An Introduction to
Model Review
Grenville Croll
Business Modelling Group
February 2002
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
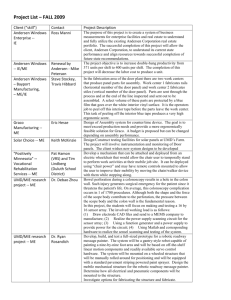
Model Review Process
Queries
responded to by
client
High Level
Review
Familiarisation
Low Level
Review
Preparation
of queries
list - issued
to client
Model
requires
alteration
?
Sensitivities
Yes
Comparisons
run between
model
versions
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model
amende
d by
client
No
Report
issued to
client
Model Risk
•
Proprietary Tool for Assessing Risk
– In the Development, Auditing & Use of spreadsheet Models
•
Recursively Decomposes model
–
–
–
–
•
Used Cells, Data/Logic Split
Formulae length, Original Formula Ratio
Number of Precedents, Logic Spatial Arrangement
Logical Interconnectedness
Outputs from Fuzzy Inference Engine
–
–
–
–
Model Risk Score (Low - High)
Cell Error Rate
Estimated Review Time
Probability of Bottom-Line Error
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
Step 1: Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
1.1 Model Maps
•
Why do we use maps?
– To ensure each original formula is checked
– To help document the review
– So that the review can be divided up between different people
•
How we run maps
– Use Review Tools - proprietary software
– Maps all sheets in Workbook
•
Map Key
–
–
–
–
–
L = Label
N = Number
F = Original Formula
^, <, + = copied form above, left, above & left
M = Long complex formula
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
1.2 Spreadsheet Map
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
1.3 Model Maps - checking formulae
•
What we look for when checking formulae
– All references to other cells or ranges are correct
– All arguments of functions are correct (e.g. IF, INDEX, MATCH, OFFSET,
VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, SUMIF)
– ROUND functions for appropriate accuracy
– Review #REF, #ERR etc to establish cause
– Check any inconsistent formulae identified from maps
– Embedded constants
– Reperform array & data table calculations
– Consistent units eg currency, weights, measures, dimensions
– Calculation produces something sensible
– Result has the correct sign (i.e. + or -, CR or DR)
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
1.4 Model Maps
•
How we check the formulae
– Tick off each original checked formula (F) on the map
– Mark queried formulae with a Q
•
Painstaking but essential
•
Independent peer review
– academically verified method of detecting & correcting errors
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Step 2: Code Review
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
2. Code Review
•
Ways we review code (VBA & Macros)
–
–
–
–
•
Print out and look through
Step through
Run complete procedure
Hit Buttons
Things we look for
– Does the code do what it is intended to do?
– Is there anything that would make it break?
• Eg macro contains absolute cell addresses
•
How we document code review
– Print out and annotate along with queries
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Step 3: Range Names
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
3. Range Names
•
Why do we need to do a range name review?
– Names in formulae
– Names in macros
– Redundant names
•
How do we do it?
– Review Tools, Report Names
– Check that range is complete and appropriate
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Step 4: Queries
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
Queries
•
Query document
– Each query is numbered uniquely
– Records each query & response from the client
– Reference Resource
• useful if queries from different reviewers/clients
•
Six Different query types
– AE, PE, C, N, I, BP
•
Before query document gets sent to the client
– Reviewed for duplicates
– Edited so it is clear and concise
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Queries - Basic types of query
•
Actual Error
– All actual errors, including Excel errors e.g. #N/A or #Div/0!
•
Potential Error
– If the value of a precedent changed, would the result be wrong?
•
Clarification
– Request for clarification of a point
•
Numbers
– Constants in formula: require confirmation and/or explanation
•
Information
– Items of interest to the modeller, but do not affect output
•
Best Practice
– Consider time constraints, materiality etc
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Responses
•
All responses reviewed and documented
•
Check that changes have been made in new version
•
Mark query as resolved or unresolved
•
Carry forward unresolved to next query list
•
Check that no queries have been missed
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Step 5: High Level Review
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
High Level Review
•
Why do we do it?
– Check big picture items that may be missed by low level review
– Consistency with Documentation
– GAAP and accounting issues
•
What does it include?
–
–
–
–
–
•
Circular references
Interest calculations
Tax calculations
Balance Sheet/P&L/Cashflow integrity
Payment of Dividends
What does it not include?
– Any input to the commercial nature of the model
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
High Level Review
•
Some High Level Checks
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
The Balance Sheet balances
Retained Earnings flow from P&L to BS
Capex causes cash outflow
Fixed Assets don’t depreciate below zero
Increase in Credit Sales impacts Trade Debtors
Is effective tax rate reasonable?
Is Interest calculated on prior period ending balance?
Do Revenues & Costs reflect production?
Is debt amortised correctly?
Are foreign currency losses reflective of GAAP?
Are financial statements in the correct format?
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Step 6: Documentation
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
Project Documentation
•
What do we do?
–
–
–
–
–
•
Check the project documentation against the model
Review term sheets, agreements, contracts, model specifications
Review work of industry experts
Interface with other specialist Andersen teams
Add items to query list as identified
Our Documentation
– Mark maps as for formulae checks
– Note from which data source the numbers have been obtained
– For each source, note where in the model the data is located
•
Changes in project documentation cause re-review
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Step 7: Comparisons
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
Step 8: Sensitivities
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
Sensitivities
•
A model review cannot deal with every possible input
– billions of data permutations & combinations
•
Comfort required on certain sensitivities
–
–
–
–
–
–
All compared against Base Case
Delayed start
high/low revenue
high/low cost of finance
high/low capex & opex
otherwise as specified by client
•
Each sensitivity methodically reviewed & documented
•
Changes in base case model cause re-run of sensitivities
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Step 9: Final Review
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
Final Review
•
Clear any outstanding queries
•
Final high level sense check
•
Final documentation & sensitivity check
•
Client made clearly aware of any outstanding queries
•
Resolved if possible
•
Document Resolutions
•
Unresolved queries appear in final report
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Step 10: Report
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
Model Review framework
10
Report
8
Sensitivities
5
High Level
Review
1
Model Maps
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.
9
Final Review
6
Documentation
2
Code Review
7
Comparisons
3
Range Names
4
Queries
Report
•
Standard letter
•
Lists exact versions of models & files
•
Models identified by filename, date, time & size in bytes
•
Reports our performance of agreed-upon-procedures
•
Reports any unresolved queries
© 2001 Andersen. All rights reserved.