Chapter 6: The States of Matter Spencer L. Seager Michael R. Slabaugh
advertisement

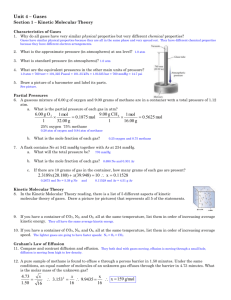
Spencer L. Seager Michael R. Slabaugh www.cengage.com/chemistry/seager Chapter 6: The States of Matter Jennifer P. Harris Chapter 6 objectives When you have completed your study of this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Demonstrate an understanding of the kinetic molecular theory of matter. (Section 6.2, 6.3, and 6.4; Exercise 6.8) 2. Use the kinetic molecular theory to explain and compare the properties of matter in different states. (Sections 6.5; Exercises 6.12 and 6.16) 3. Do calculations to convert pressure and temperature values into various units. (Section 6.6; Exercises 6.20 and 6.22) (atm and torr/mm only for pressure conversions) 4. Do calculations based on Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, and the combined gas law. (Section 6.7; Exercises 6.24, 6.32, and 6.34) 5. Do calculations based on the ideal gas law. (Section 6.8; Exercise 6.46) 6. No calculations based on Dalton’s law. (Section 6.9; Exercise 6.58) [qualitative only] 7. No calculations based on Graham’s law. (Section 6.10; Exercise 6.60) [qualitative only] 8. Classify changes of state as exothermic or endothermic. (Section 6.11; Exercise 6.64) 9. Demonstrate an understanding of the concepts of vapor pressure and evaporation. (Section 6.12; Exercise 6.68) 10. Demonstrate an understanding of the process of boiling and the concept of boiling point. (Section 6.13; Exercise 6.70) 11. Demonstrate an understanding of the processes of sublimation and melting. (Section 6.14; Exercise 6.74) 12. No calculations based on energy changes that accompany heating, cooling, or changing the state of a substance. (Section 6.15; Exercises 6.76 and 6.78) [qualitative only] PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER • All three states of matter have certain properties that help distinguish between the states. Four of these properties are density, shape, compressibility, and thermal expansion. CHARACTERISTIC PROPERTIES OF THE THREE STATES OF MATTER KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER • The kinetic molecular theory of matter is a useful tool for explaining the observed properties of matter in the three different states of solid, liquid and gas. • Postulate 1: Matter is made up of tiny particles called molecules. • Postulate 2: The particles of matter are in constant motion and therefore possess kinetic energy. • Postulate 3: The particles possess potential energy as a result of repelling or attracting each other. • Postulate 4: The average particle speed increases as the temperature increases. • Postulate 5: The particles transfer energy from one to another during collisions in which no net energy is lost from the system. KINETIC ENERGY • Kinetic energy is the energy a particle has as a result of being in motion. • Kinetic energy (KE) is calculated using the equation: mv KE 2 2 In this equation, m is the mass of a particle and v is its velocity. POTENTIAL ENERGY & FORCES • POTENTIAL ENERGY • Potential energy is the energy a particle has as a result of being attracted to or repelled by other particles. THE SOLID STATE • The solid state is characterized by a high density, a definite shape that is independent of its container, a small compressibility, and a very small thermal expansion. THE LIQUID STATE • The liquid state is characterized by a high density, an indefinite shape that depends on the shape of its container, a small compressibility, and a small thermal expansion. THE GASEOUS STATE • The gaseous state is characterized by a low density, an indefinite shape that depends on the shape of its container, a large compressibility, and a moderate thermal expansion. A KINETIC MOLECULAR VIEW OF SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, AND GASES THE GAS LAWS • The gas laws are mathematical equations that describe the behavior of gases as they are mixed, subjected to pressure or temperature changes, or allowed to diffuse. • The pressure exerted on or by a gas sample and the temperature of the sample are important quantities in gas law calculations. PRESSURE • PRESSURE • Pressure is defined as a force pushing on a unit area of surface on which the force acts. • In gas law calculations, pressure is often expressed in units related to the measurement of atmospheric pressure. • STANDARD ATMOSPHERE OF PRESSURE • A pressure of one standard atmosphere is the pressure needed to support a 760-mm (76.0-cm) column of mercury in a barometer. • ONE TORR OF PRESSURE • One torr of pressure is the pressure needed to support a 1mm column of mercury in a barometer. A pressure of 760 torr is equal to one standard atmosphere. OFTEN-USED UNITS OF PRESSURE TEMPERATURE • The temperature of a gas sample is a measurement of the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules in the sample. • The Kelvin temperature scale is used in all gas law calculations. • ABSOLUTE ZERO • A temperature of 0 K is called absolute zero. It is the temperature at which gas molecules have no kinetic energy because all motion stops. On the Celsius scale, absolute zero is equal to -273°C. PRESSURE, TEMPERATURE, & VOLUME RELATIONSHIPS FOR GASES • Mathematical equations relating the pressure, temperature, and volume of gases are called gas laws. • All of the gas laws are named after the scientists who first discovered them. BOYLE'S LAW • Boyle's law is a gas law that describes the pressure and volume behavior of a gas sample that is maintained at constant temperature. • Mathematically, Boyle's law is written as follows: k P v or PV k In these equations, P is the pressure, V is the volume, and k is an experimentally determined constant. CHARLES'S LAW • Charles's law is a gas law that describes the temperature and volume behavior of a gas sample that is maintained at constant pressure. • Mathematically, Charles's law is written as follows: V k' T or V k' T In these equations, V is the volume, T is the temperature in Kelvin, and k' is an experimentally determined constant. THE COMBINED GAS LAW • Boyle's law and Charles's law can be combined to give the combined gas law that is written mathematically as follows: PV k' ' T In this equation, P, V and T have the same meaning as before and k'' is another experimentally determined constant. • The combined gas law can be expressed in another useful form where the subscript i refers to an initial set of conditions and the subscript f refers to a final set of conditions for the same gas sample. Pi Vi Pf Vf Ti Tf GAS LAW EXAMPLE • A gas sample has a volume of 2.50 liters when it is at a temperature of 30.0°C and a pressure of 1.80 atm. What volume in liters will the sample have if the pressure is increased to 3.00 atm, and the temperature is increased to 100°C? • Solution: The problem can be solved: • using the combined gas law. • by identifying the initial and final conditions. • making sure all like quantities are in the same units. • expressing the temperatures in Kelvin. • Thus, we see that the combined gas law must be solved for Vf. GAS LAW EXAMPLE (continued) • The result is: Pi Vi Tf Vf TiPf • Substitution of appropriate values gives: Vf 1.80 atm 2.50 liters 373 K 1.85 liters 303 K 3.00 atm AVOGADRO’S LAW • Avogadro’s law states that equal volumes of gases measured at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules. • STANDARD CONDITIONS • STP = standard temperature and pressure • 0°C (273 K) • 1.00 atm • MOLAR VOLUME AT STP • 1 mole of any gas molecules has a volume of 22.4 L at STP. THE IDEAL GAS LAW • The ideal gas law allows calculations to be done in which the amount of gas varies as well as the temperature, pressure, and volume. • Mathematically, the ideal gas law is written as follows: PV= nRT In this equation, P is the pressure of a gas sample, V is the sample volume, T is the sample temperature in Kelvin, n is the number of moles of gas in the sample, and R is a constant called the universal gas constant. A commonlyused value for R is: L atm 0.0821 mol K • In calculations, the quantities V, P, and T must be expressed in units that match the units of R, liters (L), atm, and Kelvin, respectively. IDEAL GAS LAW CALCULATIONS • Example 1: A 2.50 mole sample of gas is confined in a 6.17 liter tank at a temperature of 28.0°C. What is the pressure of the gas in atm? • Solution: The ideal gas equation is first solved for P: nRT P V The known quantities are then substituted into the equation, making sure the units cancel properly to give units of atm in the answer: L atm 2.50 mol 0.0821 301K mol K P 10.0 atm 6.17 L IDEAL GAS LAW CALCULATIONS (continued) • Example 2: A 4.00 g sample of gas is found to exert a pressure of 1.71 atm when confined in a 3.60 L container at a temperature of 27°C. What is the molecular weight of the gas in grams per mole? • Solution: • The molecular weight is equal to the sample mass in grams divided by the number of moles in the sample. • Because the sample mass is known, the molecular weight can be determined by calculating the number of moles in the sample. • The ideal gas equation is first solved for n: PV n RT • The known quantities are then substituted into the equation, making sure units cancel properly to give the units of mol for the answer. IDEAL GAS LAW CALCULATIONS (continued) 1.71 atm 3.60 L n 0.250 mol L atm 0.0821 300 K mol K • The units are seen to cancel properly to give the number of moles as the answer. The molecular weight is calculated by dividing the number of grams in the sample by the number of moles in the sample: 4.00 g g mw 16.0 0.250 mol mol IDEAL GASES vs. REAL GASES • No ideal gases actually exist. • If they did exist, they would behave exactly as predicted by the gas laws at all temperatures and pressures. • Real gases deviate from the behavior predicted by the gas laws, but under normally encountered temperatures and pressures, the deviations are small. • Consequently, the gas laws can be used for real gases. • Interparticle attractions make gases behave less ideally. • The gas laws work best for gases made up of single atoms or nonpolar molecules. DALTON'S LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURES • According to Dalton's law, the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture. Ptotal Pindiv idual gases Zn(s) + NH4NO3(s) → N2(g) + 2 H2O(g) + ZnO(s) PARTIAL PRESSURE • The partial pressure of an individual gas of a mixture is the pressure the gas would exert if it were alone in the container at the same temperature as the mixture as shown in the following illustration: GRAHAM'S LAW • Graham's law is a mathematical expression that relates the rates of effusion or diffusion of two gases to the masses of the molecules of the two gases. Qualitatively it states that smaller gasses have a faster velocity at any given temperature. • EFFUSION • Effusion is a process in which a gas escapes from a container through a small hole in the container. • DIFFUSION • Diffusion is a process that causes gases to spontaneously mix when they are brought together. CHANGES IN STATE • Changes in state are often accomplished by adding or removing heat from a substance. • Changes in state caused by adding heat to a substance are classified as endothermic (heat in) processes. • Changes in state caused by removing heat are classified as exothermic (heat out) processes. ENDOTHERMIC PROCESSES • EVAPORATION OR VAPORIZATION • Evaporation or vaporization is an endothermic process in which a liquid is changed to a gas. • SUBLIMATION • Sublimation is an endothermic process in which a solid is changed to a gas without first melting to a liquid. • MELTING OR FUSION • Melting or fusion is an endothermic process in which a solid is changed to a liquid. EXOTHERMIC PROCESSES • LIQUEFACTION OR CONDENSATION • Liquefaction or condensation is an exothermic process in which a gas is changed to a liquid. • DEPOSITION OR CONDENSATION • Deposition or condensation is an exothermic process in which a gas is changed into a solid. • FREEZING OR CRYSTALLIZATION • Freezing or crystallization is an exothermic process in which a liquid is changed into a solid. VAPOR PRESSURE • Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor that is in equilibrium with its liquid. Also described as the “tendency to evaporate. BOILING POINT • The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the prevailing atmospheric pressure. • The normal or standard boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to 1 standard atmosphere (760 torr). VARIATION OF WATER BOILING POINT WITH ELEVATION SUBLIMATION AND MELTING • Sublimation is the endothermic process in which a solid is changed directly to a gas without first becoming a liquid. ENERGY AND THE STATES OF MATTER • At 760 torr, constant heat is applied until a 1 g sample of ice at -20°C is converted to steam at 120°C. • This is a five step process: (AB) heating ice to melting point, (BC) melting ice, (CD) heating liquid to boiling point, (DE) boiling water, and (EF) heating steam. SPECIFIC HEAT • The specific heat of a substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of exactly 1 g of a substance exactly 1°C. • For water, in calorie units, this value is 1 cal/gO HEATS OF FUSION & VAPORIZATION • HEAT OF FUSION • The heat of fusion of a substance is the amount of heat required to melt exactly 1g of a solid substance at constant temperature. For water, in calorie units, this value is 80 cal/g. • HEAT OF VAPORIZATION • The heat of vaporization of a substance is the amount of heat required to vaporize exactly 1g of a liquid substance at constant temperature. For water, in calorie units, this value is 540 cal/g. • HEAT OF SUBLIMATION • What would this value be for water? • Compare these values to the amount of energy required to raise 1 g of liquid water from 0oC to 100oC.