Universities can apply for Federal grants for teacher professional
advertisement

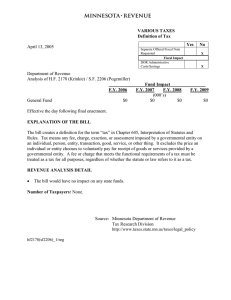
Universities can apply for Federal grants for teacher professional development programs to enhance Dual Enrollment, in the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). I quote pages 115, 129, 130, 147, 148, and 151 in the ESSA version that was was signed by President Obama on December 10, 2015. The final version of ESSA, SB1177, can be downloaded at https://www.congress.gov/114/bills/s1177/BILLS-114s1177enr.pdf . Page 5 states that appropriations for competitive programs begin on October 1, 2016. Universities and national non-profits like AMTA can apply for competitive 3-year renewable Federal Department of Education grants to provide teachers with professional development targeted at Dual Enrollment enhancement. TITLE II - PREPARING, TRAINING, AND RECRUITING HIGHQUALITY TEACHERS, PRINCIPALS, AND OTHER SCHOOL LEADERS ... SEC. 2003. AUTHORIZATION OF APPROPRIATIONS. (a) GRANTS TO STATES AND LOCAL EDUCATIONAL AGENCIES.— For the purpose of carrying out part A, there are authorized to be appropriated $2,295,830,000 for each of fiscal years 2017 through 2020. (b) NATIONAL ACTIVITIES.—For the purpose of carrying out part B, there are authorized to be appropriated— (1) $468,880,575 for each of fiscal years 2017 and 2018; (2) $469,168,000 for fiscal year 2019; and (3) $489,168,000 for fiscal year 2020. ... PART B—NATIONAL ACTIVITIES SEC. 2201. RESERVATIONS. From the amounts appropriated under section 2003(b) for a fiscal year, the Secretary shall reserve— ... (4) to carry out activities authorized under subpart 4— (A) 15.4 percent for each of fiscal years 2017 through 2019; and (B) 14.8 percent for fiscal year 2020. Subpart 4—Programs of National Significance (~$72,000,000 each year. JJ) SEC. 2241. FUNDING ALLOTMENT. From the funds reserved under section 2201(4), the Secretary— (1) shall use not less than 74 percent to carry out activities under section 2242 ... SEC. 2242. SUPPORTING EFFECTIVE EDUCATOR DEVELOPMENT. 1 (a) IN GENERAL .—From the funds reserved by the Secretary under section 2241(1) for a fiscal year, the Secretary shall award grants, on a competitive basis, to eligible entities for the purposes of ... (3) providing teachers, principals, or other school leaders with professional development activities that enhance or enable the provision of postsecondary coursework through dual or concurrent enrollment programs and early college high school settings across a local educational agency; ... (5) providing teachers, principals, or other school leaders with evidence-based professional enhancement activities, which may include activities that lead to an advanced credential. (b) PROGRAM PERIODS AND DIVERSITY OF PROJECTS.— (1) IN GENERAL—A grant awarded by the Secretary to an eligible entity under this section shall be for a period of not more than 3 years. (2) RENEWAL.—The Secretary may renew a grant awarded under this section for 1 additional 2-year period. (3) DIVERSITY OF PROJECTS —In awarding grants under this section, the Secretary shall ensure that, to the extent practicable, grants are distributed among eligible entities that will serve geographically diverse areas, including urban, suburban, and rural areas. (4) LIMITATION.—The Secretary shall not award more than 1 grant under this section to an eligible entity during a grant competition. (c) COST-SHARING.— 1) IN GENERAL.—An eligible entity that receives a grant under this section shall provide, from non-Federal sources, not less than 25 percent of the funds for the total cost for each year of activities carried out under this section. (2) ACCEPTABLE CONTRIBUTIONS.—An eligible entity that receives a grant under this section may meet the requirement of paragraph (1) by providing contributions in cash or in kind, fairly evaluated, including plant, equipment, and services. (3) WAIVERS.—The Secretary may waive or modify the requirement of paragraph (1) in cases of demonstrated financial hardship. (d) APPLICATIONS.—In order to receive a grant under this section, an eligible entity shall submit an application to the Secretary at such time and in such manner as the Secretary may reasonably require. Such application shall include, at a minimum, a certification that the services provided by an eligible entity under the grant to a local educational agency or to a school served by the local educational agency will not result in direct fees for participating students or parents. (e) PRIORITY.—In awarding grants under this section, the Secretary shall give priority to an eligible entity that will implement evidence-based activities, defined for the purpose of this subsection as activities meeting the requirements of section 8101(21)(A)(i). (f) DEFINITION OF ELIGIBLE ENTITY.—In this section, the term ‘eligible entity’ means— 2 (1) an institution of higher education that provides course materials or resources that are evidence-based in increasing academic achievement, graduation rates, or rates of postsecondary education matriculation; (2) a national nonprofit entity with a demonstrated record of raising student academic achievement, graduation rates, and rates of higher education attendance, matriculation, or completion, or of effectiveness in providing preparation and professional development activities and programs for teachers, principals, or other school leaders; ... (4) a partnership consisting of— (A) 1 or more entities described in paragraph (1) or (2); and (B) a for-profit entity. … TITLE VIII—GENERAL PROVISIONS (page 287 to 290, 298) ... (15) DUAL OR CONCURRENT ENROLLMENT PROGRAM.— The term ‘dual or concurrent enrollment program’ means a program offered by a partnership between at least one institution of higher education and at least one local educational agency through which a secondary school student who has not graduated from high school with a regular high school diploma is able to enroll in one or more postsecondary courses and earn postsecondary credit that— (A) is transferable to the institutions of higher education in the partnership; and (B) applies toward completion of a degree or recognized educational credential as described in the Higher Education Act of 1965 (20 U.S.C. 1001 et seq.). ... (17) EARLY COLLEGE HIGH SCHOOL.—The term ‘early college high school’ means a partnership between at least one local educational agency and at least one institution of higher education that allows participants to simultaneously complete requirements toward earning a regular high school diploma and earn not less than 12 credits that are transferable to the institutions of higher education in the partnership as part of an organized course of study toward a postsecondary degree or credential at no cost to the participant or participant’s family.’’; ... (21) EVIDENCE-BASED.— (A) IN GENERAL.—Except as provided in subparagraph (B), the term ‘evidence-based’, when used with respect to a State, local educational agency, or school activity, means an activity, strategy, or intervention that— (i) demonstrates a statistically significant effect on improving student outcomes or other relevant outcomes based on— (I) strong evidence from at least 1 well- designed and well-implemented experimental study; (II) moderate evidence from at least 1 well- designed and well-implemented quasiexperimental study; or (III) promising evidence from at least 1 well- designed and well-implemented correlational study with statistical controls for selection bias; or 3 (ii)(I) demonstrates a rationale based on high-quality research findings or positive evaluation that such activity, strategy, or intervention is likely to improve student outcomes or other relevant outcomes; and (II) includes ongoing efforts to examine the effects of such activity, strategy, or intervention. (42) PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT.—The term ‘professional development’ means activities that— (A) are an integral part of school and local educational agency strategies for providing educators (including teachers, principals, other school leaders, specialized instructional support personnel, paraprofessionals, and, as applicable, early childhood educators) with the knowledge and skills necessary to enable students to succeed in a well-rounded education and to meet the challenging State academic standards; and (B) are sustained (not stand-alone, 1-day, or short term workshops), intensive, collaborative, job-embedded, data-driven, and classroom-focused, and may include activities that— (i) improve and increase teachers’— (I) knowledge of the academic subjects the teachers teach; (II) understanding of how students learn; and (III) ability to analyze student work and achievement from multiple sources, including how to adjust instructional strategies, assessments, and materials based on such analysis; (ii) are an integral part of broad schoolwide and districtwide educational improvement plans; (iii) allow personalized plans for each educator to address the educator’s specific needs identified in observation or other feedback; (iv) improve classroom management skills; (v) support the recruitment, hiring, and training of effective teachers, including teachers who became certified through State and local alternative routes to certification; (vi) advance teacher understanding of— (I) effective instructional strategies that are evidence-based; and (II) strategies for improving student academic achievement or substantially increasing the knowledge and teaching skills of teachers; (vii) are aligned with, and directly related to, academic goals of the school or local educational agency; (viii) are developed with extensive participation of teachers, principals, other school leaders, parents, representatives of Indian tribes (as applicable), and administrators of schools to be served under this Act; (ix) are designed to give teachers of English learners, and other teachers and instructional staff, the knowledge and skills to provide instruction and appropriate language and academic support services to those children, including the appropriate use of curricula and assessments; (x) to the extent appropriate, provide training for teachers, principals, and other school leaders in the use of technology (including education about the harms of copyright piracy), so that technology and technology applications are effectively used in the classroom to improve teaching and learning in the curricula and academic subjects in which the teachers teach; (xi) as a whole, are regularly evaluated for their impact on increased teacher effectiveness and improved student academic achievement, with the findings of the evaluations used to improve the quality of professional development; 4 (xii) are designed to give teachers of children with disabilities or children with developmental delays, and other teachers and instructional staff, the knowledge and skills to provide instruction and academic support services, to those children, including positive behavioral interventions and supports, multi-tier system of supports, and use of accommodations; (xiii) include instruction in the use of data and assessments to inform and instruct classroom practice; (xiv) include instruction in ways that teachers, principals, other school leaders, specialized instructional support personnel, and school administrators may work more effectively with parents and families; (xv) involve the forming of partnerships with institutions of higher education, including, as applicable, Tribal Colleges and Universities as defined in section 316(b) of the Higher Education Act of 1965 (20 U.S.C. 1059c(b)), to establish school-based teacher, principal, and other school leader training programs that provide prospective teachers, novice teachers, principals, and other school leaders with an opportunity to work under the guidance of experienced teachers, principals, other school leaders, and faculty of such institutions; (xvi) create programs to enable paraprofessionals (assisting teachers employed by a local educational agency receiving assistance under part A of title I) to obtain the education necessary for those paraprofessionals to become certified and licensed teachers; (xvii) provide follow-up training to teachers who have participated in activities described in this paragraph that are designed to ensure that the knowledge and skills learned by the teachers are implemented in the classroom; and ... (50) TECHNOLOGY.—The term ‘technology’ means modern information, computer and communication technology products, services, or tools, including, the Internet and other communications networks, computer devices and other computer and communications hardware, software applications, data systems, and other electronic content (including multimedia content) and data storage. 51) UNIVERSAL DESIGN FOR LEARNING.—The term ‘universal design for learning’ has the meaning given the term in section 103 of the Higher Education Act of 1965 (20 U.S.C. 1003). (52) WELL-ROUNDED EDUCATION.—The term ‘well-rounded education’ means courses, activities, and programming in subjects such as English, reading or language arts, writing, science, technology, engineering, mathematics, foreign languages, civics and government, economics, arts, history, geography, computer science, music, career and technical education, health, physical education, and any other subject, as determined by the State or local educational agency, with the purpose of providing all students access to an enriched curriculum and educational experience.’’. 5