Genetics Study of Inheritance
advertisement

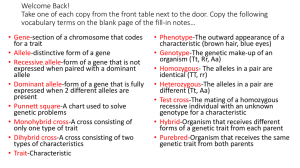
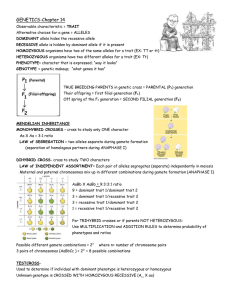
Genetics Study of Inheritance Reproduction • Asexual – Cell divides, creating an identical daughter cell • Sexual – Exchange of genetic material, both parents contribute to fertilization of egg/ovary – Increases diversity – In Animals Egg & Sperm – In Plants Pollen & Ovary Heredity • We share many similarities with our parents & siblings, but we are not genetically identical due to the mixing of genes Chromosomes • A chromosome is a rod-shaped bundle of DNA • In sexual reproduction, each “parent” contributes ½ of the offspring’s genetic info – ½ from “mom’s egg” & ½ from “dad’s sperm” • The physical characteristics that show are due to “genetics” Genes vs Alleles • A gene is a section of a chromosome that codes for a specific trait – EX: Eye Color • An allele is a variation of that instruction – EX: Brown vs blue eyes • Every gene has 2 alleles, which we represent with a single letter (capital or lowercase) – BB or Bb or bb Genotype vs Phenotype • Genotype the Genetic code – BB • Phenotype the Physical trait – Brown eyes Dominant vs Recessive Alleles • A dominant allele (represented by a capital letter), if present, shows that specific trait – BB or Bb = Brown Eyes • A recessive allele (represented by a lowercase letter), must have both alleles to show a trait – bb = Blue eyes • If both letters are the same, BB or bb, we say it is HOMOZYGOUS (dominant or recessive) • If both letters are different, Bb, we say it is HETEROZYGOUS Look at this… • HH = Does not have trait • Hh = Does not show trait, but is a carrier • hh = shows trait Trait could be anything inheritable, such as baldness or albinism Let’s watch this video… • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CBe zq1fFUEA Punnett Squares • We can predict the outcome of offspring by using a PUNNETT SQUARE Let’s Practice…