The Test of English for International Communication (TOEIC): necessity, utilization and accuracy.
advertisement

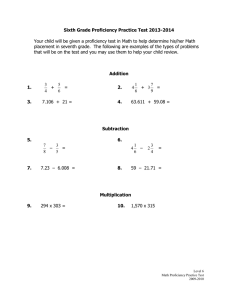
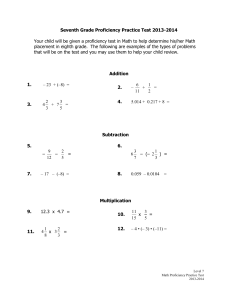
The Test of English for International Communication (TOEIC): necessity, proficiency levels, test score utilization and accuracy. Author: Paul Moritoshi Group 1 林佳佩(Alice) 郭晨亞(Yaco) 林祉含(Iris) 黃俐雯(Ruby) 1. Introduction Whether the test is necessary in principle and/or practice is approached from 3 perspectives. Since it relates to the workplace context, what should be the required proficiency level for any given work position? Do test-users apply policy relating to these required proficiency levels consistently, or do other factors intervene? If so, what are those other considerations? How accurate a test is it, not only in terms of its validity and reliability but also with respect to its fairness? 2. Background and overview Developed by the Educational Testing Service (ETS) Establish: 1979 This study: 2001 New TOEIC: 2008 (Speaking & Writing) The test uses a multiple-choice format and includes two sections, listening and reading, and takes about two hours. 3. Necessity The author talked about the test’s necessity by examining 3 perspectives: ★those of the skeptic, ★the test-user and ★the test-taker, 2.1 A Skeptic's View A skeptic might argue that the test is unnecessary. Because they think that the test’s managers’ only motivation for providing the test is to make a profit. 3.2 The Test-users’ Standpoint Corporate use Test-user: Language education The test-users might think that the test is necessary because: 3.2.1 Corporate Use For the purpose of hiring Determining placement within English language-training programs Companies recognize that English language proficiency is central to their success in the international marketplace 3.2.2 Language Education The four purposes: (1) Placement testing. (2) End-of-course assessment. (3) Pre-/post-testing. (4) Helping students to find suitable employment. Therefore, it is also necessary for the test-takers. 3.3 Necessity from the test-taker’s standpoint (1) Verify your current level of English proficiency. (2) Qualify for a new position or promotion in your company. (3) Enhance your professional credentials. (4) Set your own learning goals (5) Monitor your progress in English 4. Proficiency levels The Educational Testing Service (1997) provides an advisory proficiency scale. When deciding proficiency levels for a particular position, 52.5% of the 758 companies use this scale as the basis for setting English proficiency standards. Proficiency Scale 5. Consistent Application of Proficiency Levels Except for making admission or personal decisions, professional and social consideration are also important. 6. Accuracy 6.1.1 Construct 6.1.2 Face Concurrent 6.1 Validity 6.1.3 Criterion-related Predictive 6.1.4 Content 6. Accuracy 6.2 Reliability 6.3 Fairness 6.1.1 Construct validity A measurement that reflects the model of tests The abilities that testers need to possess in order to handle the items of target language. 6.1.2 Face validity The listening and reading parts of TOEIC tests listening and reading ability, so it has face validity. There are no speaking and writing parts of TOEIC in 2001. Therefore, it does not have face validity. Validity Listening Reading Speaking Writing Face ˇ ˇ X X 6.1.3 Criterion-related validity-1 Validity Listening Reading Speaking Writing Criterion ˇ ˇ X X 6.1.3 Criterion-related validity-2 Validity Listening Reading Speaking Writing (Concurrent) (Predictive) X No evidence X X No evidence X ˇ No evidence X X No evidence X Construct Validity Listening Reading Speaking Writing Construct X X X X Face ˇ ˇ X X Criterion-related (Concurrent) (Predictive) ˇ X No evidence ˇ X No evidence X ˇ No evidence X X No evidence Content ˇ ˇ X X 6.1.4 Content validity 6.2 Reliability 1. If all other variables remained constant, would examinees re-taking the same test obtain the same or similar scores? The higher this estimate, expressed as a reliability coefficient of between 0-1, the more reliable the test. 2. Given that an individual's scores may vary slightly, how large is the score band within which his/her 'true score' will fall? The smaller Standard Error of Measurement (SE) value, the closer test scores , the more reliable the test results are. 6.2 Reliability The reliability appears to be acceptably high because anything above 0.9 is considered “adequate for reporting and usage”. 6.3 Fairness The TOEIC test is very careful to: (1) Avoid language that is specific to U.S. English (2) Avoid contexts that may be foreign to test-takers from some cultures (3) Ensure the balanced use of names from different nationalities (4) Avoid the use of locations, people, or events that would be known in only certain regions or countries. (5) Avoid situations that are too specific to one occupational area (6) Ensure that different cultures are adequately represented ◆ So the finished test undergoes a stringent “fairness review”.