Functional Groups
advertisement
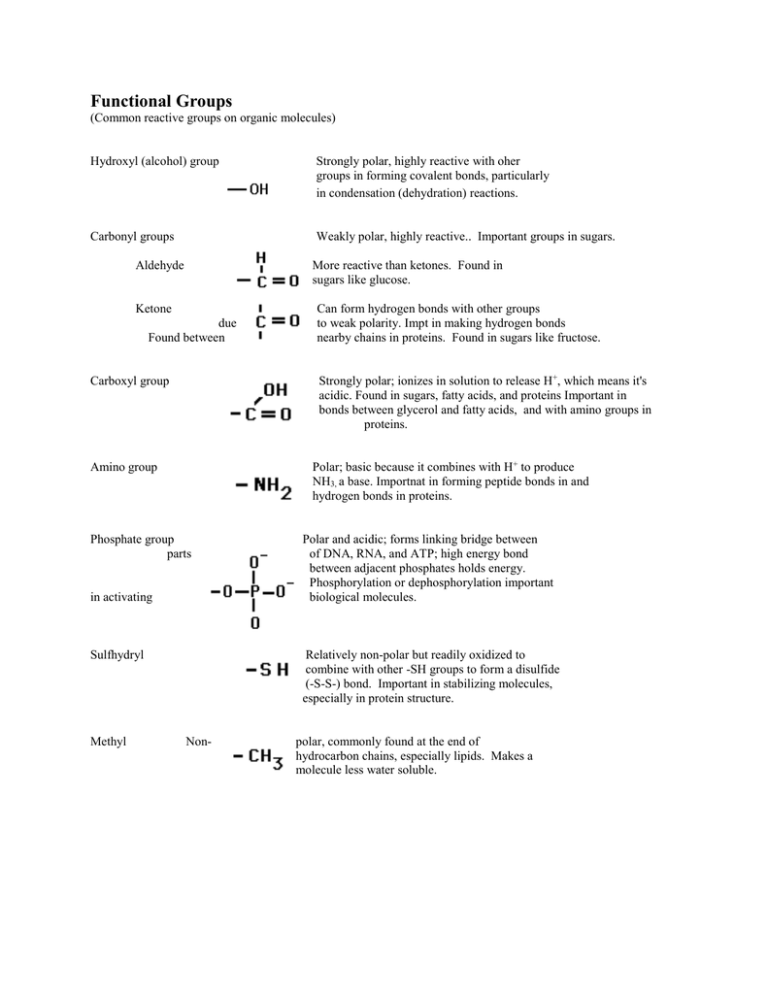
Functional Groups (Common reactive groups on organic molecules) Hydroxyl (alcohol) group Strongly polar, highly reactive with oher groups in forming covalent bonds, particularly in condensation (dehydration) reactions. Carbonyl groups Weakly polar, highly reactive.. Important groups in sugars. Aldehyde More reactive than ketones. Found in sugars like glucose. Ketone due Found between Strongly polar; ionizes in solution to release H+, which means it's acidic. Found in sugars, fatty acids, and proteins Important in bonds between glycerol and fatty acids, and with amino groups in proteins. Carboxyl group Polar; basic because it combines with H+ to produce NH3, a base. Importnat in forming peptide bonds in and hydrogen bonds in proteins. Amino group Phosphate group parts in activating Sulfhydryl Methyl Can form hydrogen bonds with other groups to weak polarity. Impt in making hydrogen bonds nearby chains in proteins. Found in sugars like fructose. Polar and acidic; forms linking bridge between of DNA, RNA, and ATP; high energy bond between adjacent phosphates holds energy. Phosphorylation or dephosphorylation important biological molecules. Relatively non-polar but readily oxidized to combine with other -SH groups to form a disulfide (-S-S-) bond. Important in stabilizing molecules, especially in protein structure. Non- polar, commonly found at the end of hydrocarbon chains, especially lipids. Makes a molecule less water soluble.







