GRID: A F L -A R
advertisement

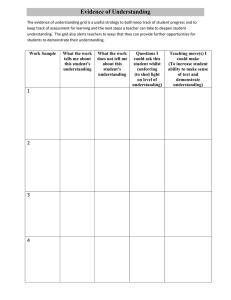
GRID: A FULLY LOCATION-AWARE ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS 指導教授:許子衡 教授 學生:翁偉傑 1 Telecommunication Systems 18:1–3, 37–60, 2001 , 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. OUTLINE Introduction Background and motivation The GRID routing protocol Eliminating the broadcast storm effect Experimental results Conclusions 2 INTRODUCTION we propose a new routing protocol called GRID, which tries to exploit location information in route discovery, packet relay, and route maintenance. the intermediate hosts of a route can perform a “handoff”. Simulation results show that our GRID routing protocol can reduce the probability of route breakage, reduce the number of route discovery packets used, and lengthen routes’ lifetime. 3 BACKGROUND AND MOTIVATION (1/3) Review of routing protocols for MANETs -MANET 是由移動主機互相溝通,沒有基站支持的網絡。 - 許多路由協議已經被提出,MANET 路由協議需要解決以下三個問題: * Route discovery:路由discovery/search必要的。 * Packet relay:轉送封包,每一個節點必須保持一個路由表。 * Route maintenance:由於流動性的原因,以建立的途徑可能會被打斷。 4 BACKGROUND AND MOTIVATION (2/3) Location-aware routing protocols LAR,使用位置信息來限制 searched zone,以減少成本。 5 BACKGROUND AND MOTIVATION (3/3) Observations and motivations Traditionally, routing information is recorded by identifying the address (e.g., IP address) of the next host to forward data packets. when forwarding a data packet, a node may indicate that “Is there anyone around location L capable of forwarding the packet for me?” 6 THE GRID ROUTING PROTOCOL (1/7) Protocol overview -Our protocol is called GRID. - The geographic area of the MANET is partitioned into 2D logical grids -Each grid is a square area of size d × d. Grids are numbered (x, y) - The responsibility of gateway hosts includes: (i) forwarding route discovery requests to neighboring grids, (ii) propagating data packets to neighboring grids, and (iii) maintaining routes which pass the grid. 7 THE GRID ROUTING PROTOCOL (2/7) 8 THE GRID ROUTING PROTOCOL (3/7) - GRID 協議為: * 使用LAR原理來限制搜尋範圍。 * 只使用 gateway host 。 * 路由表 grid-by-grid manner ,不是host-by-host manner。 * 使用 AODV 協議。 Route search and route reply * RREQ (S, s_seq,D, d_seq, id, range)。 9 THE GRID ROUTING PROTOCOL (4/7) Route search and route reply * 減少RREQ。 * RREP(S,D, d_seq) 10 THE GRID ROUTING PROTOCOL (5/7) Route maintenance maintain a route once it has been established: (i) how to maintain the gateway in each grid. (ii) how to maintain a route when its source or destination node roams around. - 為了維持 gateway 在網格裡,選擇適當 gateway 是必要的。 * 離中心點最近的。 * 避免 ping-pong effect ,直到 gateway 離開網格。 11 THE GRID ROUTING PROTOCOL (6/7) Route maintenance -Gateway 定期廣播 GATE ( g,loc ) 封包。 - 如果沒有在預定的時間內收到 GATE 封包,它會廣播一個 BID ( g,loc )。 如果 gateway 還存在,當它收到 BID 封包,它會回復一個 GATE 封包拒 決。 - 當 gateway 離開網格時,它會廣出 RETIRE ( g,T )。 - 移動到下一個新網格,不知道現有的節點,它會廣 BID ( g,loc ) 競爭。 - 為了消除可能有多個 gateway 在同一個網格,會找更接近中心的。 12 THE GRID ROUTING PROTOCOL (7/7) 13 ELIMINATING THE BROADCAST STORM EFFECT (1/2) The broadcast storm problem: - 競爭、碰撞。 * 許多廣播是多餘的。 we suggest several ways to confine the searched area: 14 ELIMINATING THE BROADCAST STORM EFFECT (2/2) let the total number of hosts in the MANET be N. Using a blind flooding, the number of hosts that will try to broadcast the RREQ will be N. let A be the number of grids to be searched. where p is the success probability of the first search and δ is the average number of hosts in a grid. 15 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS (1/6) 模擬器的性能評價和比較了AODV協議,LAR, GRID 協議。 MANET 大小1000米× 1000米。 100〜300移動節點進行了數值模擬。 隨機移動節點以每隔0.5秒進行廣播,而分為30和60 公里/小時,進行了審議。 所有移動節點有相同的傳輸距離為 300米。 16 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS (2/6) Gateway 每10秒廣播封包。網格d的大小: GRID-1, GRID-2, GRID-3 每次模擬進行500秒,運行50模擬。 17 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS (3/6) the average lifetime of a route of each compared protocol roaming speed = 30 km/h roaming speed = 60 km/h d選擇是重要的,減少線路 breakage 的可能性。 18 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS (4/6) 19 GRID- 1和GRID- 2 最佳。 LAR和AODV路由協議有相當高的成本 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS (5/6) 20 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS (6/6) 21 CONCLUSIONS we have presented a new location-aware routing protocol for MANETs. First, it offers a much less routing cost than those of the existing protocols. Second,it offers much longer route lifetime than that of existing protocols. our protocol is more resilient and less vulnerable to route breakage even under high host mobility. 22