Chapter 19
Using
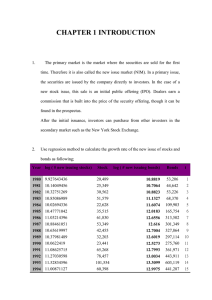
Securities
Markets for
Financing
and Investing
Opportunities
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter
Nineteen
LEARNING GOALS
1. Describe the role of securities markets.
2. Advantages & disadvantages of equity financing by
issuing stock, and the differences between common
and preferred stock.
3. Advantages & disadvantages of obtaining debt
financing by issuing bonds, and identify types and
features of bonds.
4. Explain investing in securities markets, setting &
balancing investment objectives, and managing risks.
5. Analyze investment opportunities stocks, bonds,
mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
6. Describe market indicators like the Dow Jones
Industrial Average, NASDAQ, and S&P 500.
19-2
The Function
of Securities
Markets
LG1
The BASICS of
SECURITIES MARKETS
• Securities markets are
financial marketplaces for
stocks and bonds and serve
two primary functions:
1. Assist businesses in finding
long-term funding to finance
capital needs.
2. Provide private investors a place
to buy and sell securities such
as stocks and bonds.
19-3
Securities
Regulations
and the SEC
LG2
The SECURITIES and
EXCHANGE COMMISSION
• Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) - The federal agency responsible for regulating the
various stock exchanges; created in 1934 through the
Securities and Exchange Act.
• Prospectus -- A condensed version of economic
and financial information that a company must file
with the SEC before issuing stock; the prospectus
must be sent to prospective investors.
• Initial Public Offering (IPO) -- The first offering of
a corporation’s stock, usually managed by an
investment banker.
19-4
Understanding
Stock Market
Indicators
LG9
KEY STOCK MARKET
INDICATORS
• Dow Jones Industrial Average -- The average
cost of 30 selected industrial stocks.
• Critics say the 30-company Dow is too small a
sample and suggest following the S&P 500.
• S&P 500 tracks the performance of 400
industrial, 40 financial, 40 public utility, and 20
transportation stocks.
19-5
Stock
Exchanges
STOCK EXCHANGES
LG2
• Stock Exchange -- An organization whose
members can buy and sell (exchange) securities on
behalf of companies and individual investors.
• Over-the-Counter (OTC) Markets -- Provides
smaller publically traded companies and investors
with a means to trade stocks not listed on the
national securities exchanges.
• NASDAQ -- A telecommunications network that links
dealers across the nation so they can exchange
securities electronically.
19-6
Stock
Exchanges
TOP STOCK EXCHANGES
LG2
• NYSE Euronext
• NASDAQ
• London Stock
Exchange
• Tokyo Stock Exchange
• Deutsche Borse
19-7
How Businesses
Raise Capital by
Selling Stock
LG3
LEARNING the
LANGUAGE of STOCKS
• Stocks -- Shares of
ownership in a company.
• Stock Certificate -Evidence of stock ownership.
• Dividends -- Part of a firm’s
profits that the firm may
distribute to stockholders as
either cash or additional
shares.
19-8
Advantages &
Disadvantages
of Issuing Stock
LG3
ADVANTAGES of
ISSUING STOCK
• Stockholders are owners of
a firm and never have to be
repaid their investment.
• There’s no legal obligation
to pay dividends.
• Issuing stock can improve a
firm’s balance sheet since
stock creates no debt.
19-9
Advantages &
Disadvantages
of Issuing Stock
LG3
DISADVANTAGES of
ISSUING STOCK
• Stockholders have the right to vote for a
company’s board of directors.
• Issuing new shares of stock can alter the control
of the firm.
• Dividends are paid from after-tax profits and are
not tax deductible.
• The need to keep stockholders happy can affect
management’s decisions.
19-10
Issuing Shares
of Common and
Preferred Stock
TWO CLASSES of STOCK
LG3
• Common Stock -- The most basic form; holders
have the right to vote for the board of directors and
share in the profits if dividends are approved.
• Preferred Stock -- Owners are given preference in
the payment of company dividends before common
stock dividends are distributed. Preferred stock can
also be:
- Callable
- Convertible
- Cumulative
19-11
Stock Splits
STOCK SPLITS
LG6
• Stock Splits -- An action by a company that gives
stockholders two or more shares of additional stock
for every share that they own.
• Splits cause no change in the firm’s ownership
structure and no change in the investment’s
value.
• Firms can never be forced to spilt their stocks.
19-12
Learning the
Language of
Bonds
LG4
LEARNING the
LANGUAGE of BONDS
• Bond -- A corporate certificate indicating that an
investor has lent money to a firm (or a government).
• The principal is the face
value of the bond.
• Interest -- The payment the
bond issuer makes to the
bondholders to compensate
them for the use of their
money.
19-13
Advantages &
Disadvantages
of Issuing Bonds
LG4
ADVANTAGES of
ISSUING BONDS
• Bondholders are creditors, not owners of the
firm and can’t vote on corporate matters.
• Bond interest is tax deductible.
• Bonds are a temporary source of funding and
are eventually repaid.
• Bonds can be repaid before the maturity date if
they contain a call provision.
19-14
Advantages &
Disadvantages
of Issuing Bonds
LG4
DISADVANTAGES of
ISSUING BONDS
• Bonds increase debt and can affect the
market’s perception of the firm.
• Paying interest on bonds is a legal obligation.
• If interest isn’t paid, bondholders can take legal
action.
• The face value of the bond must be repaid on
the maturity date.
19-15
Different
Classes of
Bonds
LG4
DIFFERENT CLASSES of
CORPORATE BONDS
• Corporations can issue two classes of bonds:
1. Unsecured bonds
(debenture bonds):
not backed by
specific collateral.
2. Secured bonds:
backed by
collateral (land or
equipment).
19-16
Investing in
Bonds
IMPORTANT BOND QUESTIONS
LG7
• First-time bond investors generally ask two
questions:
- Do you have to hold a bond until the maturity date?
- How can I assess the investment risk of a particular bond
issue?
• Junk Bonds -- Bonds that are high-risk and
have high default rates.
19-17
Advantages &
Disadvantages
of Issuing Bonds
BOND RATINGS
LG4
Rating
Moody’s
S&P
Fitch
Description
Aaa
AAA
AAA
Highest Quality
Aa
AA
AA
High Quality
A
A
A
Upper-Medium Grade
Baa
BBB
BBB
Medium Grade
Ba
BB
BB
Lower-Medium Grade
B
B
B
Speculative
Caa
CCC, CC
CCC
Poor
Ca
C
DDD
Highly Speculative
C
D
D
Lowest Grade
19-18
How
Investors
Buy
Securities
LG5
BUYING SECURITIES
• Stockbroker -- A registered
representative who works as
a market intermediary to buy
and sell securities for clients.
• Online trading services,
such as TD Ameritrade,
E*Trade, and Scottrade,
offer securities trading
services online to buy and
sell stocks and bonds.
19-19
Reducing Risk
by Diversifying
Investments
LG5
PRIMARY INVESTMENT SERVICES
CONSUMERS NEED
• Savings and investing advice
• Help with 401k plans
• Retirement planning
• Tax planning
• Estate planning
• Education expense planning
Source: Investment Company Institute.
19-20
Investing in
Mutual Funds &
ExchangeTraded Funds
LG8
PERCENTAGE of HOUSEHOLDS
OWNING MUTUAL FUNDS
Year
% of Households
1980
5%
1990
24%
2000
43%
2005
42%
2010
48%
Source: Investment Company Institute Factbook.
19-21
Understanding
Stock
Quotations
LG6
TOP FINANICIAL NEWS and
RESEARCH SITES
• Yahoo Finance
• DailyFinance
• MSN Money
• Forbes
• Dow Jones & Co.
19-22
Choosing the
Right
Investment
Strategy
FIVE INVESTMENT CRITERIA
LG5
1. Investment risk
2. Yield
3. Duration
4. Liquidity
5. Tax consequences
19-23
Choosing the
Right
Investment
Strategy
LG5
AVERAGE ANNUAL RETURN of
ASSET CLASSES (Since 1926)
Investment
Return
Small company stocks
12.2%
Large company stocks
9.5%
Corporate bonds
6.0%
Long-term government bonds
5.8%
Treasury bills
4.1%
The greater the risk, the greater the rewards
Source: Ibbotson Associates and Morningstar.
19-24
Understanding
Mutual Fund
Quotations
COMPARING INVESTMENTS
LG8
19-25
Reducing Risk
by Diversifying
Investments
DIVERSIFICATION
LG5
•
Diversification -- Buying several different types of
investments to spread the risk of investing.
•
If diversifying, an investor may put:
-
25% of his/her money into U.S. growth stocks
-
25% in government bonds
-
25% in dividend-paying stocks
-
10% in an international mutual fund
-
The rest in a savings account
19-26
Investing in
Mutual Funds &
ExchangeTraded Funds
LG8
INVESTING in MUTUAL FUNDS
and EXCHANGE-TRADED FUNDS
• Mutual Fund -- An organization the buys stocks
and bonds and then sells shares in those securities
to the public. The fund pools investors’ money and
buys stocks according to the fund’s purpose.
• Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) -- Collections of
stocks and bonds that are traded on securities
exchanges, but are traded more like individual stocks
than mutual funds.
19-27
Investing in
Mutual Funds &
ExchangeTraded Funds
VARIETIES of ETFs
LG8
ETF
Traditional
Description
Most common; include large U.S.
stocks, small U.S. stocks,
international stocks, or investmentgrade bonds.
Niche
Focus on an individual sector like
healthcare, high-yield bonds, or a
single country.
Exotic
Invest in unusual, more volatile
sectors such as commodities like
gold and concepts like clean
technology.
Source: Schwab and E*Trade.
19-28
Choosing the
Right
Investment
Strategy
LG5
INVESTING 101
Things to Do Before Making Your First Investment
• Take an investing class.
• Join an investment club, or reputable web site
like Motley Fool, not Motley Crue.
• Attend a conference (be very careful in selecting).
• Head to the library and pick up these books:
- The Big Short
- The Intelligent Investor
- The Myth of the Rational Market
Source: Money, November 2010.
19-29
Investing in
Stocks
SELECTING STOCKS
LG6
• Capital Gains -- The positive difference between
the price at which you bought a stock and what you
sell it for.
• Investors can also choose stocks according to
their strategy:
-
Blue-chip stocks
Growth stocks
Income stocks
Penny stocks
19-30
The SUN NEVER SETS on
STOCK OPPORTUNITIES
(Reaching Beyond Our Borders)
• Suggestions for building your financial future:
- Invest in global companies you know and that have
solid performance records.
- Invest in global stocks listed on U.S. exchanges.
- Contact U.S. brokers about American Depository
Receipts (ADRs).
- Invest in global mutual funds that focus on specific
countries or regions.
- Use extreme caution if investing in unstable
countries!
19-31
Riding the
Market’s Roller
Coaster
MARKET TURMOIL
LG9
• The stock market has its shares of ups and
downs:
- October 29, 1929 - Black
Tuesday; the market lost 13%
of its value.
- October 19, 1987 - The market
suffered its worst one-day drop
when it lost 22% of its value.
- October 27, 1997 - Fears of an
economic crisis in Asia cause
widespread panic and losses.
19-32
Investing in
Stocks
LG6
PERCEPTIONS of the MARKET
“Animal Spirits”
• Bulls: Investors who
believe stock prices
are going to rise.
• Bears: Investors who
expect stock prices to
decline.
• Bull markets are all alike, but every bear
market is bad in its own way.
• Stock market is usually the messenger of
the problem, but not always.
• Lack of confidence
19-33
Investing in
Stocks
LG6
BEAR MARKET DECLINES
in the S&P 500
Time Period
% Drop in Prices
2007-2009
52.5%
2000-2002
51%
1973-1974
48.2%
1968-1970
36.1%
1987-1988
33.5%
Source: Stock Traders Almanac 2011.
19-34
Riding the
Market’s Roller
Coaster
TURMOIL in the 2000s
LG9
• The market collapsed into a deep decline in
2000-2002 when the dot-com bubble burst.
- Investors lost $7 trillion in market value.
• Starting in 2008, the collapse of the real estate
market sent financial markets into panic.
- The U.S. government made significant investments in
private banks and offered a large stimulus package to reenergize the economy.
19-35
Riding the
Market’s Roller
Coaster
LG9
The UPS and DOWNS
of the MARKET
• Program Trading -- Giving instructions to
computers to automatically sell if the price of a stock
dips to a certain point to avoid potential losses.
‾ High Frequency Trading increases potential for
greater volatility.
• Analysts believe program trading caused the
turmoil in 1987.
• The exchanges created mechanisms to restrict
program trading.
19-36
Buying Stock
on Margin
BUYING STOCK on MARGIN
LG6
• Buying Stock on Margin -- Borrowing some of the
stock’s purchase cost from the brokerage firm.
• Margin is the portion of the
stock’s purchase price that
the investor must pay with
their own money.
• If a broker issues a margin
call, the investor has to come
up with money to cover
losses.
19-37
Riding the
Market’s Roller
Coaster LG9
WHO’S at FAULT for the
ECONOMIC CRISIS?
• Wall Street –
• Issued exotic securities;
− Securitization (Selling mortgages or contracts for upfront payment
(lead to bankruptcies of Enron ‘01 & Continental Illinois ‘84)
− Bond rating agencies gave AAA rating to MBS
• Paid excessive compensation based on bonuses
• Investment banks got the SEC to relax capital
requirements.
• Main Street –
•
•
•
•
Americans borrowed beyond their means;
Banks grew fast by giving favorable loans to homebuilders
Homeowners took out equity loans
ARM mortgage rates fueled Housing market bubble
Source: Fortune Magazine, www.fortune.com, accessed July 2011.
19-38
Riding the
Market’s Roller
Coaster
LG9
WHO’S at FAULT for the
ECONOMIC CRISIS?
• Washington
• Gramm-Leach-Billey Act allowed commercial & investment
banks to combined
• Fed kept interest rates low in a bid to boost economy
• Community Reinvestment Act required lending to people
with bad credit.
• FNMA (Fannie Mae) & FHLMC (Freddie Mac) expanded
significantly, buying ~ 90% of home mortgages
Source: Fortune Magazine, www.fortune.com, accessed July 2011.
19-39
The Role of
Investment
Bankers
LG1
INVESTMENT BANKERS
and INSTITUTIONAL INVESTORS
• Investment Bankers -- Specialists who assist in
the issue and sale of new securities.
• Institutional Investors -Large organizations such as
pension funds or mutual
funds that invest their own
funds or the funds of others.
19-
CLEANING UP the STREET
(Legal Briefcase)
• Congress passed the Dodd-Frank Financial Reform
and Consumer Protection Act into law on July 21,
2010.
• Gives the government power to seize and shutter
large financial institutions on the verge of collapse in
an effort to prevent further bailouts.
• Formed an independent consumer protection agency
housed within the Federal Reserve, protecting
borrowers against a host of financial abuses ranging
from payday loans to mortgages and credit cards.
19-41
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• What’s the primary purpose of a securities
exchange?
• What does NASDAQ stand for? How does this
exchange work?
19-42
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• Name at least two advantages and
disadvantages of a company’s issuing stock as a
form of equity financing.
• What are the major differences between common
stock and preferred stock?
19-43
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• Why are bonds considered a form of debt
financing?
• What does it mean if a firm issues a 9%
debenture bond due in 2025?
• Explain the difference between an unsecured and
secured bond.
• Why are convertible bonds attractive to
investors?
19-44
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• What is the key advantage of investing through
online brokers? What is the key disadvantage?
• What is the primary purpose of diversifying
investments?
19-45
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• What is a stock split? Why do companies
sometimes split their stock?
• What does buying stock on margin mean?
• What are mutual funds and ETFs?
• What is the key benefit to investors in investing in
a mutual fund or ETF?
19-46
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• What does the Dow Jones Industrial Average
measure? Why is it important?
• Why do the 30 companies comprising the Dow
change periodically?
• Explain program trading and the problems it can
create.
19-47