A Systems Model of Public Policy-Making FEEDBACK LOOP ENVIRONMENTS
advertisement
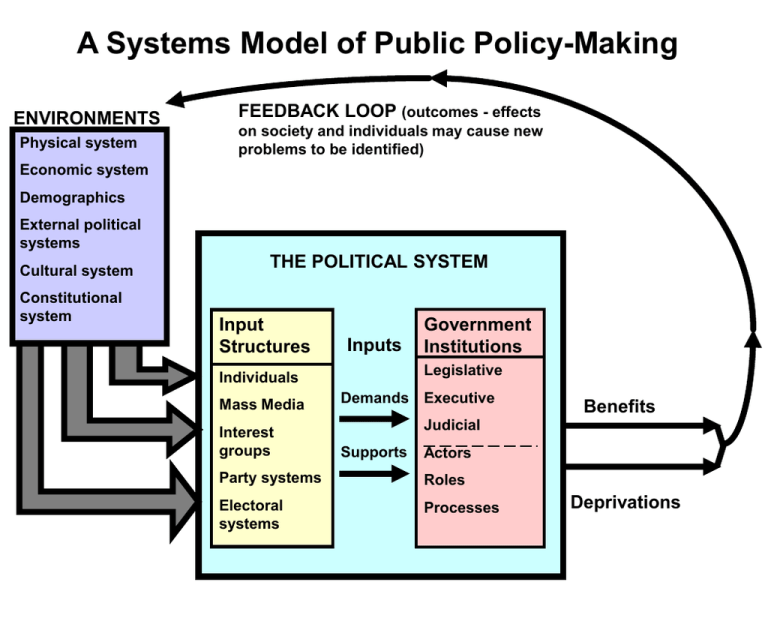
A Systems Model of Public Policy-Making ENVIRONMENTS Physical system FEEDBACK LOOP (outcomes - effects on society and individuals may cause new problems to be identified) Economic system Demographics External political systems Cultural system Constitutional system THE POLITICAL SYSTEM Input Structures Inputs Legislative Individuals Mass Media Interest groups Government Institutions Demands Executive Benefits Judicial Supports Actors Party systems Roles Electoral systems Processes Deprivations ENVIRONMENTS Physical system Economic system Demographics External political systems Cultural system Constitutional system ENVIRONMENTS - the environment is any condition or circumstance that is external to the boundaries of the political system being examined. Thus, a political system may respond to social, economic, or physical conditions, or it may respond to inputs from other (external) political systems. At any rate, it is proper to think of environmental conditions in terms of systems and in the plural. INPUT STRUCTURES - the channels, linkages, and connections from the environments to government institutions. These individuals and organizations/institutions serve to recruit political actors, nominate and elect public officials, represent people, set agendas for public discussion and action, and communicate demands and supports to public officials. THE POLITICAL SYSTEM Input Structures Individuals Mass Media Interest groups Party systems Electoral systems INPUTS - Inputs into governmental structures include demands for specific policy action and general support for the political system or one of its parts. Diffuse support contributes to the long-term maintenance and stability of the political system. THE POLITICAL SYSTEM Inputs Demands Supports GOVERNMENT INSTITUTIONS - these are the familiar legislative, executive, judicial, and bureaucratic branches of government. These institutions may be referred to as conversion structures because because they convert demands and supports into public policy outputs. Government institutions pass the laws, appropriate the money, and make rules and regulations, whether formal or informal, for implementing policies. THE POLITICAL SYSTEM Government Institutions Legislative Executive Judicial Actors Roles Processes OUTPUTS - are of two kinds: policy statements and implementing actions. Policy statements include legislative statutes, executive orders, administrative rules and regulations, and judicial decisions, as well as informal policy pronouncements. Implementing actions are those activities undertaken by administrators and other political actors to carry out the policy statement. Outputs are generally characterized as either benefits or deprivations imposed on a particular target group. THE POLITICAL SYSTEM Benefits Deprivations OUTCOMES are the short and long term effects that policies have on environmental conditions. Outcomes feed back into the policy process and have an impact on the formulation of new policies. Thus, as the feedback loop indicates, the policy process is a continual cycle. FEEDBACK LOOP (outcomes - effects on society and individuals may cause new problems to be identified) THE POLITICAL SYSTEM Benefits Deprivations THE UTILITY OF THE SYSTEMS MODEL In studying politics and public policy, the systems model can be used to: • Convey the idea of government as part of a larger system made up of political actions; • Identify the parts of the political system and the relationship of each part to the others; • Show the linkages or connections between the environments and political structures, as well as linkages among parts of the political system itself; • Demonstrate how external variables in the environments stimulate political activity and perhaps may ultimately necessitate public policies; • Allow us to develop possible explanations for government performance by focusing on the various parts and their interconnections; • Show that policy outputs and outcomes are the product of political activity occurring within the system; policy is the result of political processes.




![[CH05] Estimasi Usaha dalam Proyek](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/014618631_1-49924f60adc6d9c12ebc1ef87a169f34-300x300.png)


