The main benefit of free trade between two countries is... (A)income distribution in each country will become more equitable
advertisement

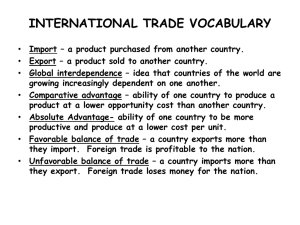
The main benefit of free trade between two countries is that (A)income distribution in each country will become more equitable (B)employment in each country will increase (C)migration from one country to the other will increase (D)each country can consume beyond its constraints of resources and productivity (E)each country will become more self-sufficient The following question is based on the diagram below, which shows the production alternatives of two countries, Alpha and Beta, producing two goods, grain and steel, using all of their available resources. The theory of comparative advantage implies that Alpha would find it advantageous to (A)export grain and import steel (B)export steel and import grain (C)export both grain and steel and import nothing (D)import both grain and steel and export nothing (E)trade 1 ton of grain for 0.5 ton of steel This table shows the production alternatives of Country A and Country B for producing computers and cars with equal amounts of resources that are fully and efficiently employed. Which of the following is true according to the data in the table? (A)Country A has an absolute and comparative advantage in the production of computers. (B)Country B has an absolute and comparative advantage in the production of computers. (C)Country B should import computers and export cars. (D)Since Country B has an absolute advantage in the production of both goods, it will not trade with Country A. (E)Neither country can benefit from trade. Mary Jane is a lawyer who can earn $150 per hour in her law practice. She is also an excellent carpenter who can build cabinets three times as fast as the best carpenter, whose hourly wage is $20 per hour. Which of the following is a correct economic statement? (A)Mary Jane has a comparative advantage in law so she should specialize in law and hire a carpenter to make her cabinets. (B)Mary Jane has an absolute and comparative advantage in both law and carpentry, so she should make her own cabinets while continuing to practice law. (C)Mary Jane is three times faster than any carpenter so she should give up her law practice to become a carpenter. (D)When carpenters work for lawyers, they should charge $150 per hour instead of $20 per hour. (E)Because Mary Jane is an excellent carpenter, when the best carpenter works for Mary Jane, he can only charge one third as much, or $6.67 per hour. Comparative advantage implies that (A)no country should specialize completely in the production of any one good (B)every country should try to export more than it imports (C)developing countries should import raw materials and export manufactured goods (D)two countries should benefit from trade unless both have equal opportunity costs in every good (E)countries should impose tariffs to protect their domestic industries The chart below shows the number of resource units the countries Gamma and Omega must use to produce one unit of food or one unit of clothing. Which of the following statements is true according to the chart above? (A)Trade should take place, with Gamma specializing in clothing production and Omega specializing in food production. (B)Trade should take place, with Gamma specializing in food production and Omega specializing in clothing production. (C)Each country should devote half of its resources to food production and half to clothing production and not trade. (D)Since Omega can produce both food and clothing using fewer resources than Gamma, it cannot benefit from trade with Gamma. (E)Since Gamma can produce both food and clothing using fewer resources than Omega, it cannot benefit from trade with Omega. A country can consume beyond its present production possibilities curve when it (A)trades with other countries, thus taking advantage of different opportunity costs (B)reduces unemployment, thus increasing output (C)experiences decreasing opportunity costs (D)faces an upward-sloping production possibilities curve (E)faces a downward-sloping production possibilities curve The following diagram shows the production possibilities curves for two countries, Country X and Country Y. Assume that both countries use equal amounts of resources in production. If the two countries engage in trade, both would be better off under which of the following conditions? (A)Country X produced both cars and planes, because it has an absolute advantage in the production of both goods. (B)Country Y produced both cars and planes, because it has a comparative advantage in the production of both goods. (C)Country X specialized in the production of cars, because it has an absolute advantage in the production of cars. (D)Country X specialized in the production of cars, because it has a comparative advantage in the production of cars. (E)Country Y specialized in the production of cars, because it has a comparative advantage in the production of cars. A farmer in Country A can harvest 20 bushels of wheat or 10 bushels of com in a day, while a fanner in Country B can harvest 8 bushels of wheat or 8 bushels of com in a day. If Country A and Country B specialize and trade, Country A will (A)export wheat and import com (B)export com and import wheat (C)export both wheat and com (D)import both wheat and com (E)benefit more from trade than will Country B Assume both Italy and Greece produce only two goods: wine and olive oil. If Italy holds a comparative advantage in the production of wine, then which of the following statements is NOT true? (A)Italy must hold an absolute advantage in the production of wine. (B)Greece holds a comparative advantage in the production of olive oil. (C)Italy’s opportunity cost of producing one additional unit of wine is lower than Greece’s. (D)Greece’s opportunity cost of producing one additional unit of olive oil is lower than Italy’s. (E)If trade is open between them, these countries have an incentive to trade. The following table shows the amount of labor required to produce a unit of com and a unit of shoes in Brazil and Spain. If both countries have equal numbers of workers, what pattern of international trade between Brazil and Spain is most likely to emerge? (A)Brazil will export both com and shoes. (B)Spain will export both com and shoes. (C)No mutually beneficial trade can occur. (D)Brazil will export corn and import shoes. (E)Brazil will import com and export shoes. If nations specialize according to their comparative advantage and engage in international trade with each other, each nation can (A)produce outside its production possibilities curve (B)consume outside its production possibilities curve (C)shift its production possibilities curve to the right (D)become more self-sufficient (E)produce more of all goods As nations specialize in production and trade in international markets, they can expect which of the following domestic improvements? I.Allocation of domestic resources II.Standard of living III.Self-sufficiency (A)I only (B)II only (C)III only (D)I and II only (E)I,II, and III The following question is based on the diagram below, which shows the production alternatives of two countries, Alpha and Beta, producing two goods, grain and steel, using all of their available resources. At what real exchange ratio, also referred to as the terms of trade, between grain (G) and steel (S) would both Alpha and Beta find it mutually advantageous to specialize and trade? (A)1 G = 3.0 S (B)1 G = 1.5 S (C)1 G = 1 S (D)1 G = 0.5 S (E)There is no real exchange ratio that would enable both countries to benefit, since Alpha has an absolute advantage in both goods. Using equal amounts of labor hours, Country X and Country Y can each produce the number of watches and radios shown in the production possibilities curves above. Based on the information, which of the following is true? (A)Country X has an absolute advantage in the production of both watches and radios and a comparative advantage in the production of watches. (B)Country Y has an absolute advantage in the production of both watches and radios and a comparative advantage in the production of radios. (C)Countries X and Y can engage in a mutually advantageous trade by exchanging 1 watch for 1 radio. (D)Country Y is willing to give up 2 watches in exchange for 1 radio horn Country X. (E)Country X is willing to give up 2 radios in exchange for 1 watch from Country Y. If two nations specialize according to the law of comparative advantage and then trade with each other, which of the following would be true? (A)A smaller number of goods would be available in each trading nation. (B)Total world production of goods would decrease. (C)Everyone within each nation would be better off. (D)Each nation would increase its consumption possibilities. (E)One nation would gain at the expense of the other nation. The following table indicates the production alternatives of two countries, A and B, which produce computers and steel using equal amounts of resources. If both countries always produce at full employment, which of the following statements must be correct? (A)Mutually advantageous trade can occur between the two countries when 1 unit of steel from Country A is exchanged for 2 computers from Country B. (B)Mutually advantageous trade can occur between the two countries when 2 units of steel from Country B are exchanged for 1 computer from Country A. (C)Country A has an absolute and comparative advantage in the production of computers, and Country B has an absolute and comparative advantage in the production of steel. (D)Country B has an absolute advantage in the production of both commodities, but a comparative advantage in the production of steel. (E)Country A has an absolute advantage in the production of both commodities, but a comparative advantage in the production of steel. Assume that Country A exports one bushel of wheat in exchange for 2.5 bushels of corn from Country B. If the terms of trade are beneficial to both countries, which of the following must be true? (A)Country A has an absolute advantage in the production of wheat. (B)The cost of producing a bushel of wheat in Country A is less than 2.5 bushels of corn. (C)The cost of producing a bushel of wheat in Country A is greater than 2.5 bushels of corn. (D)Country A is producing inside its current production possibilities curve. (E)Country A needs to use more resources to produce wheat than to produce corn.