Motivation II

Motivation II
Need Theories
Use the concepts of individual needs to explain why people have different needs at different times.
What motivates people
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Growth
Needs
Deficiency
Needs
Self-Actualization
The need to develop one’s true potential and skills (creative, autonomous tasks)
Self-Esteem
The need for feelings of adequacy, competence, and confidence (awards, prestigious titles, promotions)
Belongingness
The need for social interaction, affection, friendship
(opportunities to interact, supportive supervision)
Safety
The need for security, freedom from anxiety, order (job security, comfortable work environment, adequate pay)
Physiological
The needs for survival, such as, food, water, shelter
(minimum pay and existence level support)
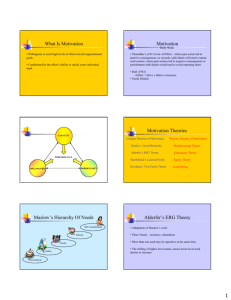
Aldefer’s ERG Theory
• Existence Needs – needs satisfied by material substances
• Relatedness Needs – the need for meaningful social relationships
• Growth Needs – need for developing one’s potential
Relationship between Maslow and Alderfer Need Theories
Higher order needs Intrinsic motivation
Basic needs
Self-Actualization
Self-Esteem
Belongingness
Safety
Physiological
Growth
Relatedness
Existence
Extrinsic motivation
McClelland’s Need Theories
•Need for Achievement (N Ach) – desire to perform challenging tasks
• Need for Affiliation (N Aff) – desire to establish and maintain friendly interpersonal relationships
• Need for Power (N Pow) – desire to have significant impact over others
Motivation II
Process Theories
Describes how need deficiencies are translated into behaviours
Equity Theory
•Comparison of inputs and outcomes
My Outcomes
My Inputs
=
Comparison Outcomes
Comparison Inputs
Responses to Inequity
• Distort one’s own inputs/outcomes
• Distort the comparison person’s inputs/outcomes
• Choose another comparison person
• Alter inputs or outcomes
• Leave the exchange relationship
Issues of Equity Theory
• The comparison other???
• Over-reward versus under-reward
• It is all perception
Effort
Expectancy Theory
Valence (value) of
Outcome 1 (V1)
Valence (value) of
Outcome 2 (V2)
(E > P)
Performance
(P > O)
Reward Outcome
Expectancy (E)
(probability of Effort leading to Performance)
Instrumentality (I)
(probability of Performance leading to Reward Outcome)
Force = E x Σ(I x V)
= expectancy x Σ instrumentalities x 2nd-level valences
= expectancy x valence of 1st-level outcome
Do theories translate across cultures?
• Reinforcement theory?
• Goal setting theory?
• Need theories?
– Maslow’s need hierarchy
– Alderfer’s ERG
– McClelland’s theory of needs
• Equity theory?
• Expectancy theory?
Moberg and motivation:
Identify the theory or concept from our discussions. To create high motivation…..
• Employees must have confidence in their capabilities to perform the job
• There should be no organizational impediments to high performance
• People must believe that high performance will lead to rewards that are desirable to them
• You must be clear and specific about the performance you desire; decide with the employee
• Be fair - reward how and when you say; make sure that the reward system is clear to all
• Offer rewards that are favoured by the employee