Using Securities Markets for Financing

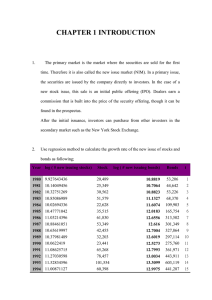
Chapter 19
Using
Securities
Markets for
Financing and Investing
Opportunities
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter
Nineteen
LEARNING GOALS
1. Describe the role of securities markets and of investment bankers.
2. Identify the stock exchanges where securities are traded.
3. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of equity financing by issuing stock, and detail the differences between common and preferred stock.
4. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of obtaining debt financing by issuing bonds, and identify the classes and features of bonds.
19-2
Chapter
Nineteen
LEARNING GOALS
5. Explain how to invest in securities markets and set investment objectives such as long-term growth, income, cash, and protection from inflation.
6. Analyze the opportunities stocks offer as investments.
7. Analyze the opportunities bonds offer as investments.
8. Explain the investment opportunities in mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
9. Describe how indicators like the Dow Jones Industrial
Average affect the market.
19-3
Profile
MARIA BARTIROMO
CNBC
• Emmy Award-winning journalist, Bartiromo’s analysis of day-to-day Wall Street has made her the face of investing.
• Started as an overnight producer for CNN before moving to CNBC .
• She ’ s lead anchor at two of
CNBC ’ s biggest shows, has written several books and numerous columns.
19-4
Chapter
Nineteen
NAME that COMPANY
When the price of their stock rises to a certain level, many companies will split the stock in order to make the stock appear more affordable. However, this company run by
America ’ s most successful investor has never split its stock even when the price of the company ’ s stock reached $150,000 a share
(that ’ s right $150,000 for one share.)
Name that company!
19-5
The Function of Securities
Markets
LG1
The BASICS of
SECURITIES MARKETS
• Securities markets are financial marketplaces for stocks and bonds and serve two primary functions:
1. Assist businesses in finding long-term funding to finance capital needs.
2. Provide private investors a place to buy and sell securities such as stocks and bonds.
19-6
The Function of Securities
Markets
LG1
TYPES of
SECURITIES MARKETS
• Securities markets are divided into primary and secondary markets:
Primary markets handle the sale of new securities.
Secondary markets handle the trading of securities between investors with the proceeds of the sale going to the seller.
• Initial Public Offering (IPO) -The first offering of a corporation’s stock.
19-7
The Role of
Investment
Bankers
LG1
INVESTMENT BANKERS and INSTITUTIONAL INVESTORS
• Investment Bankers -Specialists who assist in the issue and sale of new securities.
• Institutional Investors --
Large organizations such as pension funds or mutual funds that invest their own funds or the funds of others.
19-8
Stock
Exchanges
LG2
STOCK EXCHANGES
• Stock Exchange -An organization whose members can buy and sell (exchange) securities on behalf of companies and individual investors.
• Over-the-Counter (OTC) Market -Provides companies and investors with a means to trade stocks not listed on the national securities exchanges.
• NASDAQ -A telecommunications network that links dealers across the nation so they can exchange securities electronically.
19-9
Stock
Exchanges
LG2
TOP STOCK EXCHANGES
• NYSE Euronext
• NASDAQ
• London Stock
Exchange
• Tokyo Stock Exchange
• Deutsche Borse
19-10
A PLACE for
SMALL COMPANIES to CALL HOME
(Spotlight on Small Business)
• Since the recent financial crisis, small businesses have found it difficult to secure financing from banks.
• David Weild wants a new stock exchange where small companies can raise needed capital.
• Though this is a new idea in the U.S., China established ChiNext which is designed for startup companies.
19-11
Securities
Regulations and the SEC
LG2
The SECURITIES and
EXCHANGE COMMISSION
• Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) -
The federal agency responsible for regulating the various stock exchanges; created in 1934 through the
Securities and Exchange Act.
• Prospectus -A condensed version of economic and financial information that a company must file with the SEC before issuing stock; the prospectus must be sent to prospective investors.
19-12
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• What ’ s the primary purpose of a securities exchange?
• What does NASDAQ stand for? How does this exchange work?
19-13
How Businesses
Raise Capital by
Selling Stock
LG3
LEARNING the
LANGUAGE of STOCKS
• Stocks -Shares of ownership in a company.
• Stock Certificate --
Evidence of stock ownership.
• Dividends -Part of a firm ’ s profits that the firm may distribute to stockholders as either cash or additional shares.
19-14
Advantages &
Disadvantages of Issuing Stock
LG3
ADVANTAGES of
ISSUING STOCK
• Stockholders are owners of a firm and never have to be repaid their investment.
• There ’ s no legal obligation to pay dividends.
• Issuing stock can improve a firm ’ s balance sheet since stock creates no debt.
19-15
Advantages &
Disadvantages of Issuing Stock
LG3
DISADVANTAGES of
ISSUING STOCK
• Stockholders have the right to vote for a company ’ s board of directors.
• Issuing new shares of stock can alter the control of the firm.
• Dividends are paid from after-tax profits and are not tax deductible.
• The need to keep stockholders happy can affect management ’ s decisions.
19-16
Issuing Shares of Common and
Preferred Stock
LG3
TWO CLASSES of STOCK
• Common Stock -The most basic form; holders have the right to vote for the board of directors and share in the profits if dividends are approved.
• Preferred Stock -Owners are given preference in the payment of company dividends before common stock dividends are distributed. Preferred stock can also be:
Callable
Convertible
Cumulative
19-17
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• Name at least two advantages and disadvantages of a company’s issuing stock as a form of equity financing.
• What are the major differences between common stock and preferred stock?
19-18
Learning the
Language of
Bonds
LG4
LEARNING the
LANGUAGE of BONDS
• Bond -A corporate certificate indicating that an investor has lent money to a firm (or a government).
• The principal is the face value of the bond.
• Interest -The payment the bond issuer makes to the bondholders to compensate them for the use of their money.
19-19
Advantages &
Disadvantages of Issuing Bonds
LG4
ADVANTAGES of
ISSUING BONDS
• Bondholders are creditors, not owners of the firm and can ’ t vote on corporate matters.
• Bond interest is tax deductible.
• Bonds are a temporary source of funding and are eventually repaid.
• Bonds can be repaid before the maturity date if they contain a call provision.
19-20
Advantages &
Disadvantages of Issuing Bonds
LG4
DISADVANTAGES of
ISSUING BONDS
• Bonds increase debt and can affect the market ’ s perception of the firm.
• Paying interest on bonds is a legal obligation.
• If interest isn ’ t paid, bondholders can take legal action.
• The face value of the bond must be repaid on the maturity date.
19-21
Advantages &
Disadvantages of Issuing Bonds
LG4
BOND RATINGS
Moody ’ s
Aaa
Aa
A
Baa
Ba
B
Caa
Ca
C
Rating
S & P
AAA
AA
A
BBB
BB
B
CCC, CC
C
D
Fitch
AAA
AA
A
BBB
BB
B
CCC
DDD
D
Description
Highest Quality
High Quality
Upper-Medium Grade
Medium Grade
Lower-Medium Grade
Speculative
Poor
Highly Speculative
Lowest Grade
19-22
Different
Classes of
Bonds
LG4
DIFFERENT CLASSES of
CORPORATE BONDS
• Corporations can issue two classes of bonds:
1. Unsecured bonds
(debenture bonds): not backed by specific collateral.
2. Secured bonds : backed by collateral (land or equipment).
19-23
Special Bond
Features
LG4
SPECIAL FEATURES in
BOND ISSUES
• Sinking Fund -Reserve account set up to ensure that enough money will be available to repay bondholders on the maturity date.
• Callable bonds permit bond issuers to pay off the principal before the maturity date.
• Convertible bonds allow bondholders to convert their bonds into shares of common stock.
19-24
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• Why are bonds considered a form of debt financing?
• What does it mean if a firm issues a 9% debenture bond due in 2025?
• Explain the difference between an unsecured and secured bond.
• Why are convertible bonds attractive to investors?
19-25
How
Investors
Buy
BUYING SECURITIES
• Stockbroker -A registered representative who works as a market intermediary to buy and sell securities for clients.
• Online trading services, such as TD Ameritrade ,
E*Trade , and Scottrade , offer securities trading services online to buy and sell stocks and bonds.
19-26
MONEY GOING UP in SMOKE
(Making Ethical Decisions)
• You recently received news that your Uncle Alex passed away after a long battle with lung cancer caused by smoking. He left you $25,000 in his will, saying you were his favorite nephew.
• Your friend Jack recommends that you buy stock in a well-known multinational firm that ’ s primary product is tobacco.
• Will you invest your inheritance in a company that markets tobacco?
19-27
Choosing the
Right
Investment
Strategy
LG5
FIVE INVESTMENT CRITERIA
1. Investment risk
2. Yield
3. Duration
4. Liquidity
5. Tax consequences
19-28
Choosing the
Right
Investment
Strategy
LG5
INVESTING 101
Things to Do Before Making Your First Investment
• Take an investing class.
• Attend a conference.
• Head to the library and pick up these books:
The Big Short
The Intelligent Investor
The Myth of the Rational Market
Source: Money, November 2010.
19-29
Choosing the
Right
Investment
Strategy
LG5
AVERAGE ANNUAL RETURN of
ASSET CLASSES (Since 1926)
Investment
Small company stocks
Large company stocks
Corporate bonds
Long-term government bonds
Treasury bills
Return
12.2%
9.5%
6.0%
5.8%
4.1%
Source: Ibbotson Associates and Morningstar.
19-30
Reducing Risk by Diversifying
Investments
LG5
DIVERSIFICATION
• Diversification -Buying several different types of investments to spread the risk of investing.
• If diversifying, an investor may put:
25% of his/her money into U.S. growth stocks
25% in government bonds
25% in dividend-paying stocks
10% in an international mutual fund
The rest in a savings account
19-31
The SUN NEVER SETS on
STOCK OPPORTUNITIES
(Reaching Beyond Our Borders)
• Suggestions for building your financial future:
Invest in global companies you know and that have solid performance records.
Invest in global stocks listed on U.S. exchanges.
Contact U.S. brokers about American Depository
Receipts (ADRs).
Invest in global mutual funds that focus on specific countries or regions.
Use extreme caution if investing in unstable countries!
19-32
Reducing Risk by Diversifying
Investments
LG5
PRIMARY INVESTMENT SERVICES
CONSUMERS NEED
• Savings and investing advice
• Help with 401k plans
• Retirement planning
• Tax planning
• Estate planning
• Education expense planning
Source: Investment Company Institute.
19-33
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• What is the key advantage of investing through online brokers? What is the key disadvantage?
• What is the primary purpose of diversifying investments?
19-34
Investing in
Stocks
LG6
PERCEPTIONS of the MARKET
• Bulls : Investors who believe stock prices are going to rise.
• Bears : Investors who expect stock prices to decline.
19-35
Investing in
Stocks
LG6
BEAR MARKET DECLINES in the S&P 500
Time Period
2007-2009
2000-2002
1973-1974
1968-1970
1987-1988
% Drop in Prices
52.5%
51%
48.2%
36.1%
33.5%
Source: Stock Traders Almanac 2011.
19-36
Investing in
Stocks
LG6
SELECTING STOCKS
• Capital Gains -The positive difference between the price at which you bought a stock and what you sell it for.
• Investors can also choose stocks according to their strategy:
Blue-chip stocks
Growth stocks
Income stocks
Penny stocks
19-37
Stock Splits
LG6
STOCK SPLITS
• Stock Splits -An action by a company that gives stockholders two or more shares of additional stock for every share that they own.
• Splits cause no change in the firm ’ s ownership structure and no change in the investment ’ s value.
• Firms can never be forced to spilt their stocks.
19-38
Buying Stock on Margin
BUYING STOCK on MARGIN
LG6
• Buying Stock on Margin -Borrowing some of the stock ’ s purchase cost from the brokerage firm.
• Margin is the portion of the stock ’ s purchase price that the investor must pay with their own money.
• If a broker issues a margin call, the investor has to come up with money to cover losses.
19-39
Understanding
Stock
Quotations
LG6
UNDERSTANDING STOCK
QUOTATIONS
19-40
Understanding
Stock
Quotations
LG6
TOP FINANICIAL NEWS and
RESEARCH SITES
• Yahoo Finance
• DailyFinance
• MSN Money
• Forbes
• Dow Jones & Co.
19-41
Investing in
Bonds
LG7
IMPORTANT BOND QUESTIONS
• First-time bond investors generally ask two questions:
Do you have to hold a bond until the maturity date?
How can I assess the investment risk of a particular bond issue?
• Junk Bonds -Bonds that are high-risk and have high default rates.
19-42
Understanding
Bond
Quotations
LG7
UNDERSTANDING BOND
QUOTATIONS
19-43
Investing in
Mutual Funds &
Exchange-
Traded Funds
LG8
INVESTING in MUTUAL FUNDS and EXCHANGE-TRADED FUNDS
• Mutual Fund -An organization the buys stocks and bonds and then sells shares in those securities to the public. The fund pools investors ’ money and buys stocks according to the fund ’ s purpose.
• Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) -Collections of stocks and bonds that are traded on securities exchanges, but are traded more like individual stocks than mutual funds.
19-44
Investing in
Mutual Funds &
Exchange-
Traded Funds
LG8
WHAT MUTUAL FUNDS CAN
LEARN FROM KaChing
1. Reform the ratings system
2. Give information for free
3. Cut out useless fees
4. Be transparent
5. Share insights
Source: Fast Company, March 2010.
19-45
Investing in
Mutual Funds &
Exchange-
Traded Funds
LG8
PERCENTAGE of HOUSEHOLDS
OWNING MUTUAL FUNDS
Year
1980
1990
2000
2005
2010
% of Households
5%
24%
43%
42%
48%
Source: Investment Company Institute Factbook.
19-46
Investing in
Mutual Funds &
Exchange-
Traded Funds
LG8
VARIETIES of ETFs
ETF
Traditional
Niche
Exotic
Description
Most common; include large U.S. stocks, small U.S. stocks, international stocks, or investmentgrade bonds.
Focus on an individual sector like healthcare, high-yield bonds, or a single country.
Invest in unusual, more volatile sectors such as commodities like gold and concepts like clean technology.
Source: Schwab and E*Trade.
19-47
Understanding
Mutual Fund
Quotations
LG8
UNDERSTANDING
MUTUAL FUND QUOTATIONS
19-48
Understanding
Mutual Fund
Quotations
LG8
COMPARING INVESTMENTS
19-49
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• What is a stock split? Why do companies sometimes split their stock?
• What does buying stock on margin mean?
• What are mutual funds and ETFs?
• What is the key benefit to investors in investing in a mutual fund or ETF?
19-50
Understanding
Stock Market
Indicators
LG9
KEY STOCK MARKET
INDICATORS
• Dow Jones Industrial Average -The average cost of 30 selected industrial stocks.
• Critics say the 30-company Dow is too small a sample and suggest following the S&P 500.
• S&P 500 tracks the performance of 400 industrial, 40 financial, 40 public utility, and 20 transportation stocks.
19-51
Riding the
Market ’ s Roller
Coaster
LG9
MARKET TURMOIL
• The stock market has its shares of ups and downs:
October 29, 1929 - Black
Tuesday; the market lost 13% of its value.
October 19, 1987 - The market suffered its worst one-day drop when it lost 22% of its value.
October 27, 1997 - Fears of an economic crisis in Asia cause widespread panic and losses.
19-52
Riding the
Market ’ s Roller
Coaster
LG9
TURMOIL in the 2000s
• The market collapsed into a deep decline in
2000-2002 when the dot-com bubble burst.
Investors lost $7 trillion in market value.
• Starting in 2008 , the collapse of the real estate market sent financial markets into panic.
The U.S. government made significant investments in private banks and offered a large stimulus package to reenergize the economy.
19-53
Riding the
Market ’ s Roller
Coaster
LG9
The WALL STREET of NOW
Then
Town Car
21 Club
Transportation
Restaurant
The Penthouse Club After Hours
Johnny Walker Blue
($200)
Drink
American Express
Black
Bottle Service
Card
Pastime
Now
Zipcar
Subway
Dave & Buster’s
Bud Light
($5)
Metrocard
Trivia Night
Source: Bloomberg Businessweek, September 6, 2010.
19-54
Riding the
Market ’ s Roller
Coaster
LG9
The UPS and DOWNS of the MARKET
• Program Trading -Giving instructions to computers to automatically sell if the price of a stock dips to a certain point to avoid potential losses.
• Analysts believe program trading caused the turmoil in 1987.
• The exchanges created mechanisms to restrict program trading.
19-55
Riding the
Market ’ s Roller
Coaster
LG9
WHO ’ S at FAULT for the
ECONOMIC CRISIS?
• Wall Street Issued exotic securities; paid excessive compensation based on bonuses; and investment banks got the SEC to relax capital requirements.
• Main Street Americans lived beyond their means; lenders gave favorable loans to homebuilders; greedy homeowners took out equity loans; and teaser mortgage rates let people live large.
• Washington Gramm-Leach-Billey Act allowed commercial and investment banks to partner; housing interest rates were kept low; and Community Reinvestment
Act forced lending to people with bad credit.
Source: Fortune Magazine, www.fortune.com
, accessed July 2011.
19-56
CLEANING UP the STREET
(Legal Briefcase)
• Congress passed the Dodd-Frank Financial Reform and Consumer Protection Act into law on July 21,
2010.
• Gives the government power to seize and shutter large financial institutions on the verge of collapse in an effort to prevent further bailouts.
• Formed an independent consumer protection agency housed within the Federal Reserve, protecting borrowers against a host of financial abuses ranging from payday loans to mortgages and credit cards.
19-57
Progress
Assessment
PROGRESS ASSESSMENT
• What does the Dow Jones Industrial Average measure? Why is it important?
• Why do the 30 companies comprising the Dow change periodically?
• Explain program trading and the problems it can create.
19-58