Lab Station # 1
advertisement

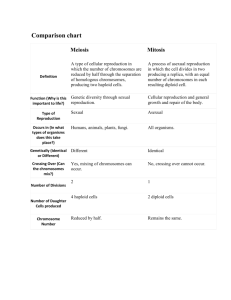
Lab Station #1 Ch. 8 Mitosis/Meiosis 1. How many parents are involved in: a. asexual reproduction? b. sexual reproduction? 2. Describe the environment that favors: a. asexual reproduction? b. sexual reproduction? 3. Describe the effect on variation for each a. asexual reproduction? b. sexual reproduction? 4. What is mitosis used for? 1. How many parents are involved in: a. asexual reproduction? b. sexual reproduction? 1 2 Describe the environment that favors: a. asexual reproduction? b. sexual reproduction? stable unstable 2. 3. Describe the effect on variation for each a. asexual reproduction? Creates clones which are identical which creates NO variation. b. 4. What is mitosis used for? Mrs. Loyd sexual reproduction? Creates a great deal of variation among the resulting individuals. growth, maintenance, repair and asexual reproduction. Page 1 of 6 7/12/2016 Lab Station #2 5. Which kind of macromolecule combines with DNA to stabilize its form and allows it to supercoil? What are they called? 6. Describe the form for DNA during interphase. 7. Describe the form for DNA during M phase. 8. Name the process that divides nuclear information. 9. Name the process that divides cytoplasm to make new cells. 5. Which kind of macromolecule combines with DNA to stabilize its form and allows it to supercoil? What are they called? PROTEIN / HISTONES 6. Describe the form of DNA during interphase CHROMATIN which is long and stretched out. 7. Describe the form for DNA during M phase. CHROMASOMES: highly condensed, supercoiled. 8. Name the process that divides nuclear information. MITOSIS 9. Name the process that divides cytoplasm to make new cells. Cytokinesis Mrs. Loyd Page 2 of 6 7/12/2016 Lab Station #3 10. Draw and label the phases in the cell cycle. a. add chromosome pictures in G1, G2 b. check points located? 11. What happens to a cell if these check points are ignored? 12. What are cells supposed to do when they get crowded and touch one another? What is this called? 13. Draw a simplistic diagram of a benign tumor and a malignant (metastasized) tumor. 14. Draw cytokinesis for a plant cell and an animal cell side by side. 10. Draw and label the phases in the cell cycle. a. add chromosome pictures in G1, G2 b. check points located? c. for what purpose? 11. What happens to a cell if these check points are ignored? a. THE CELL WILL DIVIDE OUT OF CONTROL. 12. What are cells supposed to do when they get crowded and touch one another? What is this called? a. STOP DIVIDING. CONTACT INHIBITION 13. Draw a simplistic diagram of a benign tumor and a malignant (metastasized) tumor. 14. Draw cytokinesis for a plant cell and an animal cell side by side. Mrs. Loyd Page 3 of 6 7/12/2016 Lab Station #4 Ch. 8 Mitosis/Meiosis 15. What is meiosis used for? 16. What do chromosomes do in meiosis that they DO NOT do in mitosis? 15. What is meiosis used for? IT IS A REDUCTION DIVISION 2n -> n. IT MAKES GAMETES FOR REPRODUCTION. 16. What do chromosomes do in meiosis that they DO NOT do in mitosis? SYNAPSIS: homologous chromosomes seek each other out and arrange themselves side-by-side. CROSSING OVER: homologous chromatids exchange segments. *This increases genetic diversity. HOMOLOGUES SEPARATE: this is the reduction division. This, too, increases genetic diversity due to independent assortment. Mrs. Loyd Page 4 of 6 7/12/2016 Lab Station #5 17. Draw a stick person. Circle where in the body meiosis is occurring. 18. Draw the human sex cells. 19. Draw the chromosomes in a sex cell if 2n = 6. 20. In humans, name the sex chromosomes. 17. Draw a stick person. Circle where in the body meiosis is occurring. 18. Draw the human sex cells. 19. Draw the chromosomes in a sex cell if 2n = 6. 20. In humans, name the sex chromosomes. Mrs. Loyd X and Y XX, female, XY, male, Page 5 of 6 7/12/2016 21. What can a karyotype tell you about your expectant baby? Lab Station #6 22. Why might you have a karyotype done on yourself? 23. Which human chromosomes are most tolerant of a trisomy condition? 21. What can a karyotype tell you about your expectant baby? GENDER, TRISOMIES (like trisomy 21 or Down Syndrome), MONOSOMIES, DELETIONS, INSERTIONS, TRANSLOCATIONS 22. Why might you have a karyotype done on yourself? TO DETERMINE IF YOU HAVE A CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY. 23. Which human chromosomes are most tolerant of a trisomy condition? SEX CHROMOSOMES Mrs. Loyd Page 6 of 6 7/12/2016