19 59 19 53 Indexes Prices, Wages, Interest rates Exchange rates 1 to 2 years GDP Government. Balance Unemployment Trade Balance Inventory Change 6 mos. Prices, Wages, Interest rates Exchange rates GDP 1 to 2 years Prices, Wages, Interest rates Exchange rates Government. Balance Unemployment Trade Balance Inventory Change 6 mos. Prices, Wages, Interest rates Exchange rates MODEL of the DETERMINANTS OF GDP interest rate Inflation rate $ Exchange Rate Taxes Saving Wage rate Population Growth Education Resource Chg Technology Change Curb Pollution Government. Interest rate Balance DEMAND Side Plcy Investment Government Expend. Consumption Exports Imports G SUPPLY Side Plcy Raise Tax Rates Impose Stds. Regulation Impose Price Controls Impose Output Controls Nationalization Regulation Restrict Immigration Unionization, Cut Welfare, Med Care,SSec. MONETARY POLICY Sell Bonds Raise Discount Rate Raise Reserve Requirement D P Inflation rate Unemployment $ Exchange Rate Trade Balance Saving Inventory Change Taxes Wage rate MODEL of the DETERMINANTS OF GDP interest rate Inflation rate $ Exchange Rate Taxes Saving Wage rate Population Growth Education Resource Chg Technology Change Curb Pollution Government. Interest rate Balance DEMAND Side Plcy Investment Government Expend. Consumption Exports Imports G SUPPLY Side Plcy Raise Tax Rates Impose Stds. Regulation Impose Price Controls Impose Output Controls Nationalization Regulation Restrict Immigration Unionization, Cut Welfare, Med Care,SSec. MONETARY POLICY Sell Bonds Raise Discount Rate Raise Reserve Requirement D P Inflation rate Unemployment $ Exchange Rate Trade Balance Saving Inventory Change Taxes Wage rate