Document 15957265
advertisement

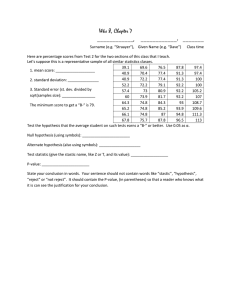
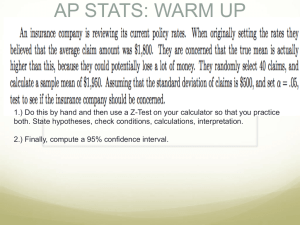
In Chapter 10 we tested a parameter from a population represented by a sample against a known population ( p p0 ). In chapter 11 we will test a parameter from two samples to find if they come from the same or different populations (i.e. p1 p2 ). We will be given two sets of sample data from the experiment. If the data from the two samples do not come from the same individuals, the two sets are independent. If the data from one sample comes from the same individuals as the second sample and the data are paired, the two sets are said to be dependent. Dependent samples are said to be matched pairs. Determine whether the following samples are independent or dependent: A. A researcher wishes to compare salaries of men vs. women and takes the data from married couples. B. A comparison of history grades from a four year university vs. a two year community college is made using a sample of 100 students from each type of institution. C. The effectiveness of a weight loss program is determined by taking the before and after weights from 50 people using the program. D. A comparison is made of weights of men ages 21 to 30 and weights of men 31 to 40, by collecting data from 50 men in each group. E. The performance of two fuels is compared by using the two fuels in each of 20 vehicles and measuring certain parameters. The procedure is the same as it was for one sample hypothesis testing. The test statistic and the p-value are found using STAT TESTS 2-PropZTest. Example: Given: x1 368, n1 541, x2 351, n2 593 Test the hypothesis p1 p2 to a significance of 0.10 BMI index is used to determine if men and women were normal weight. 750 men and 750 women ages 20 to 25 were surveyed. 203 men and 270 women were considered normal according to the index. Test the claim that there is a difference between men and women that are considered normal to a significance of 0.10. The procedure is the same as one sample hypothesis testing. The test statistic and the p-value are found using STAT TESTS 2-SampTTest. Given: n1 25, x1 50.2, s1 6.4 n2 18, x 2 42.0, s2 9.9 Test the claim that 1 2 to a significance of 0.05. Do students who first attend a community college and then transfer to a 4 year college take longer to graduate than students who only attend a 4 year college. To find out the following data was collected: Students who started at a 2 year college: n1 268, x1 5.43, s1 1.162 Students who started at a 4 year college: Test the claim that transfer students take longer to a significance of 0.01. n2 1145, x2 4.43, s2 1.015 Another method of testing hypothesis is using Confidence Interval. A B to see if H0 A B should Testing be rejected or fail to reject. If 0 is in the Confidence Interval (the lower level is negative and the upper level is positive), then Fail to Reject the Null. If the 0 is outside the Confidence Interval (both sides of the Interval is positive or both sides are negative), the Reject the Null. Data is matched pairs. The data is normally given as a table. The strategy is to test the difference between the two values of individuals using a one sample test (TTEST). As an example: After 125 134 156 105 143 148 Before 130 126 151 108 150 148 -5 8 5 -3 -7 0 Difference after before implies after before 0 or diff 0 Procedure: 1. Put “after” values in L1, and “before” values in L2. Go to the header of L3 and enter “l1-l2” and click enter. 2. STATS TESTS TTest Data. Enter 0 0, List = L3, Freq = 1, and . H1 3. The average difference is , s is d x d x 4. As usual the test statistic and p-values are the t and p, respectively. s Are sons normally taller than their fathers? To test this the following data was collected: Father 70.3 67.1 70.9 66.8 72.8 70.4 71.8 Son 74.1 69.2 66.9 69.2 68.9 70.2 70.4 Father 70.1 69.9 70.8 70.2 70.4 72.4 Son 69.3 75.8 72.3 69.2 68.6 73.9 Test the claim that sons’ height is > fathers’ or that the bottom row is bigger so that father son or father son 0 or d 0 The Critical Value for 2 Sample Hypothesis Tests of Standard Deviation is the F distribution. It looks like the Chi Squared distribution. The Notation for the Critical Value is Fsi gnificance,column,row For a Right Tailed Test: FRight F ,n11,n21 For a left Tailed Test: FLeft F Left For 1 F ,n 21,n11 a Two Tailed Test: Use the formulas above but the significance will be / 2 The Test Statistic is found by s12 F0 2 s2 The Test Statistic and p-value is found with STAT TESTS 2-SampFTest Given the following, test the claim that the standard deviation of the population represented by sample 1 is greater than that of sample 2 (i.e. 1 2 ) to a significance of 0.01. Given the sample data: n 26, s 9.9 n 21, s 6.4 1 1 2 2 Do students who plan for financial aide have more variability in SAT scores than students who do plan financial aid. To find out the following data was collected. n 26, s 119.4 n 31, s 123.1 Test 1 1 2 2 the claim that those planning financial aid (sample 1) had less variability than those that did not 1 2 to a significance of 0.05.