Mendelian Inheritance
advertisement

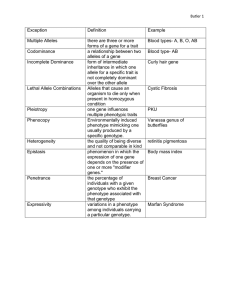
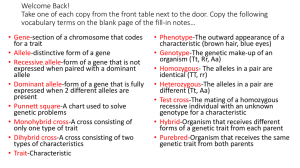
Mendelian Inheritance Conclusions: Purple colour is dominant White colour is recessive The cause of the white colour is not diluted, but co-exists with the purple colour Mendel’s Model • Alternative versions of genes account for variations in inherited characteristics – Purple or white flowers • For each characteristic, an organism inherits two alleles – one from each parent • If two alleles at a locus differ, one is dominant and the other is recessive • The two alleles separate during gamete formation Helpful definitions • Gene – Segments of DNA on a chromosome in the genome that specify the sequence of a protein • Locus – The specific location of a gene on a chromosome in the genome • Allele – any one of a number of versions of a gene occupying a given locus – Each cell has 2 copies of a chromosome » Therefore there are two possible alleles for every gene More definitions • Homozygous – Organism with a pair of identical alleles • Heterozygous – Organism with two different alleles for a particular gene • Genotype – The genetic make-up of an individual • Phenotype – The displayed traits of an individual • Pleiotropy – occurs when a single gene influences multiple phenotypic traits Genotype vs. Phenotype Performing a Testcross Independent Assortment But….then there is incomplete dominance Or….co-dominance…or even multiple alleles Epistasis - the gene at one locus alters the phenotype resulting from another gene at a separate locus B – black b – brown C – colour c – no colour Black (B) is dominant Colour (C) is dominant cc will be albino (no colour) • Quantitative trait locus – a region of DNA that is associated with a particular phenotypic trait – underlie continuous traits - the trait could have any value within a range (e.g. height) – a single phenotypic trait is usually determined by many genes – QTLs are often found on different chromosomes • Nature vs. Nurture Pedigree Charts