Eating Right, Living Well: Reducing the risk of diseases
advertisement

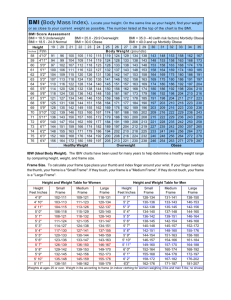
Eating Right, Living Well: Reducing the risk of diseases Assoc Prof Dr Norimah A.Karim Dept of Nutrition and Dietetics Faculty of Allied Health Sciences UKM Kuala Lumpur The problem Malaysian scene Overweight vs obesity in Malaysia MANS 2006 Overweight = 27% Obese = 12% NHMS III 2008 Overweight = 29% Obese = 14% BMI- Malaysian Adults Nutrition Survey (MANS,2006) 60 Prevalence (%) 50 40 30 49.3 20 26.7 10 12.2 9.7 0 Unde rwe ight N o rm a l O v e rwe ight BMI (kg/m 2) O be s e BMI- Malaysian Adults Nutrition Survey (MANS) by sex Obe s e 14.7 Ove rw e ight Women 24.8 Norm al 46.4 Unde rw e ight 10.1 Obe s e 9.7 Ove rw e ight Men 28.6 Norm al 52.0 Unde rw e ight 9.3 0 10 20 30 40 Pre vale nce (%) 50 60 Prevalence of Overweight in children according to age and sex 18 16.9 15.5 15.4 Percentage (% ) 16 13.8 14 11.9 12 12.6 12.4 10.0 10 9.0 7.9 8 6 6.6 6.7 4.9 4.5 4 2 0 6 7 n = 11264 UKM/Nestle study 2002 8 9 10 A g e (ye a r s ) L elak i P erem p u an 11 12 Healthy Weight Management: Eating Right, Living Well Good Eating Habits Change in food habits Exercise Managing your weight Behaviour modification Achieve Healthy Weight Lifestyle approaches that can be changed to achieve healthy weight Dietary practices Physically activity or exercise Aim to eat for health Follow a healthy balanced diet Make smart food choices What is your BMI BMI (Body Mass Index) contoh Under BMI = Normal = 60 1.6 x 1.6 weight (kg) height (m)2 = 24.5 overweight Obese weight 20 25 BMI is an indicator of obesity and underweight and normal weight 30 Relationship of BMI to Excess Mortality 300 250 Age at Issue 20-29 30-39 200 150 100 Low Risk 50 0 15 20 25 30 Moderate High Risk Risk 35 Body Mass Index Bray, 1987 40 Classification of Body Weight in Adults According to Body Mass Index, BMI Classification BMI, kg/m2 Risk of co-morbidities Underweight < 18.5 Low (but risk of other clinical problems increased) Normal range 18.5 – 24.9 Average Overweight > 25.0 Pre-Obese 25.0 –29.9 Increased Obese Class I 30.0 – 34.9 Moderate Obese Class II 35.0 – 39.9 Severe Obese Class III > 40.0 Very severe WHO, 1998 Waist Circumference Correlates abdominal fat distribution and associated ill health. Increased risk: Men > 94 cm (37 in.) Women > 80 cm (32 in.) Lower values have been proposed for Asians men > 90cm women>80cm BMI category according to sex (percent) 30 25 Underweight Normal weight Overweight Obese 20 15 10 5 0 men women Prevalence of central obesity by age group according to sex 60 51.1 47.2 50 40 37.1 30 26.1 17.1 20 10 Men Women 7.9 7.9 5.7 0 30-39 40-49 50-59 60-69 Prevalence of central obesity by BMI according to sex 60 50.6 50 43.5 men women 40 28.2 25.8 27.2 22.5 30 20 10 1.1 1.0 0 underweight normal overweight obese Good dietary practices Aim to eat for health Follow a healthy balanced diet Make smart food choices How to eat right and live well in our daily living Being healthy is about balance between good nutrition and physical activity/exercise Maintaining an ideal body weight Energy balance and body weight Energy balance Input Fat CHO Prot Stable weight Output Activity TEF BMR Energy balance and body weight Energy balance Energy balance and body weight Energy balance Balanced Diet Lemak 25 - 30% Karbohidrat 50% Protin 20% Balanced Diet Malaysian Food Pyramid Fats, oils, sugar and salt Milk, dairy products, fish, chicken, meats and legumes Fruits and vegetables Rice,noodles, breads, cereal products , and tubers Rice,noodles, breads, cereal products , and tubers Main selection, high fibre foods Eat in moderation foods which are not good sources of fibre Fat will increase caloric content of foods, thus reduce intake of fried and fatty foods Fruits and vegetables Ulam-ulaman / salads are great choices Select vegetables prepared as soups, sauted or stir fried Vegetable juices should be taken fresh and without sugar Reduce intake of vegetables prepared either fried or masak lemak Fruits and vegetables Make sure your first choice are fresh fruits Fruit juices are best drank fresh without added sugar Reduce intake of cordial drinks, fruits in heavy syrup and dried fruits Milk, dairy products, fish, chicken, meats and legumes Main selection: legumes, tofu, tempeh, egg white and fish Select chicken and meats which are not fried. Skin and excess fat should be trimmed Reduce fried fish and chicken as well as processed meat. Fats, oils, sugar and salt What are the food sources? Fats and oils Sugar Salts Ghee, butter, creamer, santan,margerine, mayonnaise, cooking oil White sugar, brown sugar, gula melaka, syrup, honey, condensed milk Salt, MSG, seasonings, ketchup Fats, oils, sugar and salt Fat + sugar Salt Healthy eating habits How • Eat slowly (> 20 mins) • Eat only when hungry Why When • Stop eating when full • If you often skip your meals, set an eating schedule and follow it Apple & Pear ? Aim for an ideal body weight Weigh yourself regularly; “regular”, once a month Calculate BMI Calculate ideal body weight (IBW) 18.5-24.9 (m)2 Eg. If you are 1.6m, then IBW = (18.5-24.9) 2.56 =47 to 64 kg Calories in breakfast foods Food serving size Roti canai 1 set Dosai 1 set Capati 1 set Nasi lemak a plate Nasi goreng a plate Nasi kerabu a plate kcal 339 340 322 687 386 535 Nasi lemak 687 kcal Nasi kerabu 535kcal mee kari 702 kcal Calories in varieties of noodles Food Mee goreng Mee kari Mee sup Mee bandung Soto ayam serving size a bowl a bowl a bowl a bowl a bowl kcal 281 702 355 491 528 Calories in varieties of rice Food serving size Nasi putih a plate Nasi lemak a plate Nasi goreng a plate Nasi kerabu a plate Nasi ayam a plate Nasi beriani a plate Nasi dagang a plate kcal 250 687 386 535 565 559 508 How can we be physically active Start being physically active Involves all movements which use energy in our daily life eg; working, recreational activities, exercise and sports How can we be physically active To increase fitness of the heart – breathing duration– at least 20-30 minutes frequency – 3-4 times a week, preferably everyday Practice an active lifestyle Select physical activities which suit you Do these activities at least 30 minutes a day ( can be totalled up to a whole day ie 10 minutes per session) Practice an active lifestyle Exercise correctly Take time to warm up before exercising Always cool down after exercising Consult your doctor if you are Over 35 years and male Over 40 years and female Have not been exercising regularly Uncertain of your health Have hypertension, diabetes, heart disease Examples of light physical activities 60 minutes everyday walking stretching Light gardening activities Examples of moderate physical activities 30 minutes everyday brisk walking cycling Walking up and down staircase (reduce using lift) Minutes activity needs to be carried our by body weight (burn 100 kcal) Game/exercise Aerobic dancing Badminton Football Golf Gardening 50 kg 23 min 26 16 34 38 80 kg 15 min 15 10 21 23 Minutes activity needs to be carried our by body weight (burn 100 kcal) Game/exercise Tennis Walking (6.4km/hr) Jogging (8.8km/hr) Running (11.2km/hr) Bicycling (8.8km/hr) 50 kg 20 22 13 10 27 80 kg 13 14 8 6 17 Take home message Invest in a good weighing scale and weigh yourself once a week Maintain a healthy weight Aim to eat for health Follow a healthy balanced diet Make smart food choices Take home message Start being physically active Invest in a pedometer (to calculate number of steps- recommended 10,000 steps per day) Select physical activities which suit you Do these activities at least 30 minutes a day, at least 3-4 times a week, preferably every day Enjoy your exercise Thank you for your attention