Final Exam BIOS 160 Anatomy and Physiology Name

BIOS 160 Anatomy and Physiology
Name
Final Exam
200 pts total. Answer the multiple choice/true-false/matching questions using the computerized answer form. These initial questions are worth 2 points apiece. Then separate the last 2 pages of the exam and answer all the short answer/essay questions. When finished, fold the last page in half lengthwise, write the first 3 letters of your last name in the blanks provided on the outer page, and insert your computer form. Finally, shove the folded last page between the pages of this stapled question section, write your name on the exam, and turn it in.
1. In the diagram of the seminiferous tubule wall to the right, what is the function of the
Sertoli cells seen among the other cells in the tubule? a. produce testosterone b. nourish the spermatocytes c. serve as diploid stem replacement cells d. develop into spermatids e. initiate cellular division
2. The cell labeled AD in the picture is most likely to be a: a. primary spermatocyte b. secondary spermatocyte c. spermatogonium d. interstitial cell e. spermatozoan
3. What is the function of the cells in the picture labeled "AE"? a. produce testosterone b. nourish the spermatocytes c. serve as diploid stem replacement cells d. develop into spermatids e. initiate cellular division
4. What urogenital structure in elderly males often enlarges and/or becomes cancerous, making urination difficult? a. the prostate b. the bulbourethral gland c. the seminal vesicles d. the testes e. the epididymis
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 1
5. In the diagram of the male urogenital system to the right, what is the organ or gland indicated by arrow
BD ? a. the prostate b. the bulbourethral gland c. the seminal vesicles d. the testes
e. the epididymis
6. Which structure at the right produces a thick, clear mucus that neutralizes any residual acidic urine which also lubricates the urethra ? (Answer using the letter combination pointing to the correct structure, being sure to fill in all the letters of the answer for this question)
7. Which structure in the picture stores sperm until they mature and become motile ? (Answer using the letter combination pointing to the correct structure, being sure to fill in all the letters of the answer for this question).
8. Which type of target cell or organ below responds to heightened levels of FSH in males? a. Sertoli cells b. the bulbourethral glands c. interstitial cells d. spermatogonia e. spermatocytes
9. In the diagram of the ovary shown to the right, what is the best name for the maturing gamete indicated by arrow "6"? a. oogonium b. ovum c. primary oocyte d. secondary oocyte e. diploid germ cell
10. Each of the whole round structures shown in the ovary cross section are called: a. oocytes b. zona pellucidae c. fimbriae d. antra e. follicles
Sagittal of an ovary showing structures labeled sequentially in stages of increasing maturation (1-6)
11. What hormone stimulates the maturation of these ovarian structures, shown in the picture? a. LH b. FSH c. estrogen d. progesterone e. human chorionic gonadotropin
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS Answer "a" if true and "b" if false.
12. The corpus luteum produces LH in order to maintain the endometrium.
13. One diploid oogonium produces four viable haploid ova through oogenesis in the ovary.
14. Gastrulation occurs before neurulation.
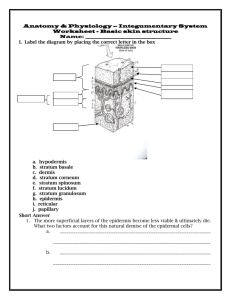
15. A fertilized female sex cell that reaches the uterus after its trip through the oviduct has actually not completed meiosis.
16. The primary germ layer known as ectoderm develops into the spinal cord and brain (among other things.)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
17. In the diagram of the external genitalia of the human female (to the right), which structure is the urethral opening? (Answer using the letter combination pointing to the correct structure, being sure to fill in all the letters of the answer for this question).
18. Which letter(s) in the diagram to the right points to a labium majorum ?
19. The "proper" or best orientation of a child during childbirth is known as the: a. breech position b. feet-downward position c. vertex position d. cervical position e. cephaloposterior position
20. Which of the following is NOT a common side effect as a result of being pregnant? a. constipation b. heartburn c. lordosis d. nausea in the third trimester e. difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
21. What is the best description of the embryonic stage labeled as AD in the picture to the right? a. gastrula b. blastula (blastocyst) c. morula d. neurula e. fetus
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 3
22. What process is depicted by arrow BE in the picture of early cleavages and development on the previous page? a. ovulation b. neurulation c. implantation d. oogenesis e. menstruation
23. The onset of true labor begins when a. Braxton-Hicks contractions begin b. the cervix is dilated to about 10 cm c. oxytocin and prostaglandins are released d. the placenta is delivered e. the amniotic sac is broken
24. The type of body section shown in the picture to the right is a section. a. coronal b. medial c. transverse d. frontal e. cross
25. Which of the following structures contains transitional epithelium? a. trachea b. kidney c. small intestine d. heart e. bladder
26. The visceral layer found around the organs of the abdominal cavity is part of what structure? a. serous membrane b. meninge c. endocardium d. mucus membrane e. stratum germinativum (basale)
27. Which is the correct sequence that new cells move through in the skin? a. stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale, stratum corneum b. stratum basale, stratum granulosum, stratum corneum, stratum spinosum, stratum lucidum c. stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum d. stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum basale, stratum corneum, stratum lucidum e. stratum lucidum, stratum basale, stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 4
28. The function of a melanocyte is to: a. phagocytize dead cells b. produce collagen fibers c. produce fatty acids d. produce a brown pigment e. sense pressure on nearby tissues
---------------------------------------------------------------------
TRUE/FALSE Answer "a" if true and "b" if false.
29. The structure labeled ab in the skin diagram to the right produces sebum.
30. The layer indicated by label " c " is made up of loose connective tissue.
31. Arrow " e " in the skin diagram to the right points to a pressure sensor/receptor (Pacinian corpuscle).
32. Thin filaments in muscle are made mostly of the protein actin.
33. The endomysium tissue layer in muscle is found wrapped around structures within (inside of) the perimysium layer.
----------------------------------------------
34. Which bone of the skull surrounds and includes the external auditory meatus? a. temporal b. occipital c. parietal d. vomer e. sphenoid
35. Which of the following sequences are in the correct order in time for how a broken bone repairs itself? a. hematoma formation
fibrocartilage callus formation
bony callus formation
bone remodeling b. fibrocartilage callus formation
bone remodeling
hematoma formation
bony callus formation c. bony callus formation
bone remodeling
hematoma formation
fibrocartilage callus formation d. bone remodeling
hematoma formation
bony callus formation
fibrocartilage callus formation e. hematoma formation
bony callus formation
fibrocartilage formation
bone remodeling
36. Arthritis is a disease involving the ________ of the body. a. ligaments b. joints c. tendons d. skeletal muscles e. smooth muscles
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 5
37. The type of muscle fascicle arrangement shown to the right where the plane cuts across the muscle is: a. unipennate b. bipinnate c. multipinnate d. parallel e. convergent
38. The bending of the person's left foot so as to face the inferior (bottom) surface inward (as shown in the picture) is known as: a. eversion b. inversion c. dorsiflexion d. plantar flexion e. extension
39. "Supination" as we used the term in this class, refers to: a. laying belly downwards on the floor b. tilting your head forwards c. turning your hand palm upwards d. kneeling e. laying belly upwards on the floor
40. The diagram to the right shows the tension created by stimuli of a skeletal muscle arriving at different frequencies.
What is the name of the condition seen in a muscle when the stimuli are extremely frequent, as shown in picture D? a. convergent twitching
A B C D b. contraction plateau c. complete tetanus d. maximally graded response e. single cohesive twitch
41. The ATP used to fuel muscle contraction can be formed in three ways: aerobic oxidative phosphorylation, direct phosphorylation of ADP by creatine phosphate, and: a. anaerobic glycolysis (fermentation), b. formation of ATP by the ATP synthase ("ATP mill") in the mitochondria c. import of extra ATP into the muscle cell from the bloodstream d. the formation of lactic acid e. the buildup of oxygen debt
42. The tissue shown in the micrograph to the right was found attached to the fifth right rib in a human skeleton. This tissue is: a. erythrocytes b. loose connective tissue c. cuboidal epithelium d. hyaline cartilage e. dense connective tissue
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 6
43. The Organ of Corti can be found in: a. the cochlea of the inner ear b. the semicircular canals of the inner ear c. the retina of the eye d. the taste buds of the tongue e. the receptor area of the site of olfaction
44. The cellular membrane of a body cell may have impermeable, leak-proof connections (as seen between intestinal cells to prevent leakage of enzymes) called: a. gap junctions b. desmosomes c. tight junctions d. loose junctions e. connexons
45. The role of the nucleolus in eukaryotic cells is to: a. transcribe rRNAs and assemble ribosomes b. transcribe mRNAs for cytoplasmic translation c. encircle and protect the chromatin d. limit transport of molecules into and out of the nuclear membrane e. conduct proteins through the cell to certain destinations
46. The movement of water across a biological membrane follows the physical laws of: a. active transport b. passive diffusion c. facilitated diffusion d. endocytosis e. exocytosis
47. Which of the following scenarios correctly describes the pathway, in order, seen in a reflex arc ? a. sensory receptor
sensory neuron
integration center in CNS
motor neuron
effector organ b. sensory neuron
sensory receptor
effector organ
integration center in CNS
sensory neuron c. effector organ
sensory receptor
sensory neuron
motor neuron
integration center in CNS d. motor neuron
sensory neuron
integration center in CNS
effector organ
sensory receptor e. integration center in CNS
sensory neuron
sensory receptor
motor neuron
effector organ
48. The function of the thalamus of the diencephalon is to: a. coordinate movement and balance b. act as a relay station for sensory information headed to the cerebral cortex c. regulate the temperature, water balance, and metabolism of the body d. produce cerebrospinal fluid e. maintain the body's "biological clock"
49. The most superficial of the meninges surrounding the brain is the: a. meningeal layer of the dura mater b. arachnoid mater c. periosteal layer of the dura mater d. pia mater e. cephalomater
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 7
50. The function of the incus (anvil), malleus (hammer), and stapes (stirrup) bones are to: a. Support and hold open the pharyngotympanic tube b. Amplify and transmit sound vibrations between the tympanic membrane and oval window c. Support the base of the tongue d. Provide anchoring points for the hypothalamus of the diencephalon e. Protect the delicate olfactory receptors
TRUE/FALSE Answer "a" if true and "b" if false.
51. The word "accommodation" in reference to the human eye refers to how well the lens fits within the pupillary gap .
52. The three kinds of papillae or tongue projections are known as filiform, fungiform, and circulaform.
53. The nerves of the parasympathetic system have ganglia relatively close to the CNS from which they arise.
54. Glucagon and aldosterone have exactly opposite effects in regulating blood glucose levels.
55. The risk of seeing "hemolytic disease" in a newborn baby is greatest if the mother is Rh positive and the father is Rh negative.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Match the hormone on the left with the organ or structure that produces it on the right. If the correct answer is more than one letter, like "abc", fill in "a" AND "b" AND "c" on your answer sheet for that question.
56. Calcitonin a. pineal body b. hypothalamus
57. Epinephrine
58. Insulin
59. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
60. Oxytocin c. anterior pituitary d. posterior pituitary e. thyroid ab. parathyroid ac. Sertoli cells of testes ad. adrenal medulla ae. adrenal cortex bc. pancreas
61. Testosterone bd. interstitial cells of testes be. ovaries cd. stomach ce. duodenum de. kidney
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 8
Use the heart diagram to the right to answer the following questions.
62. Which structure contains (in its walls) the pacemaker , or initiator of heart muscle excitation?
63. Which structure is the bicuspid (or mitral) valve?
64. Which vessel carries blood directly to the lungs?
----------------------------------------------------------------------
65. Memory B cells are important in which one of the following processes? a. the inflammatory reaction b. phagocytosis c. the secondary immune response of the humoral system d. histamine release e. the primary immune response of the humoral system
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Matching. Match the description on the left with the term on the right. If the answer has more than one letter, like "abc", fill in "a" AND "b" AND "c" on your answer sheet for that question.
66. The attraction of neutrophils and macrophages to an inflammatory
site through the broadcasting of chemical signals
67. The organ that filters and removes old erythrocytes from the a. clonal selection b. T cell "education" c. thymus d. antigen
.
blood stream.
68. The type of body defense against invading pathogens in which
circulating antibodies, made from stimulated B cells, destroy invaders. e. IgA ab. IgG ac. IgD ad. innate immunity ae. lymph node bc. spleen bd. fever be. chemotaxis cd. diapedesis ce. passive immunity de. humoral immunity
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
III IV
69. In the diagram of the immunoglobulin to the right, which regions interact directly with the antigen? a. I and VI b. II and V c. III and IV d. only region I II V e. only region V
I VI
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 9
70. In the diagram of the immunoglobulin to the in the previous question, which of the following choices indicates antibody structures composed of only constant regions? a. I and VI b. II and V c. III and IV d. only region I e. only region V
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
71. Air passing through the nasal cavity on the way to the lungs is warmed and moistened primarily in order to: a. increase the concentration of CO
2
in the inspired air b. facilitate mucous secretion by serous membranes c. reduce dehydration and cooling of the lungs d. trap and remove foreign particles from incoming air e. ensure that the air passes down the trachea and not the esophagus
72. The role of the structure indicated by arrow pointer "72" in the
diagram at the right is to: a. hold open the trachea so it won't collapse b. vibrate with the passage of air and create sounds c. provide for resonance in the skull during speech d. keep the tongue from being swallowed e. prevent food from entering the lungs
73. Why are the hyaline cartilaginous rings in the trachea shaped like the letter
"C", with openings towards the posterior surface of the neck? a. to make them lighter and decrease the weight load on tracheal tissue b. to effectively increase the diameter of the trachea, making air passage easier c. to allow for growth of the "rings" as the trachea enlarges during development d. to allow for passage of a large bolus through the posteriorly oriented esophagus e. to allow for extension of the neck that would be difficult if the "rings" were continuous
circles
74. The greater and lesser omenta ( omentum is singular) are responsible for a. supporting and holding the digestive organs and intestines together b. forming two successive layers of mucosa lining the intestinal tract c. providing for two different routes that blood can take from the intestines to the liver d. the major peristaltic movements in the stomach e. connecting the small intestine to the large intestine
75. Lack of sufficient fiber in the diet can cause _________, especially in old age. a. the formation of haustra b. an infected appendix c. the formation of diverticula d. gallstones e. kidney stones
72
22
.
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 10
76. A major source of carbohydrates in the diet are: a. fruits and vegetables b. meat and fish c. bread, cereals, and potatoes d. milk and dairy products e. fats and oils
77. High levels of sodium in the blood would cause: a. lower levels of LDLs b. a lower stroke volume in the heart c. higher blood pH d. higher blood pressure e. greater excretion of bicarbonate ions by the kidney
78. The major function of the peritubular capillaries of a nephron is: a. filtration b. transport of reabsorbed nutrients c. concentration of urine d. excretion of urea e. transport of produced urine
79. Kidneys regulate blood pH by the retention or passing of: a. urea b. carbon dioxide c. bicarbonate d. carbonic acid e. hydrochloric acid
80. The largest ridges or folds found on the intestinal lining are the: a. rugae b. microvilli c. plicae circulares d. villi e. haustra
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 11
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 12
SHORT ANSWER SHEETS
BIOS 160 Exam II Name
40 pts. total. Please write your answers in the blanks provided.
A. 2 pts. Name two structures that develop from the primary germ layer called mesoderm.
1.
2.
B. 2 pts. Describe the function of the placenta. right:
C. 2 pts. Name the part of the body indicated by arrow acd in the picture to the
D. 2 pts. Name the part of the body indicated by arrow cd in the picture to the right:
E. 2 pts. Which part of the body in the picture to the right is referred to as brachial ?
F. 2 pts. What is the function or role of the tissue type shown in the micrograph below?
G. 2pts. Name one muscle whose belly lies below the knee joint.
H. 2 pts. Name the muscle responsible for the squinting of the eyes.
I. 2 pts. Name the innermost serous membrane enclosing the heart:
(18)
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 13
J. 4 pts. Name the muscles indicated by the arrows and write their names in the blanks provided.
(the posterior head extension muscle, antagonist to the sternocleidomastoid)
(prime mover of plantar flexion, bipinnate
K. 6 pts. Fill in the blanks with the names of these structures.
(the extensions coming out)
(dark organelles found within)
(the gap)
L. 4 pts. Name the most specific type of cell in the human body which fits the following descriptions:
1) Dark blue-staining, kidney-shaped nucleus; agranular; later matures into a macrophage:
2) Dark blue nucleus, pale-blue cytoplasm; acts an intermediary between an antigen-
presenting macrophage and the activation of B and certain T cells:
M. 2 pts. Describe one of the mechanical barriers and one of the chemical barriers that are part of the nonspecific (innate) defense system.
Mechanical barrier:
Chemical barrier:
(12)
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 14
N. 4 pts. Explain what drives the interstitial (intercellular) fluid to move back into the venous capillaries in a capillary bed. Include an explanation for why the interstitial fluid won't flow into the arteriole capillaries.
O. 2 pts. The substance that prevents the walls of the lung alveoli from sticking together (through water adhesion) is known (generally) as .
(10)
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 15
First three letters of last name
BIOS 160 Final Exam pg. 16