Introductory immunity Chien-Ming Li MD, Ph.D
advertisement

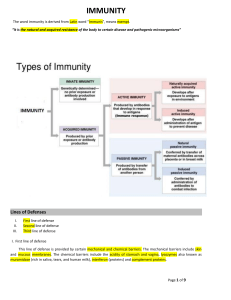
Introductory immunity Chien-Ming Li MD, Ph.D Categories of immunity 1. Innate immunity 2. Adaptive immunity 3. Passive immunity: vaccination Innate immunity • Skin and mucosa • Macrophages, dendritic cells • Complement system – Trigger inflammation – Attract macrophages to the war zone – Coat pathogens Adaptive immunity: lymphocytes-B and T cells 1. Humoral immunity 2. Cell-mediated immunity 1. Antigen presentation 1. Bacteria are eaten by macrophages 2. Parts of the bacteria are presented onto the surface of the macrophages 3. Helper T (Th) cells identify the signals 4. Th cells are activated as killer cells. Humoral immunity • B cells identify an antigen that is matches its receptors • Th cells activate these B cells • B cells divide and produce plasma cells and memory cells • Plasma cells produce antibodies attacking any cells with this antigen • Macrophages eat these marked intruders • Memory cells activate faster than ever in the aftermath Antibody or immunoglobulins 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. IgG IgD IgE IgA IgM