Finnish Economy Financial Management Rita Kattilakoski,
advertisement

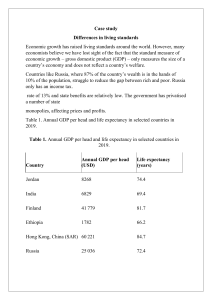
Finnish Economy Financial Management Rita Kattilakoski, Ma4n0207 INTRODUCTION HISTORY AGENDA ECONOMY Current Situation International Trade Future Republic of Finland – located in Northern Europe Population 5.5 million Majority live in the southern regions 8th largest country in Europe in terms of land area Most sparsely polulated country within the EU INTRODUCTION Åland Island – an autonomous region Capital city: Helsinki (1.4 million people live in the Helsinki area) Official languages: Finnish (89%), Swedish (6%) Sami people in the North of Finland (0.03%) Currency: Euro 1. Prior to 1809 – Part of Sweden 2. Russia took over from 1809-1917 HISTORY Highest governing body was the Senate – members were Finns Senate communicated with Russian Emperor – Russian authorities were unable to interfere Finnish became the official language 3. Independent country from 1917 to the present day (98 years) Final peace treaty with Russia in 1947 ECONOMY In the 1950s Finnish economy based on primary production and agrarian workforce – one of the poorest countries in Europe Quite fast Finland developed and is now relatively rich and economically stable country in international comparison Largest sectors: services 65% , manufacturing and refining 31% Main industrial products: paper and board, electronics and metal products Leading branches of manufacturing: engineering and high technology industries Resources: mineral (iron, chromium, copper and gold)and freshwater GDP: 204 bn € (2014) GDP per capita: at current market prices 49,055€ (2014) Monthly wages: average 3,206€; men 3,530€, women 2,891€ (2013) ECONOMY Unemployment rate: 8.7% (2014) Inflation rate: -0.34 % (2015) Member of EU since 1995 and Eurozone 2002 State Debt: 60%/ Deficit: 3.2% Warning from European Comission Europe: GDP per capita INTERNATIONAL TRADE EU makes up 60% of the total trade Largest trade flows with: Germany, Russia, UK, USA, Netherlands, Sweden and China Trade policy regulated by EU Trade accounts one-third of the GDP INTERNATIONAL TRADE INTERNATIONAL TRADE The economy is slowly coming out of a long recession Economic activity is broadly flat in 2015 But projected to strengthen in 2016 Export growth remains slow Global demand for capital goods has weakened and exports to Russia have decreased FUTURE Domestic demand low Rising unemployment, low income growth, consumer´s weak confidence The budget deficit has risen above 3% of GDP for the first time since the mid-1990s Government tries to reduces spending However structural reforms are essential to revive growth, ensure long-term fiscal sustainability and generate resources to support well-being Thank you !