Welcome to PSC 1210 Earth and Space Science for K-8 Teachers
advertisement

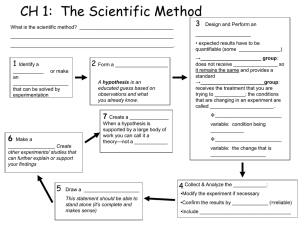
Welcome to PSC 1210 Earth and Space Science for K-8 Teachers Goals of PSC 1210 Understand important concepts in Earth and Space Science Develop science process skills Appreciate and apply the scientific method Learn using techniques you will apply as a teacher Some Science Terminology scientific fact – specific, verifiable information *Sulfur is a yellow mineral. *Granite is an igneous rock. hypothesis – possible action and/or explanation for a behavior or an observation; must be tested through experimentation *Magnetism is based on electron associations Some Science Terminology law - generalized statement of a relationship between variables in a system based on repeated experimentation; can be used to predict behavior of a system *As the temperature of a gas increases, its volume increases. theory - generalized explanation for observations based on repeated experimentation or observations *Gas behavior such as expansion with heat or increased pressure with decreasing volume is a result of particles that are far apart and moving rapidly. Some Science Terminology scientific belief something that is accepted as true based on scientific evidence but cannot be proven at that time *All protons are identical. *The sun will rise tomorrow. Scientific Method Make an observation that raises a question State a question Determine a possible reason for the observation Pose a hypothesis Design and carry out an investigation to prove or disprove the hypothesis Do an experiment Scientific Method Compile information from the experiment and decide if the hypothesis was correct Analyze/Make a conclusion If the conclusion or experimental process raises other questions, start the process again. Scientific Method • Understand variables: – Independent variable = one changed by the experimenter – Dependent variable = one that changes as a result of a change in the independent variable – Controlled variable = any property that is not being investigated and must remain the same during the experiment Scientific Method Make an observation that raises a question. Do birds prefer red or blue bird feeders? Determine a possible reason for the observation. Pose a hypothesis. Birds prefer red feeders. Design and carry out an investigation to prove or disprove the hypothesis Determine the variables: Independent = color of the feeder Dependent = # of birds at the feeder Scientific Method Determine the variables: Controlled = type of feeder, type of food, time of day recorded, height of feeder, location of feeder… Set up 3 blue and three red identical bird feeders. At a set time each day for 10 days, record how many birds are at each feeder. Record data in a suitable table. Scientific Method Compile information from the experiment. Analyze the data. Make a bar graph of the number of birds at each color feeder for each day. Decide if the hypothesis was correct. Make a conclusion The birds prefer a red feeder over a blue feeder. Science Process Skills - Basic Observing Measuring Classifying Communicating Inferring Predicting Science Process SkillsIntegrated Controlling Variables Defining Operationally Formulating Hypotheses Interpreting Data Experimenting Formulating Models What is a Misconception? Incorrect understanding of term or process Not merely a misfact Can be taught to you or you can come to it based on your personal experience Highly resistant to change Some Misconceptions in Earth/Space Science The seasons are caused by the Earth’s distance from the Sun. Continents do not move. Most rivers flow “down” from north to south. Some Misconceptions in Earth/Space Science The soil we see today has always existed. Dinosaurs and humans existed at the same time. The phases of the Moon are caused by a shadow from the Earth. Lesson Design – The 5 E’s Engagement Exploration Explanation Extension Evaluation Learning and Assessment Tools for PSC 1210 Guided Inquiry Activities Quizzes and Performance Tasks Journal Internet Explorations Projects