The Role of Sphingolipids in Lipid Raft Paramecium tetraurelia Tyler Picariello 12/7/10
advertisement

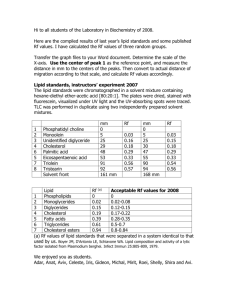
The Role of Sphingolipids in Lipid Raft Function in Paramecium tetraurelia Tyler Picariello 12/7/10 Outline • Background – Model Organism – Cilia and Lipid Rafts • Methods • Expected Results Paramecium Background • Paramecium tetraurelia is a ciliated eukaryotic organism approximately 100-150m in length • Excellent model for studying ciliary lipids and proteins • Changes in membrane potential can be observed through changes in swimming behavior http://bioinformatica.upf.edu/2008/projectes08/Dy/paramecium_intro.jpg Pantel, Haddon; Undergraduate Honors Thesis, 2007 Cilia Background 100 nm Image courtesy of Megan Valentine 0.2m http://www5.pbrc.hawaii.edu/allen/ch01/04-pm700521-14.html Lipid Rafts and their Functions Adapted from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26892/ Paramecium lipid composition and the Synthesis of Sphingolipids • P. tetraurelia has a unique lipid composition, especially in the ciliary membrane Lipids % Weight of Cell % Weight of Cilia Cholesterol 3.6 5.2 Choline Sphingolipids 2.1 2.5 Ethanolamine Sphingolipids 3.8 15.5 Kaneshiro, 1987) http://www.biol.unt.edu/~chapman/research%20projects/cotton/me tabolic_pathways.htm Lipid Rafts in Paramecium • • Lipid rafts in P. tetraurelia share important general raft properties • Resistant to cold non ionic detergent extraction • They are enriched with cholesterol, glycosphingolipids and GPI- anchored proteins Paramecium lipid rafts can be further divided into Methyl--cyclodextrin sensitive and insensitive rafts Hypothesis Disruption of sphingolipids, a key component of ciliary lipid rafts, through the depletion of the serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) gene message will result in disruption of ciliary lipid raft formation. This will in turn disrupt Folate chemoattraction and ciliary calcium channel function. Specific Aim To study the effect of serine palmitoyltransferase mRNA depletion on lipid raft formation in Paramecium. SPT mRNA depletion will be achieved through the RNAi feeding method. I. The effects of SPT mRNA depletion on lipid raft organization will be analyzed by sucrose density gradient centrifugation. II. Study the effects of SPT mRNA depletion on Folate chemoattraction using TMaze assays III. Study the effects of SPT mRNA depletion on ciliary calcium channel function using backward swimming assays. RNAi Background • • • • http://www.abcam.com/cms/displayImage.cfm?intImageID=21696 RNAi is a method used to down-regulate specific mRNA sequences Double stranded RNA (dsRNA) introduced into the cell is cleaved into segments of 20-25 nucleotides in length (siRNA) by the enzyme Dicer The guide strand of the siRNA is incorporated into the RISC complex allowing it to target and pair with the complementary mRNA sequence This results in cleavage of the mRNA sequence and downregulation of the specific gene product RNAi by feeding RNAi construct L4440 SPT gene HT115 Feed paramecium Ds RNA Adapted from Haddon Pantel and Mellissa Donovan T-Maze Assay • • • • Control Arm Test Arm • • Used to test attraction behavior Control Solution: NaCl Test Solution: Na2-Folate Paramecium are allowed to swim for 30 minutes Count the cells in each arm Iche= # cells in test arm total # of cells Density Gradient Centrifugation • Used to analyze the distribution of raft associated proteins in RNAi and control cells Cilia pellet mixed with 80% sucrose and TNE buffer to achieve a final concentration of 40% Pellet overlayed with a 5%-40% continuous linear sucrose gradient Tubes spun at 160,000 x g for 4 hours Tubes divided into fractions and used for density analysis Backward Swimming Assays • Membrane potentials will be stabilized via exposure to KCl buffer • Cells tested in high potassium and barium chloride solutions as well as sodium chloride • Time spent swimming in reverse will be measured and is directly proportional to the number of functional Ca2+ channels present in the ciliary membrane Expected Results • RNAi will result in the disruption of ciliary lipid rafts domains reflected in a shift in protein distribution in the sucrose gradient • Disruption of GPI anchored Folate binding proteins will result in decreased attraction to Folate in T-Maze Assays • Expect decreased backward swimming time due to defective voltage gated Ca2+ conductance Questions?