Mrs. Yanac Biology 1B
advertisement

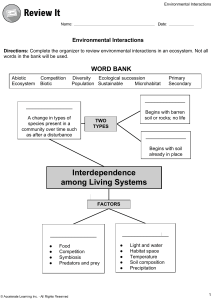
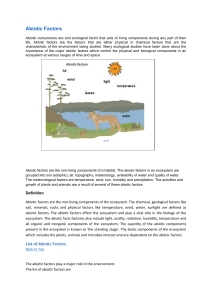
Mrs. Yanac Biology 1B Weather – DAY TO DAY condition of the atmosphere Climate – average YEAR TO YEAR situation of temperature and precipitation of an area Natural trapping of heat around the earth due to gases in the atmosphere Due to the tilt of the planet, sunlight hits the planet at different angles, resulting in different climates. Biotic – all of the living parts of the ecosystem Plants Animals Fungi Microorganisms Abiotic – all of the nonliving parts of the ecosystem Land Water Soil Light The area where an organism lives Includes both biotic & abiotic factors All the ABOITIC & BIOTIC factors in a habitat AND the way an organism uses those things The ROLE a species plays in an ECOSYSTEM No 2 species can occupy the same niche, at the same place, at the same time (competition exclusion principle) Symbiosis – a relationship where 2 organisms live closely together 1. Mutualism – Both benefit 2. Commensalism – One benefits, one is unaffected 3. Parasitism – One benefits, one is harmed Predictable changes to an ecosystem over time PRIMARY SUCCESSION – Occurs where no soil exists (on bare rock) SECONDARY SUCCESSION – Occurs in an area previously disturbed by natural disaster or human disturbance Group of ecosystems that have Certain climate (temperature & rainfall) Soil conditions Plants (flora) Animals (fauna) Examples: Tundra, Rainforest, Desert, Grasslands Freshwater Standing water Lakes & ponds Flowing water Rivers & streams Marine (salt water) Oceans Littoral zone - inshore, shallow, high light levels Limnetic zone offshore, high light levels, upper regions of water column Profundal zone aphotic Benthic zone – bottom substrate; often rich in detritus Where saltwater & freshwater mix EX: Where a river runs into the ocean Unique ecosystem Brackish water Highly diverse (both flora & fauna) Found in photic zone