Critical Thinking
advertisement

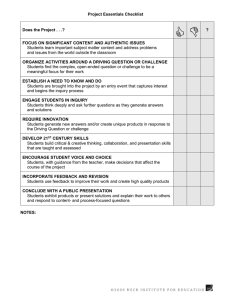
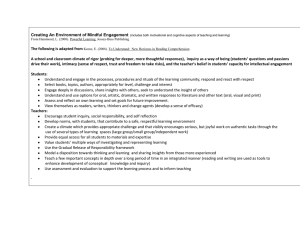
Critical Thinking Democratic Vistas: Pedagogy Greg Hatzis & Lois Libby What is “Critical Thinking?” The thoughts of others… Critical thinking is purposeful and reflective judgment about what to believe or what to do in response to observations, experience, verbal or written expressions, or arguments. (Wikipedia) Critical thinking - is exploring questions about and solutions for issues which are not clearly defined and for which there are no clear-cut answers. (American Accounting Association) What is “Critical Thinking?” The thoughts of others… Critical thinking can be defined as a process of evaluating facts in their exact arrangement and proportion in order to understand the certainty of our opinions or interpretations. (Washington State’s English College Readiness Definitions) Within the framework of skepticism, critical thinking is synonymous with informal logic. (Postmodern terms – www.thebookman-wordpress.com What is “Critical Thinking?” Take 5 minutes to reflect and write a definition that makes sense to you. In groups of 3-4, compare definitions and list the most salient concepts. Your thoughts…. Your thoughts…. What is “Critical Thinking” in a history classroom? 1. Includes the knowledge of facts, dates, names, places, events, and ideas. 2. It must also include a demonstration of a true understanding of what is being taught. Source: National Center for History in the Schools What is “Understanding?” What does a student do who really “understands” something? Understanding is more than “knowledge” Understanding is Knowing why Using knowledge wisely Making sense of new facts USING KNOWLEDGE IN NEW WAYS (Transfer of Knowledge) Source: Understanding by Design – Wiggins/McTigue Demonstrating critical thinking means going deeper, or… Raising new questions Crafting an argument Gathering evidence to support an answer/position – Identifying the significance something Taking context into account Considering alternative accounts – Examining documents, journals, diaries, artifacts, sites, art, quantitative data Comparing, contrasting, cross-referencing Making connections to one’s own life Analyzing, Applying, Synthesizing, Evaluating A simple definition…. Students will use knowledge in new ways to create something UNIQUE and ONE’S OWN Apparent Understanding vs. Genuine Understanding Fostering Critical Thinking Learner centered instruction: Problem Solving and Inquiry Problem Solving Inquiry What it looks like Students are provided information and resources with which they must answer a question. Students build their own base of knowledge in order to answer a question. What some call it “Guided Discovery” “Constructivism” Problem Solving Process Inquiry Absorb information Acquire information Use info Use info Answer Question Answer Question Problem Solving Inquiry Challenges Where do I find the information to provide? How much information do I provide? What are reliable sources? How do I teach them to find useful information? How do I teach kids to make the proper choices about information? Looking at your curriculum doc When was the last time you looked at it? What are the headings? What do these categories suggest in terms of what is valued? Where, if at all, is “critical thinking” reflected in your document? Where is critical thinking reflected in your classroom? Re-introducing, Mr. Bloom Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation Where critical thinking lives….