BIOL242 Objectives Unit 4: Chaps 23, 24 – Digestion and Metabolism
advertisement

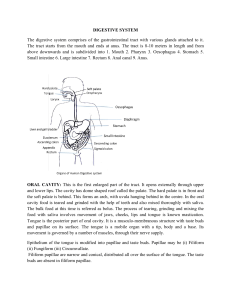
BIOL242 Objectives Unit 4: Chaps 23, 24 Chapters 23, 24 – Digestion and Metabolism 1. Know the general functions of the digestive system. Know the essential activities of the digestive system. 2. Know which parts of the digestive system comprise the digestive tract and what organs are considered the accessory organs. 2. Understand the major layers of the walls of the digestive tract and the composition and function of each layer. 4. Know the difference between peristalsis and segmentation 5. Know what changes occur to your food in the mouth. Is there any chemical digestion? What is the function of the salivary glands? Know the three types of salivary glands found in the mouth and what they contribute to the composition of saliva. 6. Know the function of the esophagus. What are some distinctive features of the esophageal wall? 7. Know the functions of the stomach. Know the anatomy of the stomach including the regions (cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus) and what is unique to each region of the stomach. What is distinctive to the histology of the stomach? 8. Know the purpose of the gastric glands in the stomach. What types of cells are found in the gastric glands? What is the function of these cells? How is HCI made in the parietal cells? What is the function of carbonic anhydrase in these cells? 9. Know the three phases of gastric activity and what happens at each phase. 10. Know what types of digestion and absorption occur in the stomach. 11. Know the general features of the small intestine. What is the key function of the small intestine? Know what features are unique to each of the sections of the small intestine. Know the function of plicae, lacteals, intestinal villi, and intestinal glands. 12. Know the general functions of the pancreas. What is found in the pancreatic juice? How is the pancreatic juice transported to the small intestine? 13. Know the functions of the liver. Understand how the blood flows though the liver lobules and what is found at the portal areas. 14. Know the function of the gall bladder. What happens when the bile is too concentrated? What hormone triggers the release for bile? Where does the bile go? What is found in bile? Intro. Human Anatomy & Physiology I & II NSCC Page 1 of 2 INTERCONNECTEDNESS BIOL242 Objectives Unit 4: Chaps 23, 24 15. Know how the following hormones function in digestion and what triggers the release: secretin, cholecystokinin, gastric inhibitory peptide, vasoactive intestinal peptide, gastrin, and enterocrinin. 16. Know the general function of the large intestine. Why is it called the large intestine? What distinctive histological features are found in the large intestine? 17. Know how the following are digested and absorbed: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, water-soluble vitamins, fat-soluble vitamins, and water. 18. Review the section 25-6 on metabolic interactions. Know what happens in the body during the absorptive state and the postabsorptive state. 19. Begin to think about the following situations and how they would change the "normal" process of digestion. a. Lack of functional parietal cells b. Liver can no longer make bile c. Jejunum length is reduced by 50% d. Pancreas is unable to deliver pancreatic juice to the small intestine e. Lactose intolerance Intro. Human Anatomy & Physiology I & II NSCC Page 2 of 2 INTERCONNECTEDNESS