Jennifer M. Marsh M.S. Fisheries Student School of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences
advertisement

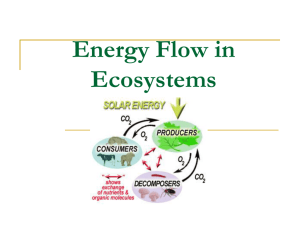
Jennifer M. Marsh M.S. Fisheries Student School of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences University of Alaska Fairbanks Trophic Pyramid Primary producers: 5 Apex Predators 4 Tertiary Consumers 3 Secondary Consumers 2 Primary Consumers 1 Primary Producers trophic level 1 Primary consumers: trophic level 2 (…) Food webs are more complex Omnivory Ontogenetic diet change Trophic Level of Catch Trophic level (TL) estimates of commercial fishery catches are used as an ecosystembased indicator for sustainability. Fishing down the food web (Pauly et al. 1998) Fishing through the food web (Essington et al. 2006) TL based on mass-balance models and gut content analysis Single TL for species No seasonal feeding dynamics and average length of catch for each species Stable isotope analysis to estimate TL Overall Goal Provide high resolution baseline information on the trophic status of the four most abundant groundfishes (arrowtooth flounder, pollock, cod, and halibut) in the GOA Objectives Examine seasonal, annual and size-class variation of trophic role (d13C & d15N) for each species; and to 2. Estimate trophic level of commercial removals and biomass for each species in the GOA. 1. Stable isotope analysis Gut content analysis provides only a snapshot of diet SIA integrates assimilated food over time Isotope values are presented in delta notation: RSAMPLE dX 1 1000 RSTANDARD where X is 15N or 13C, R is the ratio of heavy to light isotope (15N:14N or 13C:12C) δ15N has a consistent enrichment of 3.4‰ from prey to consumer δ15N can be used to assess trophic level Methods: Collection • Fish were sampled in four seasons, 20002004, off northeast side of Kodiak Island. 2000 Winter Spring X X Summer Fall X 2001 X X X 2002 X X X X X X X 2003 2004 X All fish from Area 630 7 Chapter 2: Analyses Data transformations Fitting ANCOVA models Response variable: Trophic level Covariate: length Categorical variables: years Evaluate ANCOVAs using AIC Estimate trophic level using best fit models Catch (Area 630) Biomass (Area 630) 8 ANCOVA: Full Model Yij Ai i ( X ij X i ) ij Where: μ is the average trophic level Ai is the year effect (i = 1 to 5 years) Xij is the covariate (length) measured for observation Yij (trophic level) Xbar is the average value of the covariate for treatment group i βi is the slope term for length (covariate) εij is the error term Preliminary Results 1.7 Walleye pollock TL = 5 1.6 ln (Trophic level) 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 TL = 3 1.1 1.0 0 20 40 Total length (cm) 60 80 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 5.0 Pacific cod 4.8 4.6 Trophic Level 4.4 4.2 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 4.0 3.8 3.6 3.4 3.2 0 20 40 60 Total Length (cm) 80 100 4.6 Arrowtooth flounder 4.4 Trophic Level 4.2 4.0 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 3.8 3.6 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 3.4 3.2 0 20 40 60 Total Length (cm) 80 100 TL = 5 1.6 Pacific halibut Ln(Trophic Level) 1.5 1.4 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 1.3 1.2 TL = 3 1.1 0 20 40 60 80 Total Length (cm) 100 120 140 Estimated TL of commercial catch Trophic Level Based on length distributions of observer catch data and total catch numbers from area 630 4.5 4.4 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 1999 64 61 63 62 59 Pacific cod Walleye pollock 50 2000 48 43 2001 2002 Year 43 2003 48 2004 2005 Estimated TL of commercial catch Based on length distributions of observer catch data and total catch numbers from area 630 4.5 4.4 Trophic Level 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 72 50 65 49 64 50 3.9 67 48 47 3.8 3.7 ( 68 ) 3.6 3.5 1999 Arrowtooth flounder Pacific halibut 2000 2001 2002 Year 2003 2004 2005 Estimated TL of commercial catch Based on length distributions of observer catch data and total catch numbers from area 630 4.5 4.4 Trophic Level 4.3 4.2 Arrowtooth flounder 4.1 4.0 Pacific cod 3.9 Pacific halibut 3.8 Walleye pollock 3.7 Weighted Mean 3.6 3.5 1999 2000 2001 2002 Year 2003 2004 2005 Estimated TL of fish populations Based on NMFS trawl survey estimates of size composition of fish populations from area 630 4.4 Trophic Level 4.2 4 Arrowtooth flounder Pacific cod Pacific halibut Walleye pollock Weighted Mean 3.8 3.6 3.4 3.2 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 Survey Year 2005 2010 Population estimates: Area 630 Based on NMFS trawl survey estimates of size composition of population abundance from area 630 2000 Abundance (millions) 1800 1600 1400 Arrowtooth flounder Pacific cod Pacific halibut Walleye pollock 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 Survey Year 2005 2010 Summary Pollock lowest TL, cod highest TL : commercial catch NMFS trawl survey Drop in TL of commercial catch in 2003 for Pacific cod, arrowtooth flounder and Pacific halibut TL of fish populations fluctuates after the mid 1990s for pollock and cod Conclusions Are we fishing down the food web? Estimated TL of commercial catch remained steady Only represents a fraction of the catch (higher TL predatory groundfish) Continued monitoring is suggested Advantages of stable isotope analysis Allows TL to co-vary with length Averages diet over a longer period of time Provides a TL range for each species Acknowledgements Rasmuson Fisheries Research Center (RFRC) Gulf Apex Predator prey study (NOAA Fisheries) Advisors and committee: Robert J. Foy, Nicola Hillgruber, Matthew Wooller, Gordon Kruse Alaska Stable Isotope Facility: Norma Haubenstock & Tim Howe Alexander Andrews, Lei Guo, Franz Mueter School of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences Questions? Baseline Correction d N d N TL TL 15 i i 15 3.4 ref ref Where: TLi is the trophic level of organism i, d15Ni is the measured d15N value for organism i, d15Nref is the measured d15N value for the baseline organism and TLref is the TL of the baseline organism Baseline organism = EULACHON • assigned a trophic 3.52 based on GOA Ecopath models (Aydin et al. 2007) Trophic level of catch in the GOA Walleye pollock Osmeridae 5% Misc. fish 7% Misc. prey 8% Walleye pollock 3% Percent weight of Calanoid 18% Shrimp 13% Amphipod 2% Euphausiid 44% prey items Weighted average of 1999 & 2001 Stomachs analyzed: 1263 Length range: 7 – 75 cm Average length: ≈ 38 ± 5.5 cm Data from: Food Habits of Groundfishes in the GOA in 1999 and 2000. Yang et al. (2006) Pacific cod Flatfish 3% Walleye pollock 7% Ammodytidae 12% Misc. fish 10% Other crab 16% Misc. prey 11% Percent weight of prey items Stomachs Polychaete 8% analyzed: Euphausiid 6% 1256 Length range: 9 – 104 cm Shrimp 17% Average length: ≈ 52 ± 5 cm Tanner crab 10% Arrowtooth flounder Walleye pollock 7% Flatfish 9% Percent weight Misc. prey 10% Euphausiid 14% Osmeridae 22% Shrimp 14% Ammodytidae 11% Misc. fish 13% of prey items Stomachs analyzed: 1858 Length range: 9 – 81 cm Average length: ≈ 39 ± 5 cm Pacific halibut Flatfish Misc. prey 7% 8% Walleye pollock 21% Shrimp 2% Hermit crab 11% Tanner crab 4% Ammodytida e 11% Other crab 20% Misc. fish 16% Percent weight of prey items Stomachs analyzed: 942 Length range: 13 – 126 cm Average length: ≈ 59 ± 7 cm