The Five Forces Model Developing A Strategy For The Internet Age
advertisement

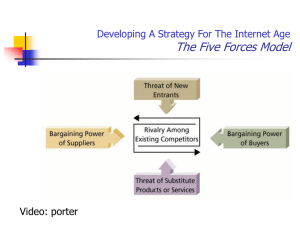
Developing A Strategy For The Internet Age The Five Forces Model Video: porter What is the major role of UTZ information systems? What are the characteristics of the information UTZ receives that would make it valuable? Analyze the industry that UTZ is in using the porter model, is it a good industry to be in? What competitive advantage do you feel Utz has? How does information play into that competitive advantage Databases and Warehouses Building Business Intelligence To make good and accurate decisions and work in the most productive and efficient way, knowledge workers today need (1) access to information and (2) tools to work with that information. Business Intelligence What is it? Business intelligence is knowledge – knowledge about your customers, your competitors, your partners, your competitive environment, and your own internal operations Where is BI found? Databases & Data warehouses Key Terms Online transaction processing (OLTP) – Operational database – the gathering of input information, processing that information, and updating existing information to reflect the gathered and processed information. database that supports OLTP. Online analytical processing (OLAP) the manipulation of information to support decision making. Business Intelligence Hierarchy of Data THE RELATIONAL DATABASE MODEL Database Relational database model A collection of information that you organize and access according to the logical structure of that information. uses a series of logically related two-dimensional tables (called relations) or files to store information in the form of a database. Relation describes each two-dimensional table or file in the relational model. The word relation here is in reference to the collection of the data within one specific table. By carefully examining the definition given to “relational databases” we can clearly identify two parts to it: 1. 2. Information – stored in a series of two dimensional tables, files, or relations. Logical structure of the information. Data dictionary – contains the logical structure for the information. Database management system (DBMS) helps you specify the logical organization for a database and access and use (manipulating) the information within a database. DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM TOOLS DBMS Engine Data Definition Subsystem Data Manipulation Subsystem Application Generation Subsystem Data Administration Subsystem The DBMS Figure 3.4 Software Subsystems of a Database Management System page 85 Traditional Approach to Data Management Database Approach to Data Management Advantages of Database Approach Improved strategic use of corporate data Reduced data redundancy Improved data integrity Easier modification and updating Data and program independence Better access to data and information Standardization of data access Framework for program development Better overall protection of the data Shared data and information resources Disadvantages of Database Approach Relatively high cost of purchasing and operating a DBMS in a mainframe operating environment Increased cost of specialized staff Increased vulnerability DATA WAREHOUSES AND DATA MINING What Is a Data Warehouse? What Are Data Mining Tools? Data Marts: Smaller Data Warehouses Important Considerations in Using a Data Warehouse Data Warehouses and Data Mining Data Warehouses Are Multidimensional Figure 3.8 A Multidimensional Data Warehouse with Information from Multiple Operational Databases Elements of a Data Warehouse Data Warehouses and Data Mining Data Marts – Smaller Data Warehouses Data mart - a subset of a data warehouse in which only a focused portion of the data warehouse information is kept. Data Marts Are Subsets of Data Warehouse Data Mining: an information analysis tool that involves the automated discovery of patterns and relationships in a data warehouse Applications Market segmentation Customer churn Fraud detection Direct marketing Market basket analysis Trend analysis How Up-to-Date Should Data Warehouse Information Be? To adjust class sizes in a university registration system To alert people to changes in weather conditions To predict scores in professional football games To adjust radio advertisements in light of demographic changes To monitor the success of a new product line in the clothing retail industry To adjust production levels of foods in a cafeteria To switch jobs to various printers in a network – by the minute. To adjust CD rates in a bank To adjust forecasted demands of tires in an auto parts store MANAGING THE INFORMATION RESOURCE IN AN ORGANIZATION Who Should Oversee the Organization’s Information? How Will Changes in Technology Affect Organizing and Managing Information? Is Information Ownership a Consideration? What Are the Ethics Involved in Managing and Organizing Information? OLTP and Data Warehousing OLTP and Data Mining Powered by SAVE THIS | EMAIL THIS | Close Senate Democrats try to stop Pentagon data-mining project Some conservatives also concerned about privacy issue