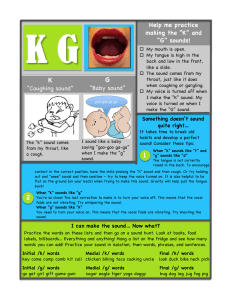
Professor: 鍾榮富教授 Students : 陳昱璇 .楊之耘. 楊玉玲 na0c0007 .Na0c0014. na0c0017
advertisement

Professor: 鍾榮富教授 Students : 陳昱璇 .楊之耘. 楊玉玲 na0c0007 .Na0c0014. na0c0017 Gestures for [ ʃ, ʒ ] - the front of the tongue is slightly domed Retroflex is exactly equivalent to apical post-alveolar Palato-alveolar is equivalent to laminal post-alveolar Apical – sounds made with the tip of the tongue Laminal - sounds made with the blade In English – the palato-alveolar sounds are the fricatives and affricates [ ʃ, ʒ, tʃ, dʒ ] French, Italian - nasals made the same or similar position Made with the front of the tongue approaching or touching the hard palate. The only true palatal in English is / /. The symbol for a voiceless palatal fricative is [ ] (8) Velar Velar stops and nasals [k, g, ŋ ] occur in English. Spanish [ɣ], a voiced velar approximant [ɰ ] - the back of the tongue is called the dorsum - these sounds are referred to as dorsal sounds Pulling the root of the tongue or the epiglottis back toward the back wall of the pharynx Pharyngeal fricatives symbols [ħ, ʕ] - occur in Semitic language, Arabic and Hebrew - no distinguish between pharyngeal and epiglottal fricatives - Caucasus contrast these two possibilities Stops Nasals Fricatives Trills, Taps, and Flaps Laterals Voiceless nasals are comparatively rare - [ ] voiceless diacritic symbol Occurs in the airstream during a fricative - [f] [s] A way to divide by auditory basis - voiceless fricative [ f, θ, s, ʃ ] - voiced fricative [z, ʒ, v, ð ] Sibilant sounds [ s, z, ʃ , ʒ ] - acoustic energy, loudness, higher pitch A way to divide by considering the plural - sibilant and nonsibilant sounds - cliff, moth, kiss, dish, church, dove, lathe, maze, rouge, judge