Overview of Adaptive Immunity Principles of Immunology 1/24/06
advertisement

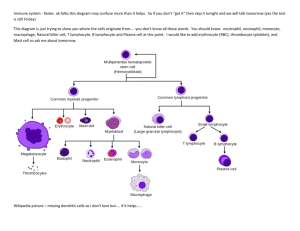
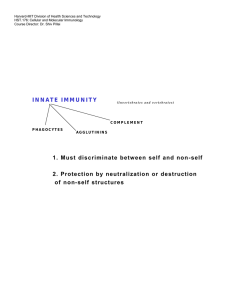
Principles of Immunology Overview of Adaptive Immunity 1/24/06 “Too many people overvalue what they are not and undervalue what they are.” M Forbes Adaptive Immunity Specific host defenses that are mediated by B and T lymphocytes following exposure to antigens, and exhibit diversity and memory. Word List Clonal selection CD 4 CD 8 Epitope Endogenous antigen Exogenous antigen Phagolyzosome Characteristics of Adaptive Immunity Antigenic specificity Diversity Immunologic memory Self recognition Interface with Innate Immune System Phagocytosis Inflammation Major Cells of Adaptive Immunity Lymphocytes B T TH TC Antigen presenting cells (APCs) Dendritic cells Macrophage B lymphocytes B Lymphocytes Originate and mature in bone marrow Membrane bound antibody Ag binding triggers division and differentiation Progeny Plasma cells Memory B cells T Lymphocytes Mature in thymus T cell receptors MHC restriction Class I Nucleated cells Reacts with CD8 Class II APCs Reacts with CD4 T Lymphocytes(cont’d) Progeny cells T helper CD4 Class II restricted Stimulates B and T cells (helper function) T cytotoxic CD8 Class I restricted Further differentiates CTLs(killing function) Memory T cells Antigen Presenting Cells Dendritic cells MHC I and II on surface Ag is internalized Stimulates T-helper cells Macrophages B lymphocytes Humoral Immunity Conferred via serum (cell-free) Antibody dependent Antibody functions Enhanced elimination Neutralization C fixation/lysis Cell-mediated Immunity Conferred via lymphocyte exchange Cell dependent Modulates humoral immunity Cytotoxic Antigen Recognition Epitopes B cells recognize epitopes alone T cells require MHC association Major molecules involved Membrane bound antibody TCR MHC I MHC II Lymphocyte Diversity Random rearrangement of gene segments 1010 potential specificities “Mature” lymphocytes are said to be “committed” Antigen Processing Exogenous antigens Phagocytosis Degradation Ag peptide/MHC II recognized by T helper Endogenous antigens Viral or tumor induced Complexes with Class I Recognized by CTLs Clonal Selection Occurs in Secondary lymphoid organs Specificity of all progeny is identical Explains secondary response Memory cells more numerous than naïve cells