Last Class! •

Last Class!
• Exam Structure
• Web sites (a cautionary tale)
• Australian Territories (see link on course web page for correction to text)
• Pacific Realm
– Maritime boundary issues
– Regions
• Antarctica
Final: Monday 25 April
C-674 2:00 – 4:00
A. Multiple choice: 20 @ 2 = 40
B. Map: 10 @1 = 10
JaKoTa, SE Asia, Australasia
C. Definitions:
¾ @ 10 = 30
“Define and illustrate with an example”
D. Essay: 1/3 @ 20 = 20
2 hours: Examination book and Scantron
Need pen, pencil, & dictionary if ESL
Final: Monday 25 April
C-674
South America to Pacific
Textbook, virtual field trips, lectures
Multiple choice are mainly regional
Definitions are mainly conceptual
Essays: Integrative, structured, compelling, creative and original
Pacific Realm
Major Geographic Qualities
• Largest total area of all realms
• Smallest land area
• Intensely fragmented & dispersed
•
High-Island vs Low-Island
dichotomy
• Politico-Geographical Transition
Pacific Realm
Survivor: Set in all Three Regions!
Regional Character
• 90% of land area in New Guinea
– West Papua (Irian Jaya before 2002 – Indonesian province)
– Papua New Guinea (PNG)
• Colonized/administered by France, Britain, US,
Australia, New Zealand
• Total Population: 8.5 Million, 60% in PNG
• Refuelling, Tourism, Minerals, Fishing
• Political Organization
– Independent States, Colonies, Dependencies, &
Administrative Units
• e.g. U.S Trust Territory or Cook Islands (NZ)
Marine Geography
• Sub-field of geography concerned with the spatial arrangement of the seas, marine resources and maritime boundaries
• Maritime boundaries
– Formerly cannon shot then 3 nautical mile limit
• UN Conference on Law of the Sea
– Territorial Sea (12 Mile Limit) - full sovereignty
– Exclusive Economic Zone (200 Miles) – control of resources:
• Oil and gas
• Fishery
• But guarantee of free passage
• High Seas – beyond 200 miles, no national claim
• Median Line boundaries
• Continental Shelf (down to 600 feet (100 fathoms) & out to 200
Miles)
– Or more depending on bathymetry and geology
Areas shown in blue are potential areas of an extended continental shelf beyond the 200 nautical mile limit (red) EEZ.
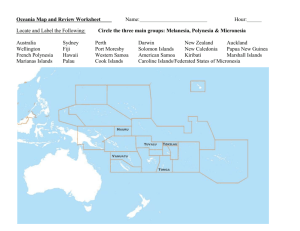
Regions of the Pacific
• Melanesia
– West Papua, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands,
Vanuatu, New Caledonia, Fiji
• Micronesia
– Largely U.S. Trust Territory 1945-1980s
– Palau, Federated States Of Micronesia, Northern
Mariana Islands, Republic Of The Marshall Islands,
Nauru, Western Kiribati, Guam
• Polynesia
– Kiribati, Cook Islands, Hawaii, Samoa, American
Samoa, Tuvalu, Tonga, French Polynesia, Marquesas
High-Islands
• Volcanic origins
• High elevations/rugged relief
• Well-watered
• Good soils, some agriculture
• Tend to have larger populations
• E.g. New Caledonia, Hawaii
Low-Islands
• Majority of realm’s islands
• Coral thus little fresh ground water
• Low elevation/relief
• Vulnerable to
– Drought
– Inundation by sea level rise/tsunami
• Fishing, coconut palm, no minerals
• Tourism and internet domains
Coral reef formation
PNG
• 5.2 million
• Since 1975
• Ethnically diverse:
– English and Tok Pisin, a creole
• Subsistence slash and burn agriculture, gathering, hunting pigs
• Since 1980s: oil, gold, copper
• Bougainville in Solomans attempted secession in 1990s
Antarctica
• Ice dome – 3.2 kms thick at pole
• 5.5 million square miles
– (compare North America 7.7 million)
• Roald Amundsen, 1911
• Ross Ice Shelf
• Multiple Claims
• The Antarctic Treaty, 1961
– Promotes scientific collaboration
– Prohibits military activity
– Territorial claims are held in abeyance