CHEM 121 Chapter 7 Winter 2014 1
advertisement

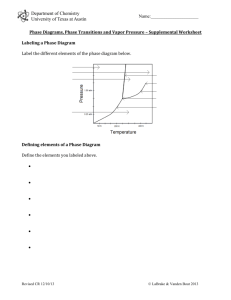
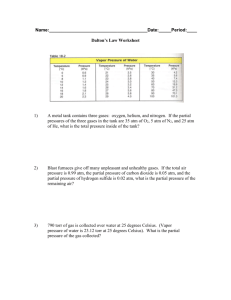
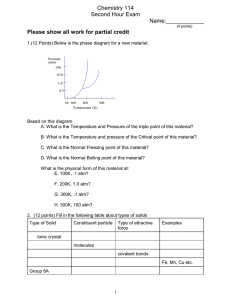
CHEM 121 Chapter 7 Winter 2014 1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter Explains matter in various states 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2 States of Matter Matter: Physical states: • • Properties of Matter: • • • • • 3 Solids • Strong attractive forces ( • ) Properties: • _________________ density • _________________ compressibility • _________________ shape • _________________ thermal expansion 4 Liquids • Medium forces ( • ) Properties: • _________________ density • _________________ compressibility • _________________ shape • _________________ thermal expansion 5 Gases • No attractive forces • High kinetic E: Properties: • _________________ density • _________________ compressibility • _________________ shape • _________________ thermal expansion 6 Measuring Pressure Pressure (P) Barometer: http://encarta.msn.com/media_461532488_ 761573986_1_1/mercury_barometer.html 7 Units of Pressure • pascal • • • atmosphere • • Millimeter of mercury • • • psi, pounds per square inch (engineering) 1 atm 760 mmHg 8 Gas Laws 4 Variables: P: T: • V: n: 9 Boyle’s Law volume occupied by a gas is __________ related to its pressure 10 3-minute practice A sample of gas has a volume of 100.0 mL at 1.0 atm. If we increase the pressure to 2.0 atm, what is the new volume of the gas (T is constant)? 11 Charles’s Law volume of a gas is __________ related to its temperature (K) 12 3-minute practice A sample of gas has a volume of 100.0 mL at 27 ˚C. If we heat the gas to 54 ˚C (keeping P constant), what is the new volume of the gas? 13 Gay-Lussac’s Law At constant volume, pressure is __________ related to temperature Combined Gas Law: 14 Avogadro’s Law The volume occupied by a gas is __________ proportional to the amount (mol) of gas (fixed T & P) At fixed T & P: equal volumes of any ideal gas have… • • 15 Gas Behavior at STP • STP: • • • Standard Molar Volume 16 3-minute practice What is the volume (mL) of 0.10 g of helium gas at STP? 17 Ideal Gas Law Combine: – Boyle’s Law – Charles’s Law – Avogadro’s Law Solve at STP… 18 A tank filled with methane at 23 ˚C and 0.991 atm is fitted with a safety valve that opens if internal pressure exceeds 1.00 x 103 torr. When the tank is placed in boiling water at exactly 100. ˚C, will the safety valve open? Initial: T= P= n= V= Final: T= P= n= V= 19 A sample of gas occupies 105 mL at 0.903 atm. If temperature remains constant, what is the volume (in L) at 26.4 kPa? Initial: P= V= n= T= Final: P= V= n= T= 20 Mixtures of Gases Each gas in a mixture acts like it is the only gas present Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures: Example: When water vapor added to pure air…. Each gas exerts __________________________________ 21 Graham’s Law • Effusion: gas leak through hole • Diffusion: spontaneous mixing of gases rateA rateB molecular mass B molecular mass A 22 3-minute practice Which will deflate more quickly: a balloon filled with helium or nitrogen? 23 Changes of State Intermolecular Forces: 24 Intermolecular Forces • dipole-dipole • polar molecules acting H like magnets O • if between H and N, O, or F _______________ H H O H O H H • London Dispersion forces • • 25 Vapor Pressure As a liquid evaporates: • • • But if closed container… Vapor Pressure: 26 Boiling • As you increase T, vapor pressure _____________ • If vapor pressure reaches atmospheric pressure… 27 Sublimation and Melting Solids have vapor pressures too! – Typically low or high? Sublimation: Melting: Decomposition: 28 Heating and Cooling Curves • Plateaus: • Slopes: 29 Specific Heat (SH) Amount of heat to raise the T of ___ of a substance by ____ How much energy is needed to raise the temperature of 20.0 g of iron by 14.5 °C? 30 Changes of State Equations • Heat of Fusion: • • Heat of fusion for water = 80 cal / g • Heat of Vaporization: • • Heat of vaporization for water = 540 cal / g 31 Solid State 32 Solid State 33