Cranial Nerves, training.seer.cancer.gov
advertisement
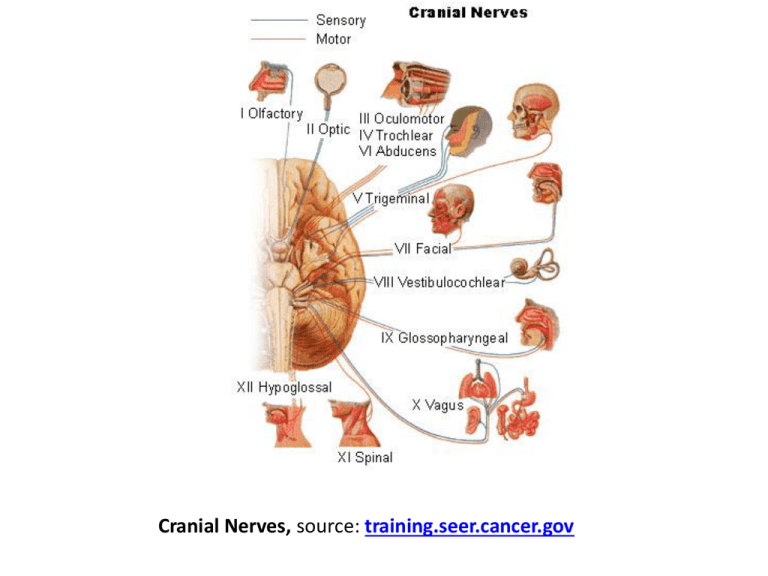
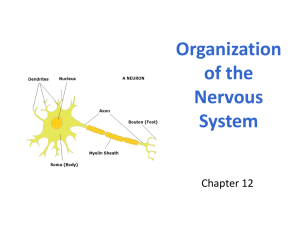
Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a Topics • • • • Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of glia in the CNS and PNS The Nervous System • Includes all neural tissue in the body General Overview Neural Tissue • Contains 2 kinds of cells: – neurons: • cells that send and receive signals – neuroglia (glial cells): • cells that support and protect neurons Organs of the Nervous System • Brain and spinal cord • Sensory receptors of sense organs (eyes, ears, etc.) • Nerves connect nervous system with other systems INTERCONNECTEDNESS Anatomical Divisions of the Nervous System 1. Central nervous system (CNS) 2. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Nervous System CNS PNS Somatic NS Autonomic NS Sympathetic Parasympathetic The Central Nervous System (CNS) • Consists of the spinal cord and brain • Contain neural tissue, connective tissues, and blood vessels • INTERCONNECTEDNESS Functions of the CNS • Are to process and coordinate: – sensory data: • from inside and outside body (“inputs”) – motor commands: • control activities of peripheral organs (e.g., skeletal muscles) [“controls’] – higher functions of brain: • intelligence, memory, learning, emotion (“outputs”) The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • Includes all neural tissue outside the CNS (nerves that control muscles and glands) Functions of the PNS 1. Deliver sensory information to the CNS 2. Carry motor commands to peripheral tissues and systems Nerves • Also called peripheral nerves: – bundles of axons with connective tissues and blood vessels – carry sensory information and motor commands in PNS: • cranial nerves—connect to brain • spinal nerves—attach to spinal cord Functional Divisions of the PNS • Afferent division: – carries sensory information – from PNS sensory receptors to CNS • Efferent division: – carries motor commands – from CNS to PNS muscles and glands SAME: Sensory is Afferent, Motor is Efferent PNS divisions • Somatic nervous system (SNS) • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) • More “layers” The Somatic Nervous System (SNS) • Controls skeletal muscle contractions: – voluntary muscle contractions – involuntary muscle contractions (reflexes) The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) • Controls subconscious actions: – contractions of smooth muscle and cardiac muscle – glandular secretions Divisions of the ANS • Sympathetic division: – has a stimulating effect • Parasympathetic division: – has a relaxing effect Nervous System CNS PNS Somatic NS Autonomic NS Sympathetic Parasympathetic Neurons • The basic functional units of the nervous system The Structure of Neurons Figure 12–1 Major Organelles of the Cell Body • • • • Large nucleus and nucleolus Cytoplasm (perikaryon) Mitochondria (produce energy) RER and ribosomes (produce neurotransmitters) • Cytoskeleton • Nissl Bodies: RER and ribosomes Dendrites • Highly branched • Dendritic spines: – many fine processes – receive information from other neurons – 80–90% of neuron surface area The Axon • Are long • Carries electrical signal (action potential) to target • Axon structure is critical to function Structures of the Axon • Axon hillock: – thick section of cell body – attaches to initial segment • Initial segment: – attaches to axon hillock • Collaterals: – branches of a single axon • Synaptic terminals with knobs: – tips of axon (knobs at ends) Movie Neurophysiology: Neuron Structure The Synapse Figure 12–2 Synapse • Synapse: Area where a neuron communicates with another cell • Presynaptic cell: – neuron that sends message • Postsynaptic cell: – cell that receives message • Synaptic cleft The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane • Area of terminal containing synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters • Chemical messengers (like ACh) • Released at presynaptic membrane • Affect receptors of postsynaptic membrane • Broken down by enzymes and, or, taken up into presynaptic cell • Are reassembled at synaptic knob Soma • What does soma mean? Major Structural Classifications of Neurons • Unipolar neurons: – found in sensory neurons of PNS • Multipolar neurons: – common in the CNS – include all skeletal muscle motor neurons – cell body (soma) – short, branched dendrites – long, single axon Unipolar Neurons • Have very long axons • Dendrites fused to axon • Cell body to 1 side Figure 12–3 (3 of 4) Multipolar Neurons • Often have long axons • Multiple dendrites, 1 axon Figure 12–3 (4 of 4) 3 Functional Classifications of Neurons • Sensory neurons: – afferent neurons of PNS • Motor neurons: – efferent neurons of PNS • Interneurons: – association neurons Sensory (Afferent) Neurons • Monitor internal environment (visceral sensory neurons) • Monitor effects of external environment (somatic sensory neurons) Motor (Efferent) Neurons • Signals from CNS motor neurons to visceral effectors pass synapses at autonomic ganglia dividing axons into: – preganglionic fibers – postganglionic fibers Interneurons • Most are located in brain, spinal cord, and autonomic ganglia: – between sensory and motor neurons • Are responsible for: – distribution of sensory information – coordination of motor activity • Are involved in higher functions: – memory, planning, learning Neuroglia are supporting cells Neuroglia • Half the volume of the nervous system • Many types of neuroglia in CNS and PNS Volume • What is volume? Neuroglia of the Central Nervous System Figure 12–4 4 Types of Neuroglia in the CNS 1. 2. 3. 4. Ependymal cells Astrocytes Microglia Oligodendrocytes 1. Ependymal Cells • Form epithelium called ependyma • Line central canal of spinal cord and ventricles of brain: – secrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – have cilia or microvilli that circulate CSF – monitor CSF – contain stem cells for repair Blood-Brain Barrier • What is this? 2. Astrocytes • Maintain blood–brain barrier (isolates CNS) • Create 3-dimensional framework for CNS • Repair damaged neural tissue • Guide neuron development • Control interstitial environment 3. Microglia • Migrate through neural tissue • Clean up cellular debris, waste products, and pathogens • Not of neural origin; related to macrophages (like osteoclasts) 4. Oligodendrocytes • Processes contact other neuron cell bodies • Wrap around axons to form myelin sheaths Myelination • Increases speed of action potentials • Myelin insulates myelinated axons • Makes nerves appear white Nodes and Internodes • Internodes: – myelinated segments of axon • Nodes: – also called nodes of Ranvier – gaps between internodes – where axons may branch White Matter and Gray Matter • White matter: – regions of CNS with many myelinated nerves • Gray matter: – unmyelinated areas of CNS 2 Neuroglia of the Peripheral Nervous System 1. Satellite cells (amphicytes) 2. Schwann cells (neurilemmacytes) 1. Satellite Cells • Surround ganglia • Regulate environment around neuron Ganglia vs Nuclei • Masses of neuron cell bodies – Called ganglia in the PNS and are surrounded by satellite cells – Called nuclei in the CNS 1. Schwann Cells • Form myelin sheath around peripheral axons (nerves) • 1 Schwann cell sheaths 1 segment of axon: – many Schwann cells sheath entire axon Schwann Cells Figure 12–5a Schwann Cells Figure 12–5b “Summary” • • • • Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of glia in the CNS and PNS