International Perspectives
advertisement

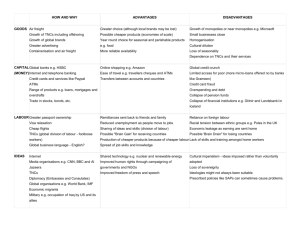
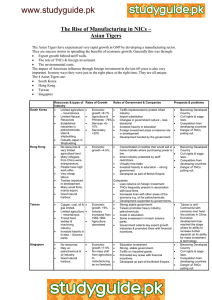
International Perspectives Historical Colonial Past • • • • Changing Land ownership Emphasis on Cash Crops Decline of local small scale industry Introduction of wage work International Perspectives Historical Colonial Past • Shift from rural to urban • Localized to capitalist system of production • Global connections in food production International Perspectives Contemporary • Focus on industrialization – Western development model • Industrial focus on Agriculture • Increased use of chemicals Agriculture • Dependency on few export crops International Perspectives Contemporary • Unequal power relations between countries of N. & S. • Heavy debt burden • Structural Adjustmentment Policy • WTO Trade rules dumping of subsidized foods by US & EU IMF – International Monetary Fund • Established after WWII. • A multilateral organization consisting of 184 member (countries). • A member country's voting power is dependent on its contribution. • U.S. has the most voting power. IMF – International Monetary Fund Initial Role of IMF • Stabilize exchange rates • Assist nations with balance of payments IMF – International Monetary Fund Current Role (Bail Outs) • • • Mexico Russia Argentina IMF – International Monetary Fund • IMF asks borrower governments to: – Assume responsibility for repaying debt of private companies both domestic and foreign • Increased the burden of debt Austerity Programs of SAPs – Structural Adjustment Policy • Increase Exports • Devalue currency, hoping for a trade surplus • Exporting more meant falling prices. • Privatize their state-run businesses • Government change laws to allow TNCS to purchase – Devaluation had made these cheap – Remove Subsidies Impact of SAPS • • • • Economic Decline. Increased Poverty. Environmental Destruction (deforestation). Women and Children’s Health (education suffered). • Debts Increased. • Paid more than received. – Mexico paid $100 billion in debt service between 1982 - 1988 Impact of SAPS • Debt Relief – Uganda received partial debt relief in exchange of severe austerity programs – U.S. Government has reduced/paid the debt Gap Between Rich and Poor Countries Have Widened • Falling commodity prices • Neoliberal economic policies supposed to stimulate growth, did not. – Made it easier for purchasing foreign assets – Capital flight • Most of global investment flow is to the countries of the Northern Hemisphere. – Latin American investors invested $300 billion in the North. Globalization of Agriculture and TNCs • Increase in long distance trade of fresh foods • The affluent class of the developed countries consume fresh produce which are cut and packaged • These fresh produce are sold at a high price which increases the profit margins of the supermarkets • Globalization of Agriculture • Developed countries agro-businesses invest capital in developing countries to take advantage of lower costs of production • Regional Trading blocs facilitates and increases fresh food markets • Globalization of diets more evident in the diets of the affluent groups in both developed and developing countries Role of TNCs in Global Food System • TNCs play roles in food production, processing, trading of foods • They operate in many countries and often engage in business with other TNCs • Cargill, largest grain trading firm has joint venture with Nippon Meat Packers to produce and process broiler chickens in Thailand • TNCs and the Global Food System • Globally dominant TNCs are mainly based in USA, EU and Japan • In deciding where to base their production and processing sites, they get favorable terms by playing different locations against each other • TNCs have joint ventures to get access to the market TNCs and Industrial Agriculture • TNCs has transformed the agricultural production • The connection between agricultural and industrial sector intensified • Agricultural inputs such as chemical fertilizer, pesticides, herbicides, farm equipments are produced in the industrial sector • Diffusion of industrial agriculture to developing countries Summary • Factors at international level Influencing access to food Unequal power relations beginning with colonialism Capitalist system of production reinforces the unequal power relations between developed and developing countries Policies of IMF, World bank and power of TNCs • Traditional methods of farming are replaced by industrial agriculture • TNCs are playing major role in the spread of industrial agriculture which has negative effects on the environment • Global influences in the diets of people are found everywhere but it is more evident amongst the privileged • For most people in the developing countries diet remains local but they do not have adequate resources to meet their needs.