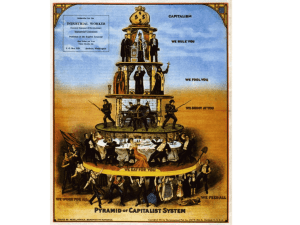
The Gilded Age The Rise of Big Labor

The Gilded Age
The Rise of Big Labor
Sources of Labor
Former Self-employed
Siblings in farming families
Immigrants (largest category)
Between 1870 and 1920 24 million immigrants arrived from:
Southern and Eastern Europe – 60%
Northern Europe – 25%
Other (Asia, Mexico, etc.) – 15%
By 1910 53% of all wage earners were of foreign birth
Effect of Mechanization on Labor
Changed employer-employee relations
Gradually reduced customary autonomy
Decision making became centralized in management
Workers generally lost control of production process
Pace of production set by managers
Increasingly impersonal
Created new categories of workers
Skilled artisans generally replaced by unskilled “machine tenders”
Supervisors, managers
Women in the Workforce
The “Boom” & “Bust” Business Cycle
Terence
Powderly,
Leader of the
Knights of
Labor
Knights of Labor
Rejected “wage slavery”
Open to all laborers, skilled and unskilled
Maintained an adversarial relationship with business
Advocated broad social and economic reforms
Producer’s cooperatives
End to Child labor
Graduated income tax
Monetary reform
The Haymarket Square Riot
Samuel
Gompers of the
AFL
The American Federation of Labor
Restricted to skilled laborers
Accepted wage system
Wanted to work with business owners
Promised amenable labor relations
The Great Railroad Strike of 1877
First nationwide strike
Began in Martinsburg, WV
Strike spread quickly along the rail routes
Strikers halted all train traffic
Unemployed and workers in other industries joined the protest
Mobs defied militia sent to disperse them
Rioting persisted for about a week
Fearing a national insurrection President
Hayes called out the army to suppress the strike
Federal troops fired into a crowd in
Pittsburg, killing 20
By the end of the strike over 100 were dead
The Great Railroad Strike of 1877
Homestead Steel Strike
Carnegie determined to gain control over every facet of production
Want to break the Amalgamated Iron, Steel and Tin Workers Union
Workers went on strike in June
Governor refused to use National Guard to disperse them
Steel Company used a private army
After day-long gun battle, governor sent in troops to restore order
Factory reopened with strikebreakers
After four months the union was forced to admit defeat
Carnegie reduced workforce by 25%
Lengthened work day
Cut wages 25%
Affected all steel workers
Within a decade, every major steel company operated without union interference
Troops Guard the Trains during the
Pullman Strike
Eugene V. Debs
Head of the
American
Railway Union and founder of the American
Socialist Party