***Please note that this review sheet is by no means... intended as a guidleline. You will be responsible for...

***Please note that this review sheet is by no means comprehensive, but instead is intended as a guidleline. You will be responsible for any material that was viewed in class, presented in lectures, or provided in your text.
Final exam review sheet
RDAs: EAR, AI, UL, DRI; AMDR
Major/minor minerals, nutrients, energy obtained from each
Diseases: marasmus, kwashiorkor, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, phenylketonuria, pellagra, beriberi, rickets, celiac disease, GERD, irritable bowel, diabetes I and II, lactose intolerance, macrocytic anemia, anorexia, bulimia, osteoporosis
Proteins, carbohydrates and lipids
Be able to distinguish the structures
Understand how each is digested (and enzymes involved)
General functions of each in the body
AMDRs, RDAs
Blood sugar regulation
Terms: transcription, translation, location in cell of each
Protein structure and denaturation
“good” vs “bad” cholesterol: LDLs, VLDLs, HDLs
Digestion, Absorption, Elimination
Know anatomy (eg, sphincters, organs)
Hormones involved, organs that produce them
Metabolism
Terms: anabolism, catabolism
Glucose metabolism: glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle, electron transport chain
Important molecules: glucose, pyruvate, lactic acid, acetyl coA, citrate, oxaloacetate, NAD+ and FAD+ (in both reduced/oxidized forms), ATP
Reactions: phosphorylation, oxidation, reduction, condensation (dehydration), hydrolysis
Fatty acid oxidation, carnitine, acetyl coA
Vitamins involved in glucose/fat metabolism
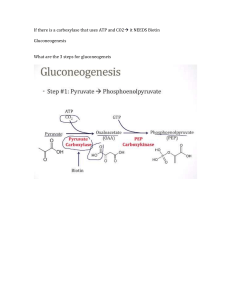
Gluconeogenesis
Nitrogen excretion after deamination
Ketogenesis, ketoacidosis
Energy production (ATPs), electron carriers
Vitamins/Minerals
Water soluble vs.
Fat soluble vitamins, major/trace minerals
General function of each
Deficiencies
Functions of fluids in the body
Sweating
Intra- vs. Extra- cellular fluids (and associated electrolytes)
Function of electrolytes
Antioxidants: which vitamins/mineral(s); generally how antioxidants work
Bone: cells, PTH, vitamin D, calcitriol, osteoporosis
Disordered Eating vs. eating disorders
Traits associated with each, physiological repercussions of each
Appetite vs. hunger
Body composition, BMI, total energy expenditure, BMR, thrifty gene theory, set-point theory, leptin, ghrelin, peptide YY, obesity, gastric bypass
Physical activity
Understand how the body utilizes energy reserves
Governmental recommendations for physical fitness
Overload principle, FIT, BMR, BMI
Pregnancy/Lactation
Development of baby from conception
fetus
Dietary needs of newborn
Roles of Oxytocin, prolactin, estrogen and progesterone
Dietary needs of lactating mother
Toddlers, preschoolers, school-aged kids, adolescents, older adults
Dietary needs (macro- and micronutrient trends), childhood overweight vs. obesity, epiphyseal plates and adolescent growth
Alcohol metabolism
Drink equivalents, proof, Alcohol dehydrogenase, aldehyde dehydrogenase
(ethanol
acetylaldehyde
acetic acid
acetyl coA), MEOS pathway, effects of alcohol on the body (brain, liver, pancreas, upper GI), hangover
Food safety
Food additives (and examples of), food preservatives (and examples of), pesticides, governmental agencies regulation/role of each, food infections vs. intoxications (and examples provided in lecture for each), food allergies, prevention of food borne illness, prevention of food spoilage, persistent organic pollutants, rBGH, governmental definitions of organic, GMOs, Modern Meat
Good luck!