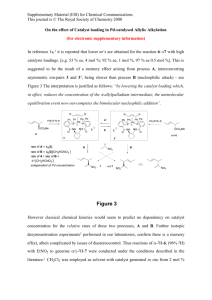
Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Enamine Iminium n
advertisement
Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design New Reactions – Enabling Valuable Bond Disconnections Activation Modes Priviledged Achitecture This Lecture – Broadened Activation Themes Previous Lecture Enamine Chiral Pool Iminium Me O Me N Me N N H R Proline-derived N H S R R R Me n Nucleophile Activation n Electrophile Activation t-Bu Imidazolidinone N H N H R RO RO O NR4 P OH N DMAP Carbene Acids and Phase Transfers Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design New Reactions – Enabling Valuable Bond Disconnections Activation Modes Priviledged Achitecture This Lecture – Broadened Activation Themes Previous Lecture Enamine Chiral Pool Iminium Me O Me N Me N N H R Proline-derived N H S R R R Me n Nucleophile Activation n Electrophile Activation t-Bu Imidazolidinone N H N H R RO RO O NR4 P OH N DMAP Carbene Acids and Phase Transfers Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design New Reactions – Enabling Valuable Bond Disconnections Activation Modes Priviledged Achitecture This Lecture – Broadened Activation Themes Previous Lecture Enamine Chiral Pool Iminium Me O Me N Me N N H R Proline-derived N H S R R R Me n Nucleophile Activation n Electrophile Activation t-Bu Imidazolidinone N H N H R RO RO O NR4 P OH N DMAP Carbene Acids and Phase Transfers Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design New Reactions – Enabling Valuable Bond Disconnections Activation Modes Priviledged Achitecture This Lecture – Broadened Activation Themes Previous Lecture Enamine Chiral Pool Iminium Me O Me N Me N N H R Proline-derived N H S R R R Me n Nucleophile Activation n Electrophile Activation t-Bu Imidazolidinone N H N H R RO RO O NR4 P OH N DMAP Carbene Acids and Phase Transfers Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design New Reactions – Enabling Valuable Bond Disconnections Activation Modes Priviledged Achitecture This Lecture – Broadened Activation Themes Previous Lecture Enamine Chiral Pool Iminium Me O Me N Me N N H R Proline-derived N H S R R R Me n Nucleophile Activation n Electrophile Activation t-Bu Imidazolidinone N H N H R RO RO O NR4 P OH N DMAP Carbene Acids and Phase Transfers Phase Transfer Catalysis (PTC) H2O, 105 °C hex Cl hex CN No Reaction NaCN Begining with Makosza and Brandstrom, Stark coined the term phase transfer catalysis Starks, R. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 195. Phase Transfer Catalysis (PTC) H2O, 105 °C hex Cl hex CN High Yield NaCN Organic Phase Bu3P(CH2)15CH3 CN Aqueous Phase NaCl NaCN (Interface) Bu3P(CH2)15CH3 Cl "The phenomenon of rate enhancement of a reaction between chemical species located in different phases by addition of a small quantity of an agent (called the 'phase-transfer catalyst') that extracts one of the reactants, most commonly an anion, across the interface into the other phase so that reaction can proceed..." – IUPAC Gold book Pioneering Studies at Merck In 1984 researchers at Merck published their work towards asymmetric alkylations Cl MeCl O Cl 10 mol % cat Cl Cl 50% aq NaOH MeO O Ph Me MeO toluene 95% yield 20 °C, 18 h 92% ee H-bond / ion pair Br OH O H N N N H N Cl O Cl CF3 phase transfer catalyst MeO -stack Dolling, U.-H.; Davis, P.; Grabowski, E. J. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 446. CF3 Pioneering Studies at Merck In 1984 researchers at Merck published their work towards asymmetric alkylations Cl MeCl O Cl 10 mol % cat Cl Cl 50% aq NaOH MeO O Ph Me MeO toluene 95% yield 20 °C, 18 h 92% ee H-bond / ion pair Br OH O H N N N H N Cl O Cl CF3 phase transfer catalyst MeO -stack Dolling, U.-H.; Davis, P.; Grabowski, E. J. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 446. CF3 Pioneering Studies at Merck In 1984 researchers at Merck published their work towards asymmetric alkylations Cl MeCl O Cl 10 mol % cat Cl Cl 50% aq NaOH MeO Ph Me MeO toluene 95% yield 20 °C, 18 h Cl Cl MeO O 92% ee Cl O 60% overall Ph Me O Cl HO Ph Me O O (+)-indacrinone MK-0197 Dolling, U.-H.; Davis, P.; Grabowski, E. J. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 446. Pioneering Studies at Merck In 1984 researchers at Merck published their work towards asymmetric alkylations Cl MeCl O Cl 10 mol % cat Cl Cl 50% aq NaOH MeO O Ph Me MeO toluene 95% yield 20 °C, 18 h 92% ee H-bond / ion pair Br OH O H N N N H N Cl O Cl CF3 phase transfer catalyst MeO -stack Dolling, U.-H.; Davis, P.; Grabowski, E. J. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 446. CF3 Asymmetric Phase Transfer Catalysis The catalyst controls the orientation of the enolate alkylation Lygo, B.; Andrews, B. I. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 518. O Ph N Ot-Bu Ph Glycine Imine Ester Organic Aqueous OH N N H Br Asymmetric Phase Transfer Catalysis The catalyst controls the orientation of the enolate alkylation Lygo, B.; Andrews, B. I. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 518. O Ph N Ot-Bu Ph Glycine Imine Ester Organic Aqueous NaOH OH N O Na Ph N Ph Ot-Bu N H Br Asymmetric Phase Transfer Catalysis The catalyst controls the orientation of the enolate alkylation Lygo, B.; Andrews, B. I. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 518. O Ph N Si face sheilded Ot-Bu ion OH Ph pairing N Glycine Imine Ester HO N Ph Ot-Bu Ph Re face open Cl Br Organic Aqueous –NaBr NaOH OH N O Na Ph N Ph Ot-Bu N H Br Asymmetric Phase Transfer Catalysis The catalyst controls the orientation of the enolate alkylation Lygo, B.; Andrews, B. I. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 518. O Ph N O Si face sheilded Ph Ot-Bu ion OH Ph Ot-Bu Ph pairing N Glycine Imine Ester N Cl HO N Ph Chlorophenylalanine Ot-Bu Ph Re face open Cl Br Organic Aqueous –NaBr NaOH OH N O Na Ph N Ph Ot-Bu N H Br Asymmetric Phase Transfer Catalysis The catalyst controls the orientation of the enolate alkylation Lygo, B.; Andrews, B. I. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 518. O Ph N O Q uickTim e™ and a decom pr essor ar e needed t o see t his pict ur e. Ph Ot-Bu Ph N Ot-Bu Ph Glycine Imine Ester Cl Chlorophenylalanine Cl Br Organic Aqueous –NaBr NaOH OH N O Na Ph N Ph Ot-Bu N H Br Switching Enantioselectivity Using Pseudoenantiomers Catalyst diastereomers give rise to the opposite product configuration PhCH2Br O N Ph 10 mol % cat O Ph N 50% aq KOH Ph Ot-Bu Ot-Bu Ph O Ph N Ot-Bu Ph toluene 20 °C, 18 h cat A 77% yield 86% ee Et Et Br OBn Br H N N cat B 85% yield 94% ee N H OBn N A From cinchonine B From cinchonidine Lygo, B.; Andrews, B. I. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 518. Advances in Catalyst Design Catalysts have been benchmarked using the benzylation of glycine imine: PhCH2Br O Ph N O 10 mol % cat Ph N Ot-Bu Ot-Bu Ph 50% aq KOH Ph toluene 20 °C, 18 h OH H Br N Ph Maruoka 1999 1 mol % 91% yield, 98% ee Ar Br H N OR N Ph Ar Ar = Ph O'Donnell 1989 10 mol % 75% yield, 66% ee N N Ar = Br R = allyl Lygo, Corey 1997 10 mol % 87% yield, 94% ee Cocatalyst: 18-crown-6 O O O O O Maruoka 2005 0.05 mol % 0.05 mol % 18-crown-6 90% yield, 98% ee O Shirakawa, S.; Marouka, K. Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis. Hoboken: Wiley, 2010. Advances in Catalyst Design Catalysts have been benchmarked using the benzylation of glycine imine: PhCH2Br O Ph N O 10 mol % cat Ph N Ot-Bu Ot-Bu Ph 50% aq KOH Ph toluene 20 °C, 18 h OH H Br N Ph Maruoka 1999 1 mol % 91% yield, 98% ee Ar Br H N OR N Ph Ar Ar = Ph O'Donnell 1989 10 mol % 75% yield, 66% ee N N Ar = Br R = allyl Lygo, Corey 1997 10 mol % 87% yield, 94% ee Cocatalyst: 18-crown-6 O O O O O Maruoka 2005 0.05 mol % 0.05 mol % 18-crown-6 90% yield, 98% ee O Shirakawa, S.; Marouka, K. Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis. Hoboken: Wiley, 2010. Advances in Catalyst Design Catalysts have been benchmarked using the benzylation of glycine imine: PhCH2Br O Ph N O 10 mol % cat Ph N Ot-Bu Ot-Bu Ph 50% aq KOH Ph toluene 20 °C, 18 h OH H Br N Ph Maruoka 1999 1 mol % 91% yield, 98% ee Ar Br H N OR N Ph Ar Ar = Ph O'Donnell 1989 10 mol % 75% yield, 66% ee N N Ar = Br R = allyl Lygo, Corey 1997 10 mol % 87% yield, 94% ee Cocatalyst: 18-crown-6 O O O O O Maruoka 2005 0.05 mol % 0.05 mol % 18-crown-6 90% yield, 98% ee O Shirakawa, S.; Marouka, K. Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis. Hoboken: Wiley, 2010. Advances in Catalyst Design Catalysts have been benchmarked using the benzylation of glycine imine: PhCH2Br O Ph N O 10 mol % cat Ph N Ot-Bu Ot-Bu Ph 50% aq KOH Ph toluene 20 °C, 18 h OH H Br N Ph Maruoka 1999 1 mol % 91% yield, 98% ee Ar Br H N OR N Ph Ar Ar = Ph O'Donnell 1989 10 mol % 75% yield, 66% ee N N Ar = Br R = allyl Lygo, Corey 1997 10 mol % 87% yield, 94% ee Cocatalyst: 18-crown-6 O O O O O Maruoka 2005 0.05 mol % 0.05 mol % 18-crown-6 90% yield, 98% ee O Shirakawa, S.; Marouka, K. Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis. Hoboken: Wiley, 2010. The PTC Activation Mode Beyond Alkylation Reactions PTC activation of carbonyls has enabled the developement of many different asymmetric reactions O Ph N O Ot-Bu p-Cl-Ph N O Ot-Bu Ph N Me Ph Ot-Bu Ph CN 90%, 98% ee 85%, 98% ee 85%, 91% ee glycine–alkylation glycine alkylation–allylation glycine–Michael Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44 , 625. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 5228. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1097. OH Boc O c-hex Ot-Bu NH2 NH O O PMB CO2Et Ot-Bu NH2 O2N NO2 83% 96:4 anti, 98% ee 95%, 9:1 syn 82% ee 78%, 85% ee glycine–aldol glycine–Mannich -ketoester SNAr Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4564. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 4980. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9685. Recent review: Ooi, T.; Maruoka, K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4222. The PTC Activation Mode Beyond Alkylation Reactions PTC activation of carbonyls has enabled the developement of many different asymmetric reactions SO2Mes HN O O Me t-Bu Ph CN O Ph SO2Ph Ph H 94%, 94% ee 99%, 96% ee 70%, 81% ee Strecker enone epoxidation Darzens epoxidation J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2548. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 6844. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 1407. MeO O F Cl O F3C N H Boc CO2Et N O N Boc O NH t-BuO Boc N Ph 94%, 84% ee 99%, 92% ee 79%, 84% ee -ketoester fluorination -ketoester amination aziridation J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 2494. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9466. Synthesis 2005, 2022. Recent review: Hashimoto, T.; Maruoka, K. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5656. Phase Transfer Catalysis Since the original reports the area continues to be a strong sector of organocatalysis research ISI web of knowledge references containing the key phrase "phase transfer catalysis" total 3698 60 Dolling’s (+)-indacrinone 40 synthesis 30 20 10 0 2009 2004 1999 1994 1989 1984 Year Publications 50 Carbenes as Organocatalysts Carbenes were long suspected as catalytic intermediates Carbenes as Organocatalysts Carbenes were long suspected as catalytic intermediates Breslow, R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 14, 3719. Carbenes as Organocatalysts Carbenes were long suspected as catalytic intermediates Me Me H2N H2N HO HO N N N N S S N H N Me Thiazolium Salt of Thiamine Coenzyme (vitamin B1) Me Nature's Carbene Organocatalyst For many years a carbene catalyst for the enantioselective benzoin condensation was elusive O H S N R S N Ph O R Ph N S base S N R H OH Ph O Ph S OH Ph Benzoin Product R N R O Ph Ph OH O H Ph Breslow-type Intermediate Carbenes as Organocatalysts Carbenes were long suspected as catalytic intermediates Me Me H2N H2N HO HO N N N N S S N H N Me Thiazolium Salt of Thiamine Coenzyme (vitamin B1) Me Nature's Carbene Organocatalyst For many years a carbene catalyst for the enantioselective benzoin condensation was elusive O H S N R S N Ph O R Ph N S base S N R H OH Ph O Ph S OH Ph Benzoin Product R N R O Ph Ph OH O H Ph Breslow-type Intermediate Carbenes as Organocatalysts Carbenes were long suspected as catalytic intermediates Me Me H2N H2N HO HO N N N N S S H N Me N Me Thiazolium Salt of Thiamine Coenzyme (vitamin B1) Nature's Carbene Organocatalyst For many years a carbene catalyst for the enantioselective benzoin condensation was elusive n The newly proposed intermediate exhibits umpolung reactivity O H cat S N O R Ph Ph Ph electrophilic OH Breslow-type Intermediate Before we can get new reactions we need better catalysts acyl anion synthon novel reactivty patterns Carbenes as Organocatalysts Carbenes were long suspected as catalytic intermediates Me Me H2N H2N HO HO N N N N S S H N Me N Me Thiazolium Salt of Thiamine Coenzyme (vitamin B1) Nature's Carbene Organocatalyst For many years a carbene catalyst for the enantioselective benzoin condensation was elusive n The newly proposed intermediate exhibits umpolung reactivity O H cat S N O R Ph Ph Ph electrophilic OH Breslow-type Intermediate Before we can get new reactions we need better catalysts acyl anion synthon novel reactivty patterns Carbenes as Organocatalysts Carbenes were long suspected as catalytic intermediates Me Me H2N H2N HO HO N N N N S S H N Me N Me Thiazolium Salt of Thiamine Coenzyme (vitamin B1) Nature's Carbene Organocatalyst For many years a carbene catalyst for the enantioselective benzoin condensation was elusive n The newly proposed intermediate exhibits umpolung reactivity O H cat S N O R Ph Ph Ph electrophilic OH Breslow-type Intermediate Before we can get new reactions we need better catalysts acyl anion synthon novel reactivty patterns Carbenes as Organocatalysts Isolated in 1991 by Arduengo while working at DuPont Mes N N KOtBu Mes Mes N N Mes Bulky groups prevent dimerization Cl H Arduengo III, A. J.; Harlow, R. L.; Kline, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 361. In 1995 Enders and Teles develop stable triazole-based carbenes Ph N Ph N Ph NaOCH3 N Ph CH3OH 70 °C N Ph N Ph N 80 °C N Ph 0.1 mbar OCH3 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 1021. Ph N N Ph Asymmetric Carbene Catalysts 10 mol % O H Ph KOt-Bu O OH Ph Ph THF The genesis of a new platform for asymmetric catalysis 1966 Sheehan Hunneman Ph S N 1997 Leeper O 2002 Enders O O N N O c-hex Ph N N Cl 22% ee N Ph t-Bu t-Bu 80% ee N BF4 83% 90% ee 2002 Chiral triazole are made and are efficient and selective for the benzoin condensation Sheehan, J.; Hunneman, D. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 3666. Knight, R. L.; Leeper, F. J. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 3611. Enders, D.; Kallfass, U. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1743. Carbenes: Generic Activation Platform It was soon realized that carbenes activate carbonyls for a number of useful reactions O H O base N Ph N N O triazolium salt N N electrophile N Ph t-Bu Ph O N Ph N N t-Bu t-Bu Ph carbene O Breslow-type Nucleophile O N Ph N N t-Bu Ph OH electrophile n Alkene geometry controlled by bulky group n Re face shielded by t-Bu Generically activated towards electrophiles Recent Advance in Carbene Catalysis After the initial disclosures in the 1990's the Stetter reaction has been championed by Rovis O N N O BF4 N CO2Et O CO2Et Rovis 2002 OMe 94% yield 20 mol % O 94% ee O KHMDS xylenes Kerr, M. S.; Read de Alaniz, J.; Rovis, T. J. Am Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 10298. The Rovis catalyst design has been have been proven to be excellent for many more reactions O N N N Ph O BF4 H Et O 20 mol % KOt-Bu THF Enders, D.; Niemeier, O.; Raabe, G. Synlett 2006, 2431. O Et OH Enders 2006 88% yield 94% ee Recent Advance in Carbene Catalysis After the initial disclosures in the 1990's the Stetter reaction has been championed by Rovis O N N O BF4 N CO2Et O CO2Et Rovis 2002 OMe 94% yield 20 mol % O 94% ee O KHMDS xylenes Kerr, M. S.; Read de Alaniz, J.; Rovis, T. J. Am Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 10298. The Rovis catalyst design has been have been proven to be excellent for many more reactions O N N N Ph O BF4 H Et O 20 mol % KOt-Bu THF Enders, D.; Niemeier, O.; Raabe, G. Synlett 2006, 2431. O Et OH Enders 2006 88% yield 94% ee Beyond the Stetter and Bezoin Reactions Azadiene Diels–Alder O N N O O S N BF4 O N Ph O 10 mol % OEt H MeO Mes O PMBO2S OEt N DIPEA Ph O toluene/THF 90%, 50:1 dr 99% ee Bode 2006 O Mes N Mes N N Mes N N O OH O O OEt N N N OH O O O N OEt O OEt N Ph He, M.; Struble, J. R.; Bode, J. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8418. O S OMe Beyond the Stetter and Bezoin Reactions Azadiene Diels–Alder O N N O O S N BF4 O N Ph O 10 mol % OEt H MeO Mes O PMBO2S OEt N DIPEA Ph O toluene/THF 90%, 50:1 dr 99% ee Bode 2006 O Mes N Mes N N Mes N N O OH O O OEt N N N OH O O O N OEt O OEt N Ph He, M.; Struble, J. R.; Bode, J. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8418. O S OMe Beyond the Stetter and Bezoin Reactions Azadiene Diels–Alder O N N O O S N BF4 O N Ph O 10 mol % OEt H MeO Mes O PMBO2S OEt N DIPEA Ph O toluene/THF 90%, 50:1 dr 99% ee Bode 2006 O Mes N Mes N N Mes N N O OH O O OEt N N N OH O O O N OEt O OEt N Ph He, M.; Struble, J. R.; Bode, J. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8418. O S OMe Substrate Activation Towards New Reactivity -chloroaldehydes provide access to alternate manifolds for e.g. esterification N 10 mol % O H HO Ph Ph Ph N O N Cl Ph O Ph Cl -chloroaldehyde NEt3 alcohol ester Cl Cl N Ph N N N Cl N N Ph N OH Ph OH Ph Ph N N O Ph n Oxy Diels–Alder reaction O O O N O H Ph Cl Mes Me CO2Me N N Cl 0.5 mol % EtOAc, NEt3 O Ph CO2Me 88%, >20:1 dr, 99% ee Reynolds, N. T.; de Alaniz, J. R.; Rovis, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9518. He, M.; Uc, G. J.; Bode, J. W. J Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15088. Substrate Activation Towards New Reactivity -chloroaldehydes provide access to alternate manifolds for e.g. esterification N 10 mol % O H HO Ph Ph Ph N O N Cl Ph O Ph Cl -chloroaldehyde NEt3 alcohol ester Cl Cl N Ph N N N Cl N N Ph N OH Ph OH Ph Ph N N O Ph n Oxy Diels–Alder reaction O O O N O H Ph Cl Mes Me CO2Me N N Cl 0.5 mol % EtOAc, NEt3 O Ph CO2Me 88%, >20:1 dr, 99% ee Reynolds, N. T.; de Alaniz, J. R.; Rovis, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9518. He, M.; Uc, G. J.; Bode, J. W. J Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15088. Substrate Activation Towards New Reactivity -chloroaldehydes provide access to alternate manifolds for e.g. esterification N 10 mol % O H HO Ph Ph Ph N O N Cl Ph O Ph Cl -chloroaldehyde NEt3 alcohol ester Cl Cl N Ph N N N Cl N N Ph N OH Ph OH Ph Ph N N O Ph n Oxy Diels–Alder reaction O O O N O H Ph Cl Mes Me CO2Me N N Cl 0.5 mol % EtOAc, NEt3 O Ph CO2Me 88%, >20:1 dr, 99% ee Reynolds, N. T.; de Alaniz, J. R.; Rovis, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9518. He, M.; Uc, G. J.; Bode, J. W. J Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15088. Hydrogen-Bonding Catalysis 10 mol % H-bond catalysis O N N H H R F3C N H Me O R CF3 S S R CF3 N H CF3 krel 8.8 times faster with catalyst Me H O n Typically a 2-20 kcal/mol interaction n Activates electrophiles ~30 new reactions Jacobsen–Akiyama Wittkopp, A.; Schreiner, P. R. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 407. Early examples using cinchonia alkaloidsas H-bonding catalysts SH O cinchonidine 1 mol % H O N H O Me Me t-Bu N - S t-Bu H Me Me ArS H O Me Me 75% ee Doyle, A. G.; Jacobsen, E. N. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5713. Hiemstra, H.; Wynberg, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 417. Hydrogen-Bonding Catalysis 10 mol % H-bond catalysis O N N H H R F3C N H Me O R CF3 S S R CF3 N H CF3 krel 8.8 times faster with catalyst Me H O n Typically a 2-20 kcal/mol interaction n Activates electrophiles ~30 new reactions Jacobsen–Akiyama Wittkopp, A.; Schreiner, P. R. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 407. Early examples using cinchonia alkaloidsas H-bonding catalysts SH O cinchonidine 1 mol % H O N H O Me Me t-Bu N - S t-Bu H Me Me ArS H O Me Me 75% ee Doyle, A. G.; Jacobsen, E. N. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5713. Hiemstra, H.; Wynberg, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 417. Hydrogen-Bonding Catalysis 10 mol % H-bond catalysis O N N H H R F3C N H Me O R CF3 S S R CF3 N H CF3 krel 8.8 times faster with catalyst Me H O n Typically a 2-20 kcal/mol interaction n Activates electrophiles ~30 new reactions Jacobsen–Akiyama Wittkopp, A.; Schreiner, P. R. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 407. Early examples using cinchonia alkaloidsas H-bonding catalysts SH O cinchonidine 1 mol % H O N H O Me Me t-Bu N - S t-Bu H Me Me ArS H O Me Me 75% ee Doyle, A. G.; Jacobsen, E. N. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5713. Hiemstra, H.; Wynberg, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 417. Hydrogen-Bonding Catalysis 10 mol % H-bond catalysis O N N H H R F3C N H Me O R CF3 S S R CF3 N H CF3 krel 8.8 times faster with catalyst Me H O n Typically a 2-20 kcal/mol interaction n Activates electrophiles ~30 new reactions Jacobsen–Akiyama Wittkopp, A.; Schreiner, P. R. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 407. Early examples using cinchonia alkaloidsas H-bonding catalysts SH O cinchonidine 1 mol % H O N H O Me Me t-Bu N - S t-Bu H Me Me ArS H O Me Me 75% ee Doyle, A. G.; Jacobsen, E. N. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5713. Hiemstra, H.; Wynberg, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 417. Early Examples of Hydrogen Bonding Catalysis A small dipeptide was designed by Inoue to mimic oxynitrilase O O H H N HN NH N O HN Ph Ph CN H O N C O HCN 97%, 97% ee 2 mol %, toluene, –20 °C NH OH H Ph Ph Ph H H N H O Asymmetric Strecker reaction using Corey's guanidine H-bonding catalyst Ph N HCN Ph Ph toluene, –40 °C N Ph N Ph HN Ph N H Ph Ph CN 10 mol % Ph N N Ph N Ph N R H H CN Ph N N H H N CN Ph Tanaka, K.; Mori, A.; Inoue, S. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 181. Grogan, M. J.; Corey, E. J. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 157. N Early Examples of Hydrogen Bonding Catalysis A small dipeptide was designed by Inoue to mimic oxynitrilase O O H H N HN NH N O HN Ph Ph CN H O N C O HCN 97%, 97% ee 2 mol %, toluene, –20 °C NH OH H Ph Ph Ph H H N H O Asymmetric Strecker reaction using Corey's guanidine H-bonding catalyst Ph N HCN Ph Ph toluene, –40 °C N Ph N Ph HN Ph N H Ph Ph CN 10 mol % Ph N N Ph N Ph N R H H CN Ph N N H H N CN Ph Tanaka, K.; Mori, A.; Inoue, S. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 181. Grogan, M. J.; Corey, E. J. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 157. N Early Examples of Hydrogen Bonding Catalysis A small dipeptide was designed by Inoue to mimic oxynitrilase O O H H N HN NH N O HN Ph Ph CN H O N C O HCN 97%, 97% ee 2 mol %, toluene, –20 °C NH OH H Ph Ph Ph H H N H O Asymmetric Strecker reaction using Corey's guanidine H-bonding catalyst Ph N HCN Ph Ph toluene, –40 °C N Ph N Ph HN Ph N H Ph Ph CN 10 mol % Ph N N Ph N Ph N R H H CN Ph N N H H N CN Ph Tanaka, K.; Mori, A.; Inoue, S. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 181. Grogan, M. J.; Corey, E. J. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 157. N Discovery of Acid Mediated Strecker Reactions – Jacobsen Thioureas Parallel synthetic ligand libraries were evaluated with various metals O N F3C ligand library / metal N TBSCN H CN TFA Modifed Schiff bases were prepared in a combinatorial fashion on a solid support R O R1 O R N H N M H N 5 N H Target Catalyst Architecture Ru R2 N H O O R R2 O 69% conv 13% ee N HO No Metal 12 Metals R3 R4 Sigman, M. S.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4901. 59% conv 19% ee Discovery of Acid Mediated Strecker Reactions – Jacobsen Thioureas Parallel synthetic ligand libraries were evaluated with various metals O N F3C ligand library / metal N TBSCN H CN TFA Modifed Schiff bases were prepared in a combinatorial fashion on a solid support R O R1 O R N H N M H N 5 N H Target Catalyst Architecture Ru R2 N H O O R R2 O 69% conv 13% ee N HO No Metal 12 Metals R3 R4 Sigman, M. S.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4901. 59% conv 19% ee Discovery of Acid Mediated Strecker Reactions – Jacobsen Thioureas Parallel synthetic ligand libraries were evaluated with various metals O N F3C ligand library / metal N TBSCN H CN TFA Modifed Schiff bases were prepared in a combinatorial fashion on a solid support R O R1 O R N H N M H N 5 N H Target Catalyst Architecture Ru R2 N H O O R R2 O 69% conv 13% ee N HO No Metal 12 Metals R3 R4 Sigman, M. S.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4901. 59% conv 19% ee Discovery of Acid Mediated Strecker Reactions – Jacobsen Thioureas The structure was quickly optimized to provide an efficient Strecker catalyst R1 O N H H N 5 R2 O N H t-Bu Systematic R2 N H O Ph H N N H optimization N O N H O N HO HO Catalyst Lead New Catalyst R3 R4 t-Bu O 2 mol % cat N toluene, –78 °C F3C N TBSCN H CN TFA 78% conv 91% ee Sigman, M. S.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4901. OMe Discovery of Acid Mediated Strecker Reactions – Jacobsen Thioureas The structure was quickly optimized to provide an efficient Strecker catalyst R1 O N H H N 5 R2 O N H t-Bu Systematic R2 N H O Ph H N N H optimization N O N H O N HO HO Catalyst Lead New Catalyst R3 R4 t-Bu O 2 mol % cat N toluene, –78 °C F3C N TBSCN H CN TFA 78% conv 91% ee Sigman, M. S.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4901. OMe How Do These New Catalysts Function? t-Bu Ph H N O N H Knock-out studies show that the urea functional group is essential N H O N Hydrogen bonding established as the activation mode HO n Weaker product binding enables turnover OBz t-Bu DFT and NMR Studies: X X Me N H Me Me N H Me Me X N N H Me H Me HCN Me N Me N N N H H Me Me Me NH CN X=O –8.5 kcal/mol –5.0 kcal/mol X=S –10 kcal/mol –6.3 kcal/mol Vachal, P.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 120, 10012. How Do These New Catalysts Function? t-Bu Ph H N O N H Knock-out studies show that the urea functional group is essential N H O N Hydrogen bonding established as the activation mode HO n Weaker product binding enables turnover OBz t-Bu DFT and NMR Studies: X X Me N H Me Me N H Me Me X N N H Me H Me HCN Me N Me N N N H H Me Me Me NH CN X=O –8.5 kcal/mol –5.0 kcal/mol X=S –10 kcal/mol –6.3 kcal/mol Vachal, P.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 120, 10012. Urea Stereochemical Model Me t-Bu CN S Q uickTim e™ and a decom pr essor ar e needed t o see t his pict ur e. N Ph N N H N H P O h M e N HO OBz t-Bu With a better understanding of how these catalysts work new reaction methods can be developed Strecker reaction with aldimine or ketoimine 1 mol % cat N Ph HCN toluene, –78 °C O F3C N Ph R t-Bu R TFA t-Bu CN R =H 99% ee R = Me 86% ee Vachal, P.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 120, 10012. Urea Stereochemical Model Me t-Bu CN S Q uickTim e™ and a decom pr essor ar e needed t o see t his pict ur e. N Ph N N H N H P O h M e N HO OBz t-Bu With a better understanding of how these catalysts work new reaction methods can be developed Strecker reaction with aldimine or ketoimine 1 mol % cat N Ph HCN toluene, –78 °C O F3C N Ph R t-Bu R TFA t-Bu CN R =H 99% ee R = Me 86% ee Vachal, P.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 120, 10012. Urea Catalyzed Reactions Enantioselective Mannich Reaction Boc H OTBS N Oi-Pr Ph t-Bu 5 mol % cat –40 °C toluene, 48 h TFA O NHBoc i-PrO H N Ph S N H N H O Ph N HO 90% conv, 91% ee OCOt-Bu t-Bu Wenzel, A. G.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12964. Enantioselective Acyl Pictet–Spengler Reaction N N H Et Et 10 mol % cat Ac-Cl lutidine –78 °C NAc N H N N H i-Bu Et Et 81% conv, 93% ee Taylor, M. S.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10558. S t-Bu i-Bu O N H Me N Ph Urea Catalyzed Reactions Enantioselective Mannich Reaction Boc H OTBS N Oi-Pr Ph t-Bu 5 mol % cat –40 °C toluene, 48 h TFA O NHBoc i-PrO H N Ph S N H N H O Ph N HO 90% conv, 91% ee OCOt-Bu t-Bu Wenzel, A. G.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12964. Enantioselective Acyl Pictet–Spengler Reaction N N H Et Et 10 mol % cat Ac-Cl lutidine –78 °C NAc N H N N H i-Bu Et Et 81% conv, 93% ee Taylor, M. S.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10558. S t-Bu i-Bu O N H Me N Ph Urea Catalyzed Reactions Enantioselective Aza-Henry Reaction Boc 10 mol % cat 4 °C toluene, i-Pr2NEt N H EtNO2 Ph Boc NH t-Bu NO2 Ph 4 Å MS Me2N Me S N H N H O NHAc >95% conv, 91% ee 15:1 syn Yoon, T.; Jacobsen, E. N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 124, 466. Enantioselective Hydrophosphorylation O O Ar O P O Ar N H Ph 10 mol % cat Ar Ar = 2-nitrophenyl P Ph Me2N HN 4 °C Et2O S N H O Ar Ph O t-Bu N H O Ph N HO 87% yield, 98% ee t-Bu Joly, G. D.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4108. OCOt-Bu Urea Catalyzed Reactions Enantioselective Aza-Henry Reaction Boc 10 mol % cat 4 °C toluene, i-Pr2NEt N H EtNO2 Ph Boc NH t-Bu NO2 Ph 4 Å MS Me2N Me S N H N H O NHAc >95% conv, 91% ee 15:1 syn Yoon, T.; Jacobsen, E. N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 124, 466. Enantioselective Hydrophosphorylation O O Ar O P O Ar N H Ph 10 mol % cat Ar Ar = 2-nitrophenyl P Ph Me2N HN 4 °C Et2O S N H O Ar Ph O t-Bu N H O Ph N HO 87% yield, 98% ee t-Bu Joly, G. D.; Jacobsen, E. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4102. OCOt-Bu Bifunctional Urea Catalysts Enantioselective Michael Addition O O EtO O 10 mol % cat Ph OEt NO2 O EtO toluene , 23 °C OEt NO2 Ph Both thiourea and tertiary amine are needed S CF3 CF3 R S AcHN NMe2 F3C N H S N H F3C N H N N H H Me2N O O H N H NMe2 N 10 mol % NEt3 14%, 35% ee 57%, 0% ee 86%, 93% ee Ph Okino, T.; Hoashi, Y.; Takemoto, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 128, 12672. Nu Bifunctional Urea Catalysts Enantioselective Michael Addition O O EtO O 10 mol % cat Ph OEt NO2 O EtO toluene , 23 °C OEt NO2 Ph Both thiourea and tertiary amine are needed S CF3 CF3 R S AcHN NMe2 F3C N H S N H F3C N H N N H H Me2N O O H N H NMe2 N 10 mol % NEt3 14%, 35% ee 57%, 0% ee 86%, 93% ee Ph Okino, T.; Hoashi, Y.; Takemoto, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 128, 12672. Nu Urea Catalyzed Double Michael Cascade Enantioselective Double Michael Addition O O O Me O OEt Ph NO2 O OEt O 10 mol % cat Me Me OEt Ph NO2 toluene , –20 °C Ph NO2 87% yield >99% de 92% ee CF3 S catalyst = F3C N H N H NMe2 Hoashi, Y.; Yabuta, T.; Takemoto, Y. Tettrahdron Lett. 2003, 45, 9185. Rawal's Discovery of H-Bonding Catalyzed Diels–Alder OMe OMe TBSO H solvent O Me N O krel solvent 1 THF O AcCl Me Benzene 1.3 t-BuOH 280 i-PrOH 630 Huang, Y.; Rawal, V. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9662. Observed that the hetero Diels–Alder reaction is accelerated in alcohol solvent This observation was turned into an asymmetric reaction using a chiral H-donor catalyst Ar TBSO H Ph O Me N Me 20 mol % cat AcCl O Ph Me OH Me OH O 70% yield 99% ee Huang, Y.; Unni, A. K.; Thadani, A. N.; Rawal, V. H. Nature 2003, 424, 146. Ar Ar Ar = Ar Rawal's Discovery of H-Bonding Catalyzed Diels–Alder OMe OMe TBSO H solvent O Me N O krel solvent 1 THF O AcCl Me Benzene 1.3 t-BuOH 280 i-PrOH 630 Huang, Y.; Rawal, V. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9662. Observed that the hetero Diels–Alder reaction is accelerated in alcohol solvent This observation was turned into an asymmetric reaction using a chiral H-donor catalyst Ar TBSO H Ph O Me N Me 20 mol % cat AcCl O Ph Me OH Me OH O 70% yield 99% ee Huang, Y.; Unni, A. K.; Thadani, A. N.; Rawal, V. H. Nature 2003, 424, 146. Ar Ar Ar = Ar Mechanism of Rawal's H-Bonding Diels–Alder Reaction Is single or double point activation in operation? P Carbonyl h P h O Activation O O O H O O O H H H H H O H R O P P h h H R H R Single or Double–point activation Q uickTim e™ and a decom pr essor ar e needed t o see t his pict ur e. Re–Face Open R P h P h O H H O H O P P h h Single–Point Activation Unni, A. K.; Takenaka, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Rawal, V. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1336. Mechanism of Rawal's H-Bonding Diels–Alder Reaction Is single or double point activation in operation? P Carbonyl h P h O Activation O O O H O O O H H H H H O H R O P P h h H R H R Single or Double–point activation Q uickTim e™ and a decom pr essor ar e needed t o see t his pict ur e. Re–Face Open R P h P h O H H O H O P P h h Single–Point Activation Unni, A. K.; Takenaka, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Rawal, V. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1336. Chiral Phosphoric Acids Long used for chiral resolutions R O Used as a ligand for Lewis acid catalysis O P O OH n 2004 Terada and Akiyama use as Brønsted acid catalyst R N Ph R= n Size of R group very important for enantioselectivity Boc H O Me O Ac 2 mol % cat Me Boc CH2Cl2 H N Ac Ph R= R= R= 92% yield 95% yield 88% yield 99% yield 12% ee 56% ee 90% ee 95% ee H Akiyama, T.; Itoh, K.; Yokota, K.; Fuchibe, K. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1566. Uraguchi, D.; Terada, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5356. Chiral Phosphoric Acids Long used for chiral resolutions R O Used as a ligand for Lewis acid catalysis O P O OH n 2004 Terada and Akiyama use as Brønsted acid catalyst R N Ph R= n Size of R group very important for enantioselectivity Boc H O Me O Ac 2 mol % cat Me Boc CH2Cl2 H N Ac Ph R= R= R= 92% yield 95% yield 88% yield 99% yield 12% ee 56% ee 90% ee 95% ee H Akiyama, T.; Itoh, K.; Yokota, K.; Fuchibe, K. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1566. Uraguchi, D.; Terada, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5356. Chiral Phosphoric Acids Long used for chiral resolutions R O Used as a ligand for Lewis acid catalysis O P O OH n 2004 Terada and Akiyama use as Brønsted acid catalyst R N Ph R= n Size of R group very important for enantioselectivity Boc H O Me O Ac 2 mol % cat Me Boc CH2Cl2 H N Ac Ph R= R= R= 92% yield 95% yield 88% yield 99% yield 12% ee 56% ee 90% ee 95% ee H Akiyama, T.; Itoh, K.; Yokota, K.; Fuchibe, K. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1566. Uraguchi, D.; Terada, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5356. Chiral Phosphoric Acids Long used for chiral resolutions R O Used as a ligand for Lewis acid catalysis O P O OH n 2004 Terada and Akiyama use as Brønsted acid catalyst R N Ph R= n Size of R group very important for enantioselectivity Boc H O Me O Ac 2 mol % cat Me Boc CH2Cl2 H N Ac Ph R= R= R= 92% yield 95% yield 88% yield 99% yield 12% ee 56% ee 90% ee 95% ee H Akiyama, T.; Itoh, K.; Yokota, K.; Fuchibe, K. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1566. Uraguchi, D.; Terada, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5356. Chiral Phosphoric Acids Long used for chiral resolutions R O Used as a ligand for Lewis acid catalysis O P O OH n 2004 Terada and Akiyama use as Brønsted acid catalyst R N Ph R= n Size of R group very important for enantioselectivity Boc H O Me O Ac 2 mol % cat Me Boc CH2Cl2 H N Ac Ph R= R= R= 92% yield 95% yield 88% yield 99% yield 12% ee 56% ee 90% ee 95% ee H Akiyama, T.; Itoh, K.; Yokota, K.; Fuchibe, K. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1566. Uraguchi, D.; Terada, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5356. New Reactivity – Imine Amination No known reaction metal or N Boc organocatalytic H2N Ts Ph Boc H N H N SO2Me Ph Boc-imine tosyl-amine enantioenriched aminal (differentially protected) 5 mol % cat Ph O Ph O O Et2O, 1 h, 21 °C P OH 86% yield 93% ee (S)-VAPOL Rowlan, G. B.; Zang, H.; Rowland, E. B.; Chennamadhavuni, S.; Wang, Y.; Antilla, J. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15696. New Reactivity – Imine Amination No known reaction metal or N Boc organocatalytic H2N Ts Ph Boc H N H N SO2Me Ph Boc-imine tosyl-amine enantioenriched aminal (differentially protected) 5 mol % cat Ph O Ph O O Et2O, 1 h, 21 °C P OH 86% yield 93% ee (S)-VAPOL Rowlan, G. B.; Zang, H.; Rowland, E. B.; Chennamadhavuni, S.; Wang, Y.; Antilla, J. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15696. Consideration of priviledged architecture and stereogenicity Transfer Hydrogenation Friedel–Crafts Me2N OMe H O O CO2Et A H Me H X B important important chiral synthon chiral synthon Perhaps the most important stereogenicity for biomedical applications Amine conjugate addition NH2 biomedically relevant center NR2 93–97% ee X Y O There are vast technologies for the construction of amine stereogenicity Favourite: Ellman imine, most general–dogma breaking Me Me SR Me S O N DIBAL Me Me tert-butanesulfinamide Me Me SR Me S O H N Me Me 20:1 dr, 86% yield There are vast technologies for the construction of amine stereogenicity Favourite: Ellman imine, most general–dogma breaking Me SR Me Me S O N DIBAL Me Me Me SR Me S H N O Me tert-butanesulfinamide Me Me 20:1 dr, 86% yield Reductive Amination: Simultaneous fragment coupling and C–N bond formation O F NaBH4 Me NH2 Me N –H2O F Me N NH O Me O fragment 1 fragment 2 no enantioselective catalytic reductive amination-coupling Organic Catalyzed Reductions in Biological Systems NADH: Natures Reduction (Hydrogenation) Reagent (Coenzyme) H O NH2 CONH2 OH Me alanine transferase H NH3 O N methyl pyruvate O enzyme R catalyst NADH OH Me alanine Q uickTim e™ and a TI FF ( Uncom pr essed) decom pr essor ar e needed t o see t his pict ur e. H2N H + N N H H R N Me H His O O active site NADH reduction R HN O H H NH HN Arg NHR Selective reduction of pyruvate imines to create amino acids Could this organocatalytic sequence be utilized in the redution of carbon–carbon double bonds Organic Catalyzed Reductions in Laboratory Systems Hantzsch ester as a useful surrogate for NADH reductions in the lab H O H MeO2C NH2R Me Me N Me acetophenone MeO Me NADH analog O H N phenylethyl amine catalyst O H + H N Me catalyst H R NHR CO2Me R Me Me H-bonded or Bronsted acid organic iminium reduction Can we translate a biochemical concept to a laboratory reaction Can we develop a useful transformation on the basis of established Bronsted acid catalysts Organic Catalyzed Reductions in Laboratory Systems Hantzsch ester as a useful surrogate for NADH reductions in the lab H O H MeO2C NHR CO2Me NH2R Me Me N Me catalyst H acetophenone Me NADH analog phenylethyl amine catalyst MeO Me O H R N H catalyst O H + N R O X OH Me Me H-bonded or Bronsted acid organic iminium reduction X Y Y O O P O OH simple carboxylic or phosphonic acids Can we translate a biochemical concept to a laboratory reaction Can we develop a useful transformation on the basis of established Bronsted acid catalysts Organocatalysis and the advent of Bronsted Acid/H-bonded catalysis Pioneers CF3 Ph Me2N O O S N N H H CF3 Ph OH Yamamoto R OH OH O Ph OH Ph Rawal Jacobsen Akiyama, Terada OH OH Schaus O O P O OH Organocatalysis and the advent of Bronsted Acid/H-bonded catalysis H O H MeO2C NH2PMP CO2Me NHPMP Me Me N Me 80°C, toluene 20 mol% catalyst Me H acetophenone Pioneers CF3 Ph Me2N O O S N N H H CF3 Ph OH Yamamoto R OH OH O Ph OH Ph Rawal Jacobsen Akiyama, Terada OH OH Schaus O O P O OH Organocatalysis and the advent of Bronsted Acid/H-bonded catalysis H O H MeO2C NH2PMP CO2Me NHPMP Me Me N Me 80°C, toluene 20 mol% catalyst Me H acetophenone Pioneers CF3 Ph Me2N O O S N N H H CF3 Ph OH Yamamoto R OH OH O Ph OH Ph Jacobsen Rawal No reaction No reaction No reaction Akiyama, Terada OH OH Schaus O No reaction O P O OH 43% yield 7%ee Attempts to develop a Bronsted Acid Catalyst for Reductive Amination H O H MeO2C CO2Me NH2PMP NHPMP Me Me N Me H acetophenone H O O H OH P O Me O N O 80°C, toluene 20 mol% catalyst Me 7% ee Attempts to develop a Bronsted Acid Catalyst for Reductive Amination H O H MeO2C CO2Me NH2PMP NHPMP Me Me N Me H Me 80°C, toluene 20 mol% catalyst 7% ee acetophenone R O O OH P O R R H O O H OH P O Me O N O Yield %ee Attempts to develop a Bronsted Acid Catalyst for Reductive Amination H O H MeO2C CO2Me NH2PMP NHPMP Me Me N Me H Me 80°C, toluene 20 mol% catalyst 7% ee acetophenone R O O OH P O R R H O O H OH P O Yield %ee H 43 7 Me O Ph(NO2)2 45 16 N O Ph(CF3)2 39 65 2-Nap 56 40 Attempts to develop a Bronsted Acid Catalyst for Reductive Amination H O H MeO2C CO2Me NH2PMP NHPMP Me Me N Me H Me 80°C, toluene 20 mol% catalyst 7% ee acetophenone R O O OH P O R R H O O H OH P O Yield %ee H 43 7 Me O Ph(NO2)2 45 16 N O Ph(CF3)2 39 65 2-Nap 56 40 Ph3Si 90 85 The impact of additives and temperature on the reductive amination H O TPS H MeO2C CO2Me 80°C, toluene 20 mol% cat Me Me N NH2PMP Me H NHPMP Me O O OH P TPS catalyst What is the impact of the water biproduct additive Time Yield %ee -- 28 h 90 85 H2O (1eq) 72 h 35 77 H2O (2eq) 72 h <10 72 MgSO4 20 h 79 83 Na2SO4 36 h 83 85 What is the scope of this transformation with respect to ketones? O The impact of additives and temperature on the reductive amination H O TPS H MeO2C CO2Me N Me H O Me 80°C, toluene 20 mol% cat Me Me NH2PMP NHPMP O OH P O TPS catalyst What is the impact of the water biproduct additive Time Yield %ee -- 28 h 90 85 H2O (1eq) 72 h 35 77 H2O (2eq) 72 h <10 72 MgSO4 20 h 79 83 Na2SO4 36 h 83 6h 85 5A mol sieves Temp Time Yield %ee 80° 6h 85 90 85 60° 22 h 90 93 90 40° 36 h 86 95 What is the scope of this transformation with respect to ketones? The scope of the reductive amination with respect to aryl ketones H O TPS H MeO2C CO2Me Me Me N Me H X NH2PMP NHPMP O O TPS O (m) 95% ee (p) 94% ee F O catalyst (o) 83% ee Me OH P X 5A mol sieves Scope of the ketone component O Me 90% ee 85% ee 77% yield 75% yield MeO 60-85% yield O O Me Me 95% ee 75% yield Cl O Me 40°C, toluene 10 mol% cat 95% ee O 71% yield O2N Are there other systems that are successful in this transformation? 96% ee Me 73% yield The scope of the reductive amination R O N H H MeO2C O Me CO2Me N H Me 40°C, toluene 10 mol% cat Scope of the ketone-ketimine component O N O 97% ee 82% yield R O HN O NH2PMP 5A mol sieves Me TPS O O OH P TPS catalyst O The scope of the reductive amination R O N H H MeO2C O Me CO2Me N Me H 40°C, toluene 10 mol% cat Scope of the ketone-ketimine component O N O 97% ee 82% yield Et O N O 79% ee 27% yield R O HN O NH2PMP 5A mol sieves Me TPS O O OH P TPS catalyst O MM3-Calculations Provide Good Prediction of Asymmetric Environment Si-face MM3-structure MM3-Calculations Provide Good Prediction of Asymmetric Environment OMe OMe HEH, N HN 10 mol% cat Me 5Å MS, 50 °C benzene Me 71% yield 95% ee O2N O2N Si-face Si-face MM3-structure X-ray structure Crystal grown in toluene at –20 ÞC in glove box The scope of the reductive amination: alkyl ketones H R Me Me O H MeO2C O NH2PMP CO2Me N Me H 40°C, toluene 10 mol% cat 5A mol sieves Scope of the alkyl ketone component O Et 91% ee Me TPS 71% yield NHPMP R Me O OH P TPS catalyst O The scope of the reductive amination: alkyl ketones H R Me O H MeO2C O NH2PMP CO2Me Me N TPS Me H O NHPMP 40°C, toluene 10 mol% cat R Me OH P O TPS catalyst 5A mol sieves Scope of the alkyl ketone component O O Et 91% ee 71% yield Me NHPMP 86% ee Me BzO 49% yield 91% ee Me 72% yield 50% yield Me O O O 86% ee Me 94% ee 75% yield 92% ee Cl This reductive amination process appears to be general for methyl ketones 68% yield The scope of the reductive amination: aryl amines H MeO2C O R H Me Me CO2Me N Me H TPS O RNH2 O NHR 40°C, toluene 10 mol% cat 5A mol sieves R Me OH P O TPS catalyst Scope of the amine component O CF3 HN HN HN Me Me 93% ee Ts N S 93% ee 90% yield Me 91% ee 70% yield 90% ee 92% yield Ts N N HN Me Me 55% yield 73% yield HN 95% ee HN Me 90% ee 75% yield With Storer, Carrera, Ni. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 84 Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design S R Activation Modes N H N H R RO O P RO OH H-Bonding, Brønsted Acids R R Novel Reactivity NR4 Carbene, Phase Transfer Priviledged Achitecture Chiral Pool MacMiIlan, D. W. C. Nature 2008, 455, 304. Valuable New Bond Disconnections Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design S R Activation Modes N H N H R RO O P RO OH H-Bonding, Brønsted Acids R R Novel Reactivity NR4 Carbene, Phase Transfer Priviledged Achitecture Chiral Pool MacMiIlan, D. W. C. Nature 2008, 455, 304. Valuable New Bond Disconnections Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design S R Activation Modes N H N H R RO O P RO OH H-Bonding, Brønsted Acids R R Novel Reactivity NR4 Carbene, Phase Transfer Priviledged Achitecture Chiral Pool MacMiIlan, D. W. C. Nature 2008, 455, 304. Valuable New Bond Disconnections Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design S R Activation Modes N H N H R RO O P RO OH H-Bonding, Brønsted Acids R R Novel Reactivity NR4 Carbene, Phase Transfer Priviledged Achitecture Chiral Pool MacMiIlan, D. W. C. Nature 2008, 455, 304. Valuable New Bond Disconnections Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design S R Activation Modes N H N H R RO O P RO OH H-Bonding, Brønsted Acids R R Novel Reactivity NR4 Carbene, Phase Transfer Priviledged Achitecture Chiral Pool MacMiIlan, D. W. C. Nature 2008, 455, 304. Valuable New Bond Disconnections Activation Modes Are Enabled by Priviledged Catalyst Achitectures Catalysis Platform / Concept Chemical Methodology Catalyst Design S R Activation Modes N H N H R RO O P RO OH H-Bonding, Brønsted Acids R R Novel Reactivity NR4 Carbene, Phase Transfer Priviledged Achitecture Chiral Pool MacMiIlan, D. W. C. Nature 2008, 455, 304. Valuable New Bond Disconnections