Document 15698731
advertisement

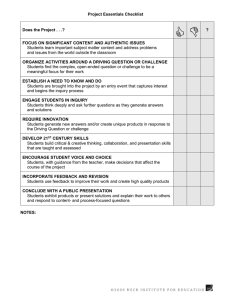
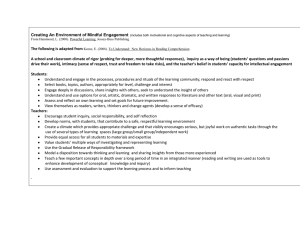
Scientific Inquiry Learning Science by Doing Science Kendall Hunt Publishing Company Overview • • • • • • • • • What is Inquiry? How did it originate? Why is it important? How does inquiry-based instruction compare to traditional instruction? What does inquiry-based learning look like in the classroom? Proof of Effectiveness Inquiry is Powerful Learning Inquiry and the Nature of Science By Design: A Journey of Excellence Through Science Inquiry Defined • Inquiry is a dynamic approach to learning that involves – exploring the world, – asking questions, – making discoveries, and – rigorously testing those discoveries in the search for new understanding. Designed With A Purpose • Curriculum designed under this definition recognizes students’ drive to learn, engages students in central concepts and principles, leads students to indepth exploration of authentic and important topics, uses performance-based assessments and encourages collaboration. Origins of Inquiry • After the launch of Sputnik by the Soviet Union, science instruction received renewed attention in curriculum design. • New curricula were developed in the U.S. many with an inquiry focus. • For Nearly 40 years, the literature in science education has documented increased achievement and improved retention of science concepts when student are taught using curriculum materials that have and inquiry approach. • Unfortunately, our traditional educational system has worked in a way that discourages the natural process of inquiry. Students become less prone to ask questions as they move through the grade levels. In traditional schools, students learn not to ask too many questions, instead to listen and repeat the expected answers. Importance of Inquiry • Education is not about preparing students for a world that is static and fixed. • Education must prepare learners to cope with changes that will increase in complexity throughout their lives and many of which cannot be foreseen at this time. • Most learners will probably deal with several job changes, move to several different locations, be involved in complex social changes, and other such issues. Education cannot give learners all the information that they need to know, but rather it must provide the tools for continuing to learn. Importance of Inquiry • Within a conceptual framework, inquiry learning and active learner involvement can lead to important outcomes in the classroom. • Students who actively make observations, collect, analyze, and synthesize information, and draw conclusions are developing useful problem-solving skills. • These skills can be applied to future "need to know" situations that students will encounter both at school and at work. So, What is the Difference? Traditional Science Instruction vs. Inquiry-Based Instruction Traditional Instruction • Focuses on mastery of content, with less emphasis on the development of skills and the nurturing of inquiring attitudes • Is teacher centered; teacher gives information about "what is known" • Student is receiver of information, teacher is dispenser. • Assessment is focused on "one right answer." • Concerned with preparation for the next grade level and in-school success, not with helping a student learn to learn through life • Tends to be a closed system • Resources limited to what is in class or school building • Focuses on learning technology rather than using technology to enhance learning Inquiry-Based Instruction • More student centered, with the teacher as a facilitator of learning • Emphasis on "how we come to know" and less on "what we know" • Assessment is focused on determining the progress of skills development in addition to content understanding • Concerned with in-school success equally with preparation for life-long learning • Open systems where students are encouraged to search and make use of resources beyond the classroom and the school • Uses technology to connect students appropriately with local and world communities which are rich sources • Can be done in lectures that provoke students to think and question as well as labs and group projects • Focuses on the how instead of the what What It Looks Like: Traditional vs. Inquiry Inquiry Is Powerful Learning • Students are naturally curious about the world around them • Students must first be engaged in the content to learn • Synthesizing the information on their own is more powerful than a lecture • This style of learning provides the opportunity for continued research • Inquiry prepares students to be life-long learners The Abilities of Inquiry! Students should learn science by asking appropriate questions and conducting valid experiments or collecting relative data, not by memorizing dogmatic steps and copious facts…. Inquiry allows students to develop a love for science through investigation and discovery. This is how science happens and this is why scientists love science. Proof of Effectiveness • Educational studies show that student learning increases after the use of an inquiry-based science curriculum. • Inquiry Instructional Models (Bybee, 2006) The BSCS 5E instructional model: Origins, effectiveness, and applications • Formative Assessment (Black and Wiliam, 1998) Assessment and classroom learning • Reflective Practice (NBPTS, 2000; Vandevoort, Amrein-Beardsley, & Berliner, 2004) A Distinction that Matters; National Board Certified Teachers and Their Students’ Achievement Inquiry and the Nature of Science • Inquiry instruction is a hallmark of current science education reform efforts. • The typical school laboratory is “cookbookstyle.” Students are given the exact steps to follow and are asked to confirm known results • Many typical laboratory learning experiences use the stereotypical ‘scientific method’ which portrays the work of scientists as following a rigid, linear path. • These are NOT accurate views of how science works and are NOT inquiry. By Design: A Journey To Excellence Through Science • Will help children understand the world they live in and instill in them a willingness to explore and make sense of the world around them. • Will provide all students with stimulating experiences in the life, earth, physical sciences and technology, and health while simultaneously developing their criticalthinking and problem-solving skills along with strengthening their faith. • Will provide children with the opportunity to learn age-appropriate concepts and skills and to acquire scientific attitudes and habits of mind. By Design: A Journey To Excellence Through Science • Will provide teachers with a variety of strategies with which to assess student learning • Will offer teachers opportunities to link the teaching of science with the development of skills in mathematics, language arts, and social studies • Will encourage the use of cooperative learning to help students develop the valuable skill of working together By Design: A Journey to Excellence Through Science. • By Design will help develop life long learning skills. • By Design will give you the practical framework of inquiry you and your students need to be successful.