• Agenda
advertisement

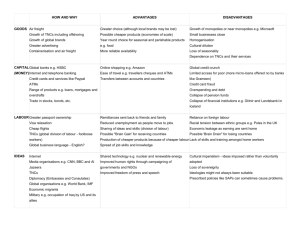
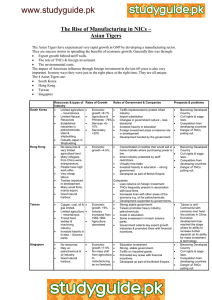
Agenda Last week: • • • • Review Keiretsu model of Transnational organization Transnational Production Networks • • • Headquarters R&D Production Subcontracting Garment Industry video This week: • • • • Exam Strategic Alliances Economic landscape TNCs & States Exam Chaps 7-9, 18 Chaps 10-14 + stockyards Student seminars Chaps 5-6 in support of the above SubContracting Commercial subcontracting • Entire product • To spec, under principal’s brand name • Retailer – buyer-driven production network • Producer – producer-driven production network Industrial subcontracting • Processes OR components • Plating, packaging OR accessory parts (buttons & zips) • OEM vs. Aftermarket auto parts Motives for Subcontracting Specialty subcontracting Cost-saving subcontracting Complementary/intermittant • Specialty products or processes • E.g. sweatshop labour • Employment/capacity buffer Relationships with subcontractors Principal may provide: Cooperation between subcontractor and principal in design Proximity may be important Domestic or international • Materials • Specs & technical advice • Finance or capital equipment Strategic Alliances Collaboration across borders Between competitors • New rivalry, competition & collaboration Joint Venture Networks of alliances • Constellations of economic power • Collective competition Strategic Alliances as Constellations in the Computer Industry Imagine the second tier of subcontractors! Note international links No archrivals Motives for Strategic Alliances Specific strategic objective • • Sharing risk Sharing consequences: rewards/costs Research • Cooperation/universities/venture capital Technology • Sharing/cooperation/licensing Market • Access, service infrastructure, promotion Economic Landscape Economic Landscape Intra-organizational networks Interorganizational networks Localized clusters Embedded in regions • HQ, R&D Labs, Production, Service agents • SME’s, Multilocational firms, TNCs • Firm-place relations (symbiosis) • Place-place relations TNCs and States: Issues Size of TNCs and states Cooperative and competing Supportive and conflictual Conflicting Objectives How are TNC/state objectives in conflict? • Performance • Technology • High order functions • Responsiveness • (to whom?) Regulatory Arbitrage What is regulatory? What is arbitrage? What is regulatory arbitrage Belfast Public Abattoir c. 1890s TNCs & Host Economies Fig. 9.2! Nature of the subsidiary: Function • Mode of entry • Local resource processing • Import substitution • Export platform TNCs & Host Economies Potential Areas of Conflict: • Capital • Transfer pricing • Technology • ‘Know-how’ but not ‘know-why’ • Appropriate technology • Trade and linkages • Concentration • Employment TNCs & Home Economies Employment impact of Outward Investment Bargaining Power: TNCs & States Upon entry To reduce exit • Michelin bill • Vote with their feet Locational Tournaments Macromarketing Competitive bidding for investment